Author: Ing. Mayuly Rodríguez, October 25, 2023.
Introduction
The incorporation of robotic inspection in the Oil & Gas industry has become a key point to face the multiple challenges associated with structural integrity, safety and operational efficiency. Increasing energy demands drive companies in the sector to improve and sustain the operation of facilities, through the inspection of equipment or systems due to the extension of all their processes.
Inspection robots, with their advanced functions, are positioned at the epicenter of a transformation towards new technologies that facilitate inspections and effective maintenance, providing a viable solution to operate in extreme environments typical of this industrial sector. That is why today the operational optimization of the Oil & Gas industry depends on the effectiveness of the inspections and the obtaining of precise data, which this technology is providing.
Disruptive impact of inspection robots for the Oil & Gas sector
Inspection robots have introduced a disruptive change in how inspections are carried out. These robots, equipped with advanced sensor technology, navigate complex and adverse environments, providing critical data that helps detect and identify problems in facilities.
In addition, the possibility of autonomous inspections in facilities, where robots manage equipment, take samples and perform simple maintenance tasks, has gained ground in recent years, reflecting a growth in interest in developing facilities specifically designed with robots. . On the other hand, it frees up human resources for other critical activities, while reducing costs and improving operational efficiency.
Robotic technology in general is segmented into three areas, covering all environments where the Oil & Gas sector has facilities and requires inspection services: aerial, terrestrial and underwater, which are described below 1 :
Aerial Robot : Called UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle), they cover any robot capable of flying, either under remote control by a human or, after appropriate programming and configuration, with various levels of autonomy that allow it to fly without human intervention. This technology, due to its efficiency and advantages, optimizes inspections at height.
They are generally used for visual inspection in remote areas and dangerous, such as pipelines and confined spaces, UAVs also excel in tasks such as thickness measurements, detailed mapping, leak detection, environmental monitoring and have a great contribution in responses to emergencies on the high seas.
Ground robot : They can be mobile and have the function of moving on difficult terrain, making them suitable for inspections in dangerous environments. Through a variety of sensors, cameras, lights and measurement systems, ground inspection robots collect and transmit real-time data for analysis, thereby contributing to the accurate and timely assessment of the structural and operational integrity of infrastructure. These are called crawlers, crawlers, climbers, snake type, magnetic, teleoperated, among others, each one performs a function depending on the need for the task or inspection to be carried out.
Underwater robot: These navigate in the water using propellers, which define their degree of freedom, their ability to move in various directions and achieve different orientations. They have a wide variety of applications in the area of inspection, monitoring and specific maintenance; There are two types: remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs).
The ROVs are remotely controlled by human operators, with multipurpose functions for the inspection and monitoring of underwater assets, transmitting high-resolution videos and images to the operator, in real time. Ideal for detailed inspections, repairs and maintenance operations that require real-time human intervention and supervision.
AUVs are fully autonomous, suitable for mapping, monitoring and data collection missions over large areas or in hazardous environments where autonomous operation is beneficial. They transmit the data in real time or download it once they return to the station. They have limited maneuverability compared to ROVs, but are designed to cover large areas and perform continuous mapping and monitoring tasks.
In general terms and adapted to each environment where they are used (marine platforms, storage tanks, docks, process platforms, oil pipelines, among others), this technology’s principle is to reduce inspection costs, improve safety, optimize the operational efficiency of processes, without requiring operational stops and over time automating multiple inspection processes to optimize the management of industrial assets.
Robotic inspection and its operational and sustainable impulse in the Oil & Gas industry
This industrial sector is in constant search for improvement in its operations, pursuing not only the optimization of resources, but also greater safety and a reduced environmental footprint. The incorporation of robotic technologies in inspection operations has contributed to more efficient and responsible management; Below are some contributions:
Strategic resource allocation: The ability of robots to provide accurate, real-time data on asset conditions allows for better planning and allocation of resources for maintenance and repair, which in turn improves operational efficiency.
Additionally, the information obtained through robotic inspections allows companies to make decisions about resource allocation. For example, when identifying areas that require investment in maintenance or upgrades, investments focused on critical systems are prioritized.
Improved operational security: It is one of the main benefits from the adoption of this technology. These robots minimize workers’ exposure to hazardous environments and adverse conditions, thereby reducing the risks associated with traditional inspections.
Additionally, its potential to detect structural issues or leaks with high precision contributes to rapid response, improving the integrity and safety of operations. The use of robots also allows immediate action to be taken in emergency situations. For example, in the event of an incident, they are deployed to assess the situation, minimizing personnel exposure to hazardous environments and also assisting with effective emergency management.
Good quality control: Its implementation has evolved quality assurance in this industrial sector. The multiple robotic inspection solutions on the market are equipped with high-quality camera systems, leak detectors, non-destructive testing (NDT) equipment, and software to geographically tag data during the inspection, allowing for accurate and efficient evaluation. of the integrity of the assets.
The ability to provide real-time data and advanced data analysis systems process large amounts of information quickly, providing instant feedback with the inspector or operator to verify quality standards and proactively respond to any detected deviations.
Optimize maintenance: Robots perform regular inspections and real-time monitoring, detecting potential problems before they become serious failures. Early detection allows for precise intervention, reducing downtime and costs associated with repairs and reactive maintenance.
