By Brian S. White. Textual note taken from Carestream NDT dated April 15, 2024
Introduction – Industry 4.0 and the role of cyber-physical systems
Industrial revolutions historically in the past have been associated with the alignment of disruptive technological advancements (steam power, electricity, microelectronics, and computers or telecommunication technologies) with profound shifts in economic power and social behaviors in ample regions of our world.
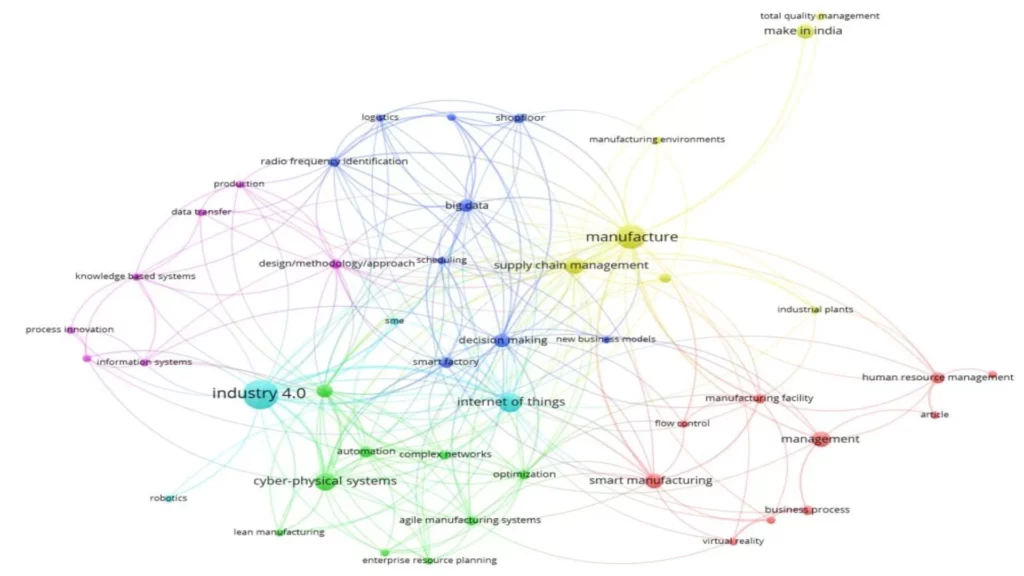
Although the term “Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0” was formally introduced at the 2011 Hannover Fair, the notion was nurtured from decades of previous research and the support of government projects such as the advanced technologies strategy of Germany. The notion of Industry 4.0 has its foundation in the integration of intelligent digital technologies into manufacturing and industrial processes. Although the concept is difficult to integrate into a single definition, it incorporates concepts such as cyber-physical systems (CPS), cyber physical production systems (CPPS), internet of industrial things (IIOT), digital twins and threads, vendor-neutral digital data storage and transmission protocols (such as DICONDE) and the interconnected synergy between those technologies as is shown in Figure 1.
Industry 5.0 – An almost simultaneous revolution
The notion of Industry 5.0 has also been championed since 2017 by academics and other key stakeholders inside and outside industrial ecosystems, including authorities such as the European Commission (EC). In January of 2021, the EC released the document “Industry 5.0: Towards a Sustainable, Human-centric, and Resilient European Industry” in response to an increasingly complex and exponentially changing social and geopolitical global landscape. This document defines a Vision for Industry 5.0: “We propose moves past a narrow and traditional focus on technology-or economic enabled growth of the existing extractive, production and consumption-driven economic model to a more transformative view of growth that is focused on human progress and well-being based on reducing and shifting consumption to new forms of sustainable, circular and regenerative economic value creation and equitable prosperity”. Industry 5.0 reflects a shift from a focus on economic value to a focus on societal value. It makes production more sustainable and places the well-being of the worker at the center of the production process. It envisions humans working alongside advanced technology and artificial intelligence.





A Parallel Path for Harvesting the Benefits of the Digitalization and Digital Transformation of Imaging Processes
This supplementary and mutually enriching focus of technology-driven Industry 4.0 and value-creation-driven Industry 5.0 is creating unparalleled opportunities for digital radiography imaging processes to expand and enrich imaging capabilities. Digital imaging, including digital radiography, is not only inexorably linked to the computer and telecommunication technologies associated with Industry 3.0 and to cyber-physical systems of Industry 4.0 but also, they empower people to generate essential information and knowledge that enable substantial value-creation human decision-making processes while generating a reduced environmental impact aligned with an Industry 5.0 approach.
For readers interested in exploring how digital radiography (DR) can be integrated to your imaging processes: https://www.carestream.com/en/us/nondestructive-testing-ndt-solutions
Here are some supplementary information resources from Carestream NDT’s products and services portfolio:
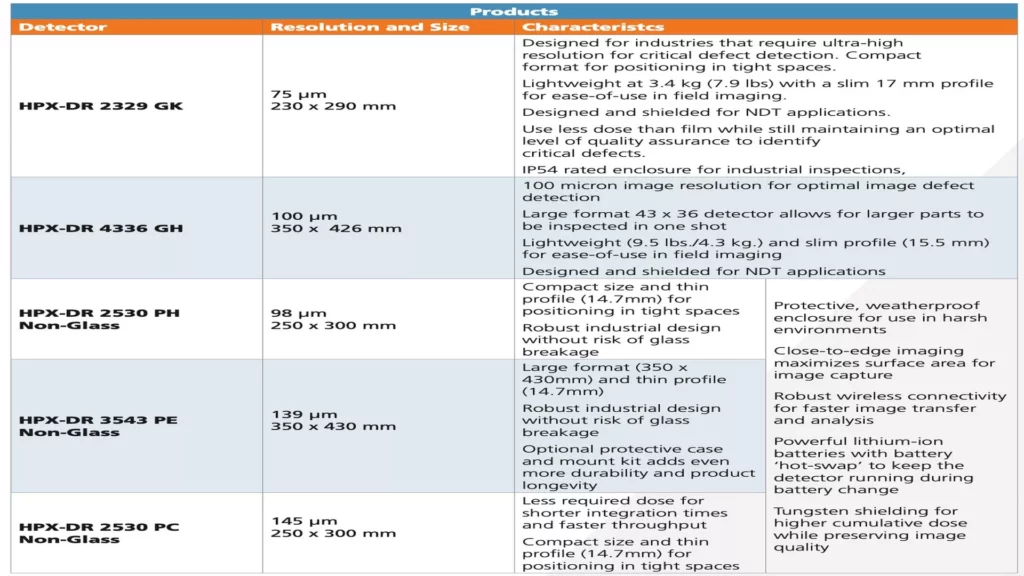
Products:
Software:
INDUSTREX Digital Viewing Software,
Training:
Advanced Industrial Radiographic Training Academy
References:
- Trotta, Dennis, and Patrizia Garengo. “Industry 4.0 key research topics: A bibliometric review.” In 2018 7th international conference on industrial technology and management (ICITM), pp. 113-117. IEEE, 2018
- Xu, Xun, Yuqian Lu, Birgit Vogel-Heuser, and Lihui Wang. “Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0—Inception, conception and perception.” Journal of manufacturing systems 61 (2021): 530-535
- European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation, Renda, A., Schwaag Serger, S., Tataj, D. et al., Industry 5.0, a transformative vision for Europe – Governing systemic transformations towards a sustainable industry, Publications Office of the European Union, 2021, https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2777/17322.
Don’t miss any of our posts and follow us on social media!
Inspenet.com YouTube LinkedIn Facebook Instagram
Source: www.carestream.com













