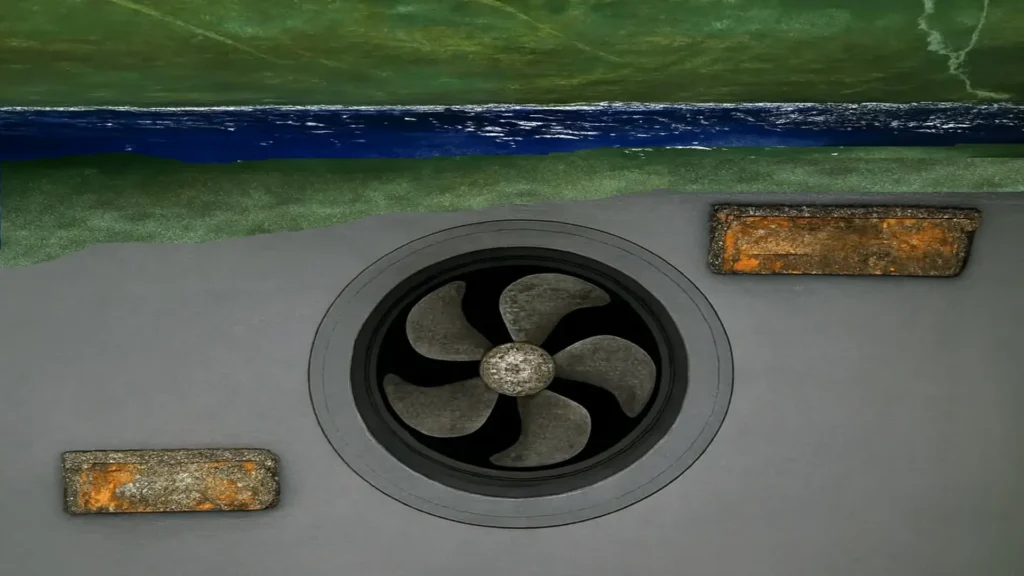

Sacrificial anode control in marine infrastructure
Sacrificial anode control in marine infrastructure ensures effective cathodic protection, structural integrity, and extended service life in seawater environments.

Sacrificial anode control in marine infrastructure ensures effective cathodic protection, structural integrity, and extended service life in seawater environments.

Fractional distillation requires advanced control to operate efficiently and stably in refineries.

Failure analysis on metallic materials is a technical process that combines corrosion, fractography, metallography, and root cause diagnosis to identify the origin and progression of failures, enhancing the reliability and safety of industrial assets.
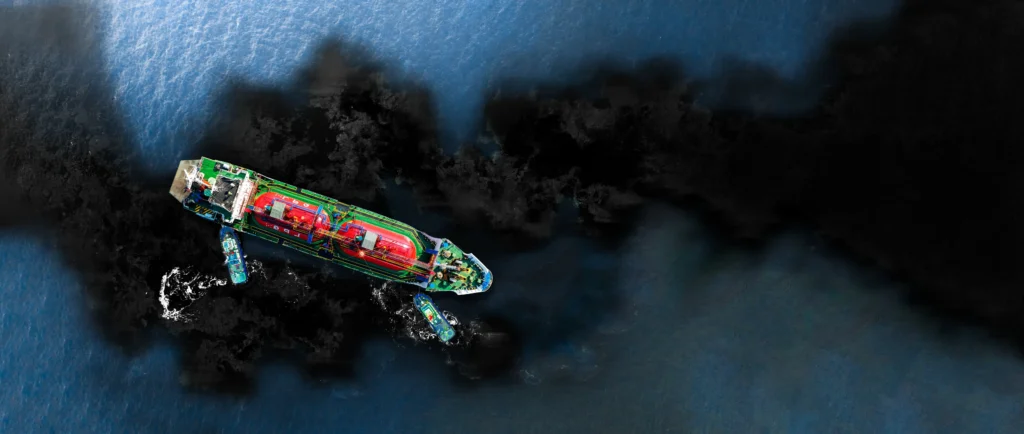

