Cathodic protection is a control method to prevent corrosion in buried and submerged metallic structures. It allows to prolong the useful life of the structures, obtaining high benefits for the safety and reliability of the facilities, and a significant reduction in costs during the life of the assets.
It is commonly used to protect numerous structures against corrosion , such as: tanks, containers, pipelines, boats, docks, piles, among others. And its principle is based on an electrochemical process that consists of converting the exposed metal (structure to protect) into a cathode and reducing the potential for corrosion. There are two methods of cathodic protection (CP): by sacrificial anodes and by impressed current.
For cathodic protection a protective current is necessary. Which can be generated in two ways: On the one hand, with active galvanic anodes (sacrificial anodes) of magnesium or zinc, using the potential difference between the material to be protected and the less noble (more active) anode material; on the other hand, by protective current equipment as an impressed current source in connection with inert passive anodes such as metal oxide-coated titanium and iron-silicon or iron alloys.
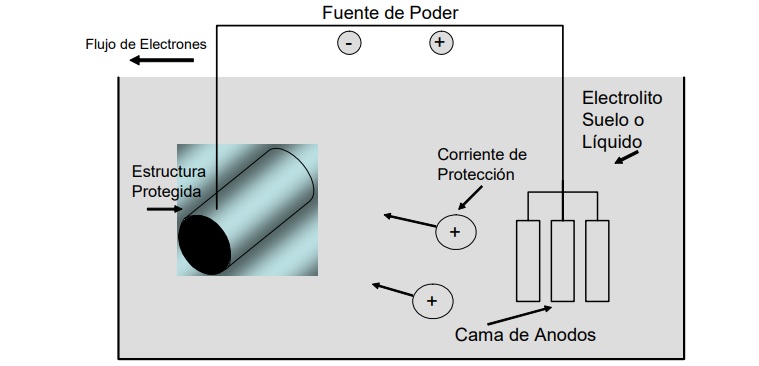
Despite being a long-standing technique, cathodic protection has evolved significantly in recent decades, thanks to new technologies and best practices. However, many companies still employ outdated techniques and technologies in cathodic protection, which can increase the risks of failure and decrease the efficiency of these systems.
Therefore, it is important for companies to be aligned with the latest technologies and best practices in cathodic protection to ensure the integrity of industrial assets.
This article covers the latest PC technologies and best practices and how businesses can ensure they align with them.
Emerging technologies in cathodic protection
Remote monitoring technology.
This technology allows engineers to remotely monitor the performance of cathodic protection systems, making it easy to identify problems early and implement corrective measures before failures occur. This technology allows operators to control and monitor cathodic protection from anywhere in the world. Achieving in this way improve efficiency and security by allowing constant monitoring of the systems.
high energy anodes.
These anodes can generate higher currents and produce a more efficient protection potential than conventional anodes. Additionally, these anodes have a longer life, reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Corrosion sensors.
They can measure the degree of corrosion in real time and automatically adjust the protection current to ensure optimal protection, allowing engineers to take preventive action before irreparable damage occurs. Additionally, corrosion sensors can be used in combination with remote monitoring technology for greater efficiency.
Advanced Anode Materials: New anode materials are being developed that are more effective and longer lasting than traditional materials. For example, platinum-coated titanium anodes have a longer life and are more effective than magnesium anodes.
Active cathodic protection systems:
Active cathodic protection systems are a new technology that employs a pulsating protection current instead of a direct current. This allows for more effective protection in areas of high resistivity.
Advanced modeling and simulation: These advances allow engineers and scientists to better understand corrosion mechanisms and design more effective cathodic protection systems. Computer simulation can predict how these systems will perform under different conditions and help optimize their design.
Recommended Practices in Cathodic Protection
In addition to the latest technologies, there are a number of best practices in cathodic protection that companies must follow to ensure the integrity of their assets.
— Appropriate selection of cathodic protection materials.
These materials must be carefully selected based on the environmental conditions and the characteristics of the exposed metal, in addition they must be compatible with the surrounding environment to avoid contamination and environmental risks.
—Proper installation of cathodic protection systems.
The installation must be carried out by trained and experienced personnel to guarantee a correct and safe arrangement, according to the manufacturer’s specifications and the safety regulations for the correct installation of these systems.
—Inspection and regular maintenance of cathodic protection systems.
It is important that these systems are regularly inspected to detect and correct any problems or defects. In addition, it is advisable to carry out maintenance to guarantee their optimum operation.
—Training and updating.
It is recommended that companies train their engineers and operations staff to keep them up to date on the latest technologies and best practices. In this way it is guaranteed that the personnel is trained on the latest techniques and technologies in cathodic protection, which improves the efficiency and safety of the system.
— External Corrosion Direct Assessment (ECDA) is a NACE International recommended practice for piping system integrity assessment that focuses on detecting areas of high probability of external corrosion. ECDA uses a risk-based approach to enable owners and operators of piping systems to make informed decisions about the need for repair or replacement of sections of piping, which can reduce the risk of failure and improve system safety in general.
Benefits of alignment with the latest technologies
Companies that are aligned with the latest technologies and best practices in cathodic protection can enjoy a number of benefits, such as: reduced risk of failure, increased system efficiency, reduced maintenance and replacement costs, and improved safety. and environmental protection. It is important that companies are aware of these latest advances in cathodic protection. Companies like Vecor Pipeline Integrity provide the latest PC technologies against corrosion, offering the best solutions for asset integrity.
Conclusion
To ensure asset integrity and avoid costly safety and environmental issues, it is critical that companies align with the latest technologies and best practices in cathodic protection. Remote monitoring technology, high energy anodes and corrosion sensors, can significantly improve the effectiveness and safety of these protection systems. Additionally, recommended practices such as proper material selection, proper installation, regular inspection and maintenance, and personnel training are relevant to ensuring the efficiency of these systems in controlling corrosion.

