Author: Ing. Mario Toyo, August 19, 2023
Introduction
In the vast and dynamic universe of the energy industry, every minute counts. Operations in the Oil & Gas sector, the engine of the global economy, depend to a large extent on efficiency and optimization at all levels.
However, there is a pervasive challenge that lurks in these operations: “ the stops ”. Planned downtime is essential for facility maintenance and improvement, but it can also be costly and complex to manage. How, then, can we turn these downtimes into opportunities to maximize operational efficiency and available resources?
This article presents a comprehensive analysis of the strategies and technologies that are revolutionizing the approaches used by the Oil and Gas industry to manage detention processes. Specifically in Shutdown Management, which covers more than the interruption of production. Includes planning, implementation and optimal adjustment of procedures; represents the skill of minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency.
We begin by reviewing the key events that will define the success of the shutdown, then the cutting-edge technologies that are revolutionizing shutdown management in the Oil & Gas industry, such as automation, the Internet of Things (IoT), augmented reality and more. they are changing the way we plan and execute shutdowns.
We’ll also look at strategies that aim to reduce interruptions, maximize productivity, and ultimately ensure that every moment of downtime becomes an opportunity for continuous improvement.
Program of key events in shutdown management
Control document structured systematically and sequentially based on the different activities required throughout the plant shutdown management process. Typically generated through project planning and control software
The purpose of this document is to indicate in detail the start and end dates of the main activities and their duration, definition of resources, assignment of responsibilities and control of the tasks associated with the phase of managerial integration and development of the scope of the shutdown. of the plant, using as support a management checklist based on the needs of the management plan and a referential time baseline (See figure 1).
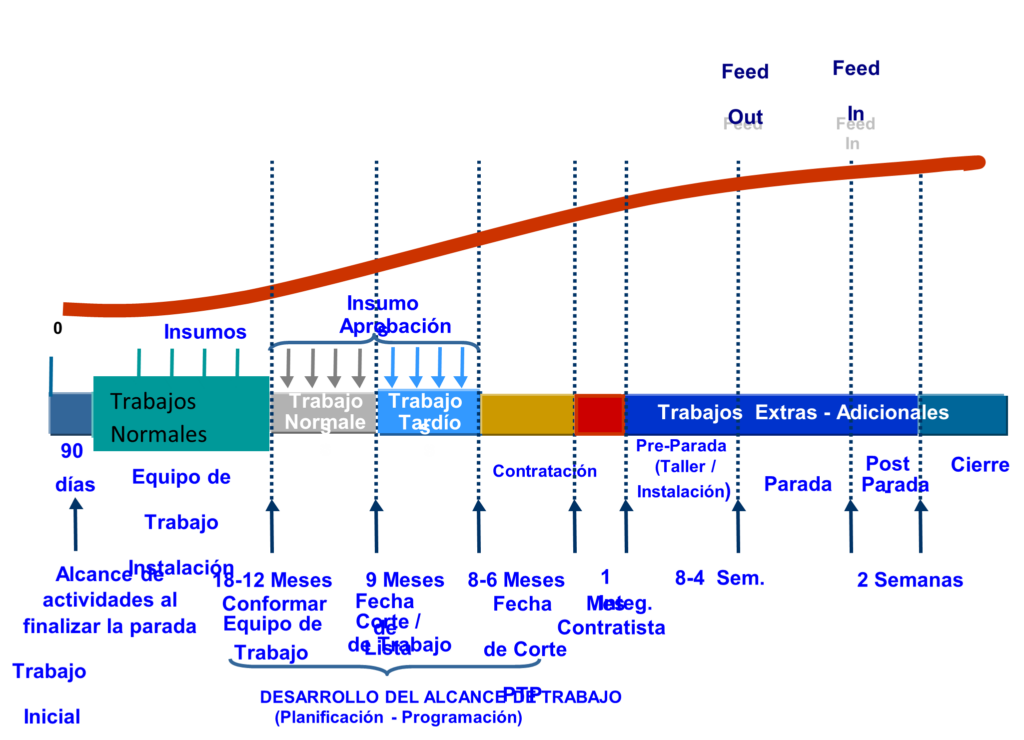
This model defines as main activities that can encompass processes, sub-processes or elements that have a high incidence in the phases of management integration and development of the scope of the shutdown management process, they can be presented in the form of preceding or proceeding events and in the form of independent, since the flow of processes in the managerial model develops both sequentially and in parallel.