Spills continue to affect maritime safety and coastal ecosystems, requiring robust industrial preparedness and international technical cooperation to reduce operational impacts.
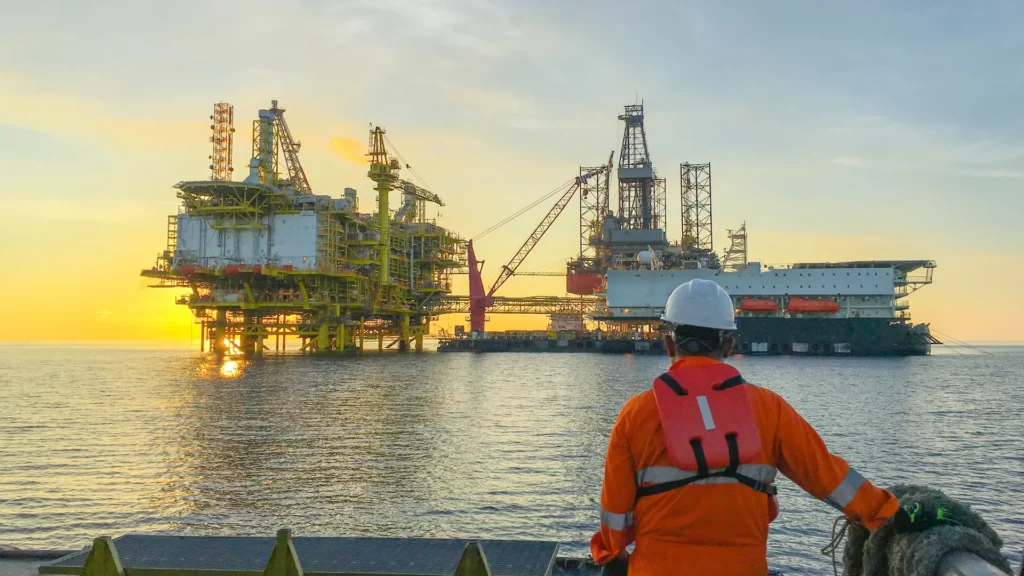

A vision of the role of engineering and human talent in the safe and efficient operation of offshore platforms.
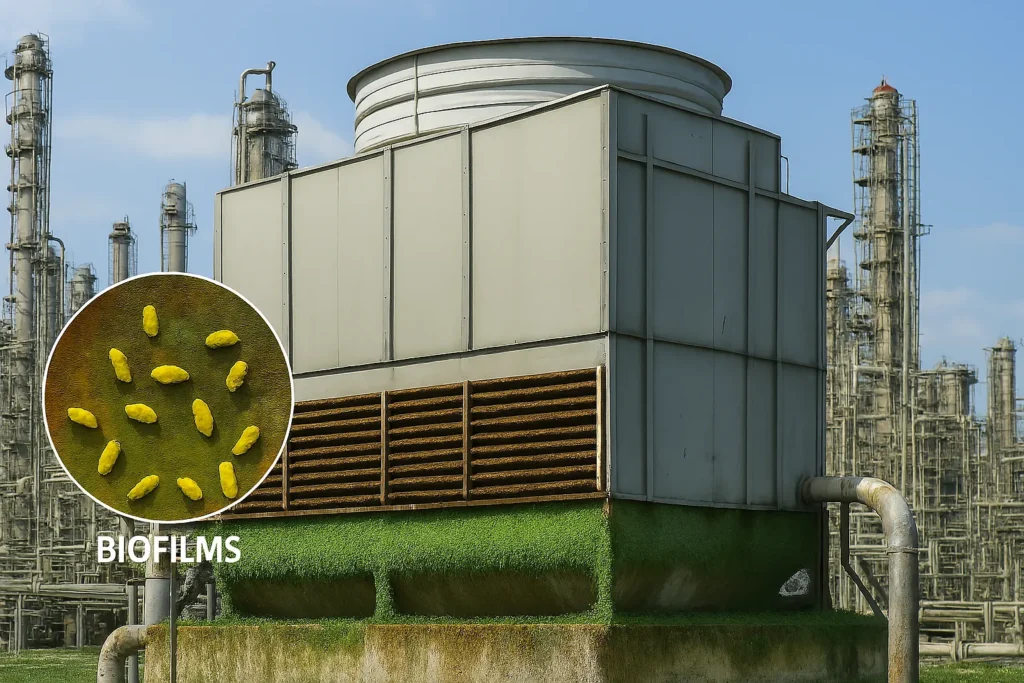