Additionally, the data collected by inspection robots is used to plan and schedule maintenance more accurately. By analyzing trends and patterns in data over time, companies predict when and where a problem is likely to occur.
A contribution to environmental sustainability: These machines, in addition to inspecting, detect leaks in real time, allowing a rapid response to mitigate accidents with environmental consequences. Additionally, by identifying areas of corrosion and other structural damage, they prevent incidents that could result in spills or harmful emissions into the environment.
This type of inspection reduces the need for manual operations that are prone to errors and therefore environmental incidents and these operations also use heavy equipment that generates carbon emissions.
The precision and efficiency of inspection robots in detecting and monitoring structural conditions contributes to a cleaner and more sustainable operation. The data collected helps companies continually improve their operations, minimizing their environmental footprint and aligning with regulations and evolving sustainability expectations.
Cost savings: Automating inspection tasks using robots not only improves operational efficiency, but also results in significant savings. These machines are designed to operate in adverse conditions without requiring breaks, reducing the time to complete inspections and, therefore, operating costs. Additionally, by detecting problems early, companies avoid costly repairs and operational downtime.
Technology in development
The trajectory of robotic inspection has shown constant evolution, reaching notable milestones in innovation. With each advance, expectations rise towards even more remarkable discoveries. Here is an emerging technology in underwater robotic inspection:
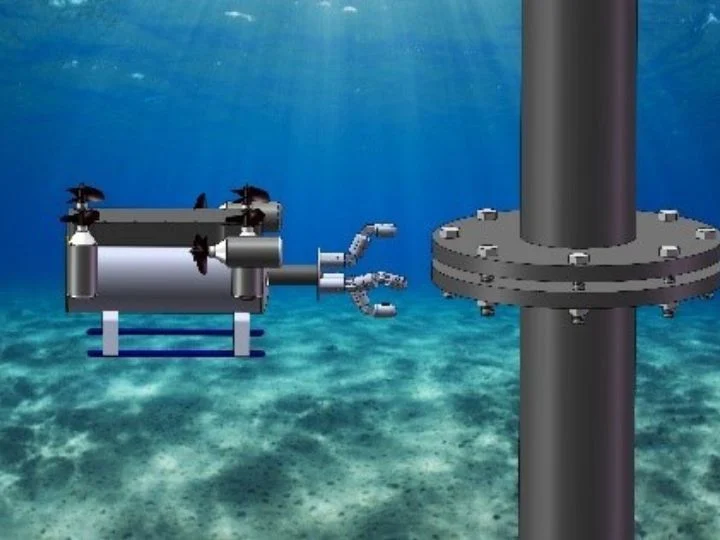
Researchers at the University of Houston are developing an autonomous robot to detect potential leaks and structural failures in underwater pipelines, in response to the increase in serious accidents in the oil and gas industry.
The new technology, called SmartTouch (see image), incorporates remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) equipped with smart touch sensors, video cameras and sonar for detailed inspections, promising to make inspections safer, more cost-effective and efficient by reducing the need for human intervention in deep environments. An ROV prototype has been successfully tested in the laboratory and in Galveston Bay, demonstrating the viability of this technology for critical underwater inspections, with preliminary studies being funded by the Subsea Systems Institute at UH 2 .
Companies leading robotic inspection technology
Multiple companies are at the forefront of the continuous development of this leading technology, promoting a better future for the Oil & Gas industry. Companies such as Gecko Robotics, GE Research, National Grid, Siemens, Autonomous Control Systems Laboratory and Samsung Group emerge in the introduction of disruptive inspection robots for this industrial sector.
Gecko Robotics, has developed wall-climbing robots that perform non-destructive testing inspections on tanks, boilers, pressure vessels, pipelines and more. Using specially designed sensor payloads, robots can inspect wall thickness, pitting, and many other forms of degradation. They have the ability to collect amounts of continuous data information compared to previous methods 3 .
While the GE Research company focuses on machinery management through aerial inspection robotics, a branch of field services, which enhances the conservation capabilities of industrial assets, increasing their safety and efficiency. By integrating with Digital Twin technology, the management and understanding of industrial infrastructure is simplified. They design equipment for the inspection of structures that performs precise and short-range inspections, contributing to better management of the physical-digital environment in various sectors, including the oil industry 4 .
Conclusions
The global robotic inspection market is experiencing great advancements; There is a growing demand for robotic solutions in inspection to ensure accurate and efficient defect detection. The integration of digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning into these robots is improving their ability to adapt, learn and make decisions in real time. The increasing adoption of robots allows for safer and more flexible inspection processes.
The constant evolution of these technologies and their integration into daily operations is optimizing operational efficiency, improving safety, minimizing costs and contributing to greater environmental sustainability.
References
- https://jpt.spe.org/emerging-robotic-technologies-for-oil-and-gas-operations?gclid=CjwKCAjws9ipBhB1EiwAccEi1MZMNzE36MmkKTdMTk526_BEo1XPu3SlTP5lbwlg3MeKyn7_6LggIxoCnjsQAvD_BwE
- https://www.uh.edu/news-events/stories/2023/august-2023/08312023-pipeline-robot.php
- https://www.geckorobotics.com/
- https://www.ge.com/research/project/robotics-aerial-inspection-repair


