It is worth noting; that the application of this model is the basis for a successful execution; the rest would be the effectiveness of doing things and the commitment to the project variables.
More than 200 stops were worked under this model and the expected objectives were always achieved.
Digital Strategies for the Reduction of Interruptions .
- Precise and Pioneering Automation
Automation stands as the fundamental pillar in the fight against unnecessary interruptions. Advanced control systems monitor processes in real time, detecting anomalies in operations before they can worsen. This not only reduces downtime, but also optimizes overall operation and prevents costly losses.
Precise, pioneering automation is one of the most important strategies for improving shutdown efficiency in the oil and gas industry. By automating tasks, companies can reduce downtime, improve security and increase productivity.
There are a number of tasks that can be automated, including:
- fault diagnosis
- preventive maintenance
- inventory management
- project management
All this for the respective analysis and good decision-making, minimizing the inactivity that may arise and affect the stop in question.
- The Internet of Things (IoT)
The convergence of the IoT with the Oil & Gas industry has unleashed a new era of shutdown management. Connected devices and smart sensors collect crucial data on equipment status and operating conditions. This facilitates constant monitoring and accurate prediction of problems, enabling informed decision making and planning optimization.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) can help companies train employees for shutdowns in a safe and effective way. AR and VR can help employees view equipment and facilities in 3D, and can help employees learn how to perform maintenance tasks safely. In fig. 2 there is an example.

Project Management Software
- Project management software can help companies plan and manage shutdowns efficiently. The software can help companies create schedules, assign resources, and track the progress of shutdowns. Examples of some: Oracle Primavera P6, Clarizen, Monday.com.
- Modeling and simulation tools
Modeling and simulation tools can help companies understand the impact of shutdowns on plant performance. The tools can help companies identify bottlenecks and develop strategies to improve shutdown efficiency.
Some of these tools are: ASPEN HYSYS, ANSYS, MATLAB.
Strategies for Maximizing Operational Efficiency
- Maintenance based on accurate data
Adopting a data-driven approach to maintenance has become an essential practice. By analyzing real-time and historical data, companies can anticipate potential failures and carry out appropriate preventative maintenance. This translates into more planned downtime and a significant reduction in unscheduled downtime.
- The scope of work . It is the document that describes the work that must be carried out at the stop. The cost and time of the project will depend on it; therefore, you must be precise, complete and clear in your activities.
- Stop activities . Only all those interrelated Assets will be intervened; that they can only do maintenance with the plant out of service. The rest is done in the Routine.
- Other data:
- Be clear and concise.
- Use language that all stakeholders can understand.
- Be specific about the work that needs to be done.
- Include all project deliverables.
- Set deadline dates for the project.
- Set a budget for the project.
- Identify project risks.
- Identify change management methods.
Shutdown planning is no longer an isolated task (Fig. 3). Interdepartmental collaboration and transparent communication are critical to success. The implementation of collaborative project management tools fosters fluid communication between teams, avoiding conflicts and ensuring efficient execution. In addition, you must take into account:
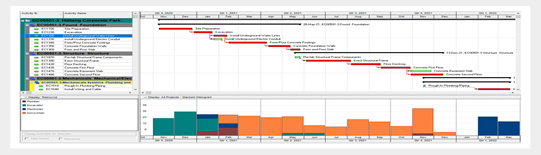
Planning and coordination : It is important to plan and coordinate the stops carefully. This will help ensure shutdowns are carried out efficiently and there is minimal interruption to production.