The combination of pH variations, dissolved gases, and microbiological activity in cooling systems generates corrosion and deposits that affect mechanical integrity and thermal efficiency.
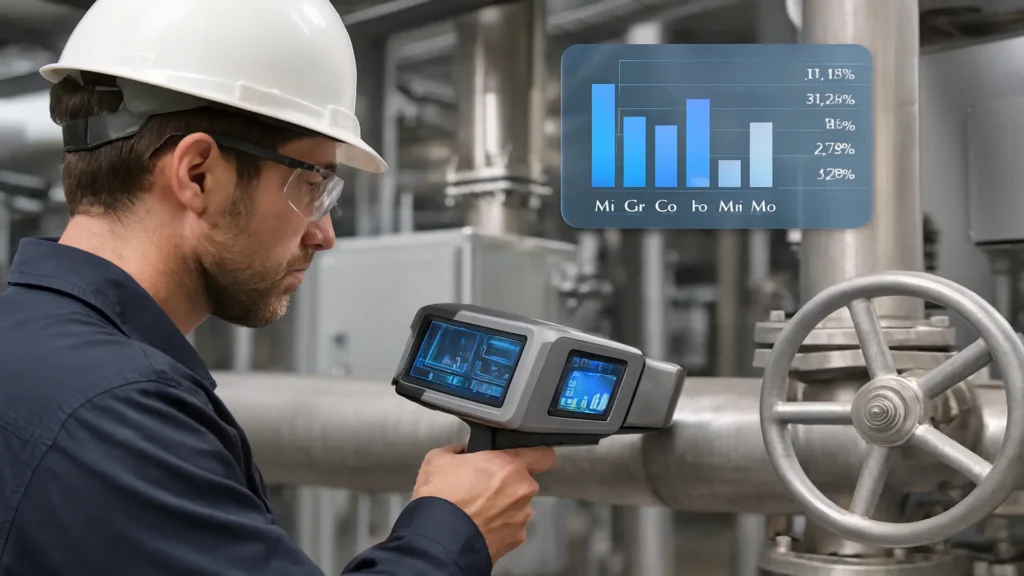

API 578 establishes a standardized framework for positive material identification (PMI) in the process and petroleum industries.
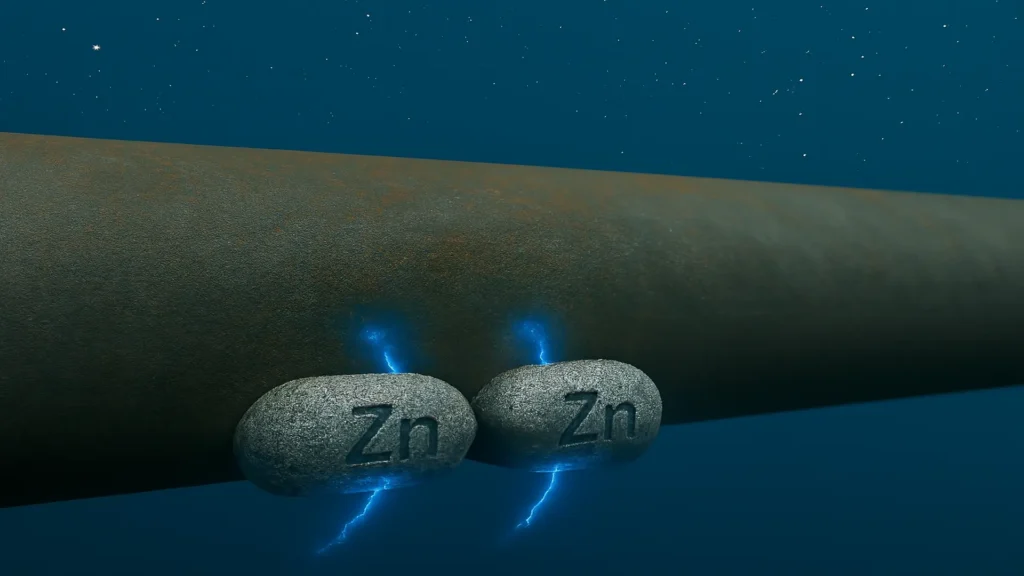

Sacrificial anodes are metal components designed to corrode in a controlled manner, transferring protective current to the cathodic structure and preserving its integrity against electrochemical corrosion processes.
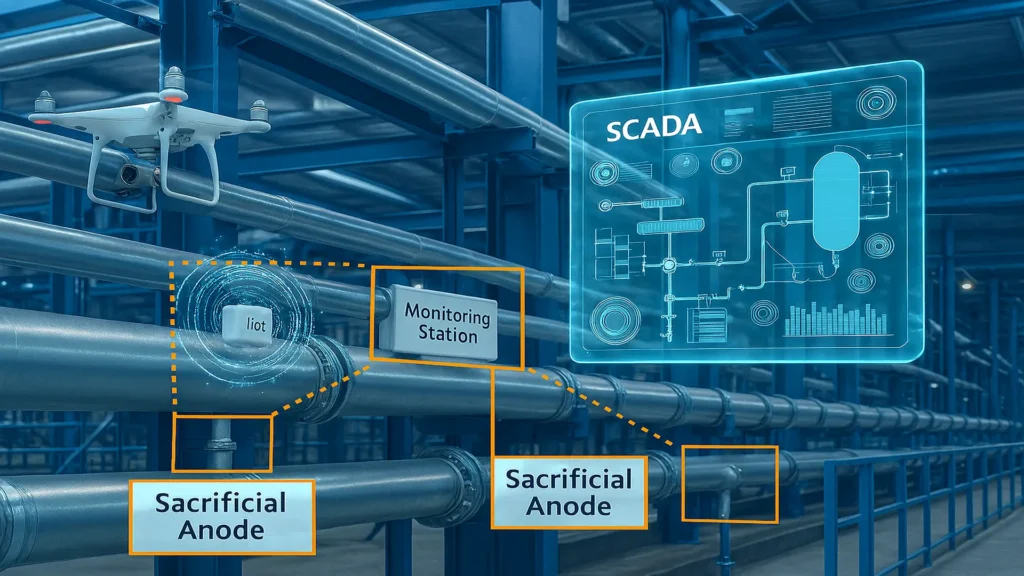
Innovations in cathodic protection are redefining corrosion prevention with more efficient and sustainable systems.
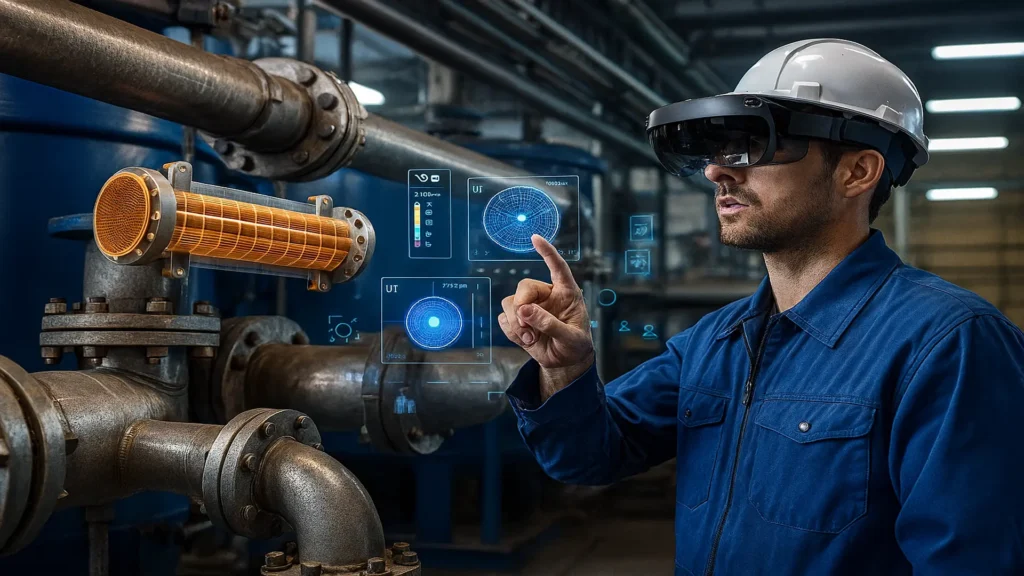