- Proper Equipment and Materials : It is important to have the proper equipment and materials available for stops. This will help ensure shutdowns are completed quickly and efficiently.
- Trained personnel: It is important to have trained personnel for the stops. The knowledge acquired will be the fundamental basis for decision-making and therefore in the expected results. The staff must have:
- Management and knowledge of security, through courses and training
- Control and management of International standards such as: API, ASME, ASNT, AAMP and others, to ensure the mechanical integrity of assets.
- Management of Procedures
- Effective supervision of contractor companies certified to carry out this activity.
This will help ensure that stops are carried out safely and effectively.
- Safety Procedures: It is important to have safety procedures in place for stops. These procedures will help ensure employees are safe during shutdowns.
- Application of Lean Principles
Lean principles, known for their focus on efficiency and waste elimination, find fertile ground in shutdown management. Identifying and eliminating redundant and superfluous processes speeds up the execution of shutdowns, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Here are the five key principles of Lean:
- Identify the value. The first step is to identify the value that the customer seeks in a product or service. This can include things like quality, price, availability, and convenience.
- Map the value stream . Once the value has been identified, the next step is to map the value stream. This involves identifying all the steps involved in creating and delivering the product or service.
- Create flow . The third principle of Lean is to create flow. This means removing delays and roadblocks that slow the flow of value.
- Work on demand . The fourth principle of Lean is to work on demand. This means producing only what the customer needs, when they need it.
- continuous improvement . The fifth and final principle of Lean is continuous improvement. This means constantly looking for ways to improve the process of creating and delivering the product or service.
- Adequate equipment and materials
It is important to have the right equipment and materials available for the stops. This will help ensure shutdowns are completed quickly and efficiently.
Interesting Facts about the Theme.
- Success Stories and Sector Experts
- In 2016, an oil and gas company was able to reduce the downtime of a plant shutdown from 10 days to 5 days using Delta Catalitic’s “Effective Plant Shutdown Management” model. There are a number of factors that this model uses that can contribute to efficient shutdown, including:
- Planning: Careful planning is essential to any successful shutdown. This includes identifying the jobs that need to be done, estimating the time and resources needed, and developing a communication plan.
- Equipment: Make sure you have the right equipment to get the job done. This includes tools, equipment, and qualified personnel.
- Procedures : Make sure you have clear and concise procedures for getting the jobs done. This will help ensure jobs are completed safely and efficiently.
- Quality control : Make sure you control the quality of the work that is done. This will help ensure jobs are completed correctly and equipment is in good condition.
- Communication: Be sure to communicate with employees, contractors, and other stakeholders throughout the outage. This will help ensure everyone is on the same page and jobs are completed on time and on budget.
These are just a few factors in how the Catalytic Delta model can help companies reduce downtime, increase efficiency and improve safety.
- Current and Future Innovations
- Digital Twins for Advanced Simulations
Digital twins, accurate virtual recreations of physical equipment and processes, are revolutionizing the way outages are approached. These virtual replicas allow the simulation and optimization of processes before implementing changes in the real world, minimizing risks and reducing downtime.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Failure Prediction
AI is positioned as an essential tool in the early detection of problems. By analyzing large data sets, AI algorithms can identify subtle patterns that indicate impending problems. This state-of-the-art technology allows timely interventions and avoids costly downtime.
Conclusions
Efficient shutdown management in the Oil & Gas industry is not just an aspiration; it is an unavoidable necessity in a world where competition and optimization are essential. Asset management through a good work model, emerging technologies such as automation, IoT, AR and digital twins, combined with strategies such as data-driven maintenance and interdepartmental collaboration, are paving the way towards a future in which stops are shorter, more efficient and more profitable.
Success stories and present and future innovations highlight the urgency of adopting advanced solutions in stop management. Ultimately, the convergence of technology and strategy is forging a path towards a horizon where the Oil & Gas industry will shine with unmatched efficiency.
Act Now and Optimize Your Energy Future!


