Immersive training in NDT with VR/MR in industrial inspections combines VR and MR to train inspectors safely and efficiently, simulating real equipment and scenarios without risk or excessive costs.
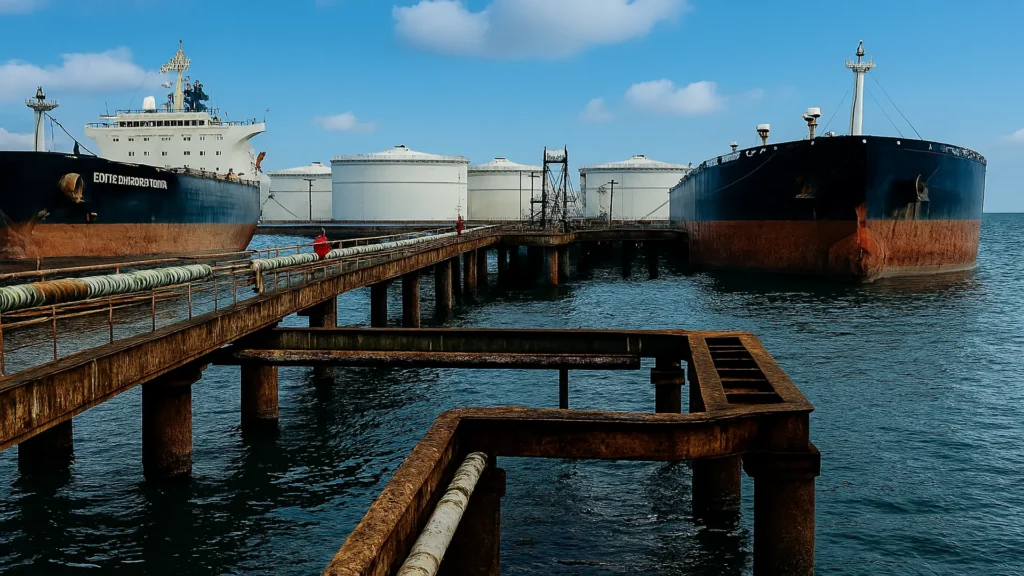

Corrosion at liquid product port terminals is a critical risk that affects the safety and operability of docks and metal structures.
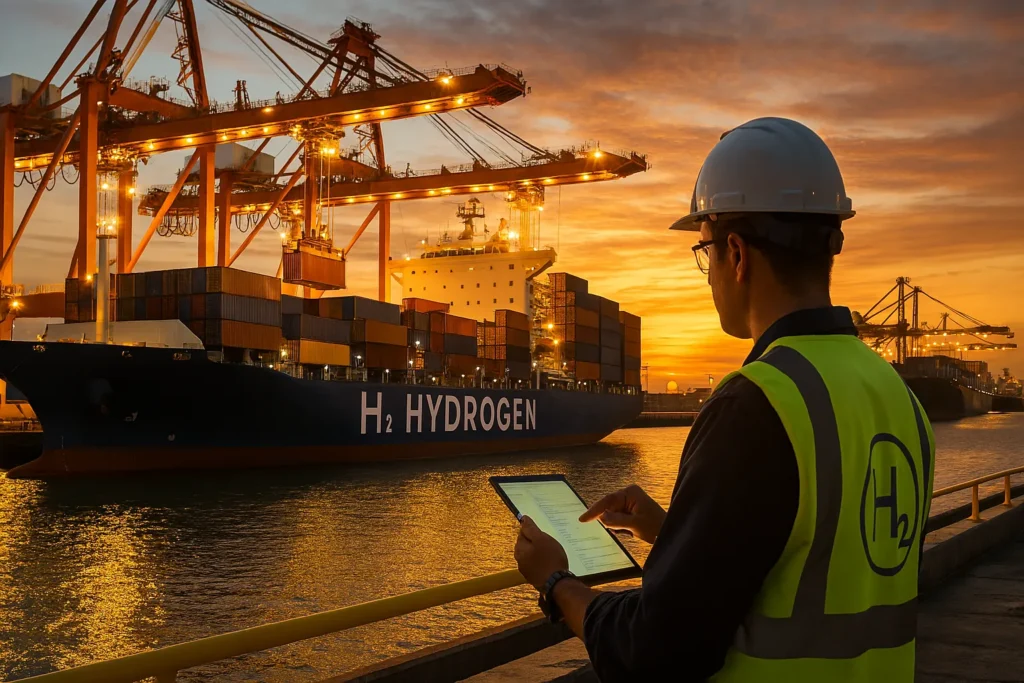

The transition to clean fuels at maritime terminals depends on both technology and human management.