Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Importance of composite materials
- Challenges in evaluating composite materials
- Types of Non-Destructive Testing for composite materials
- Advantages of Non-Destructive Testing on composite materials
- Recent technological developments
- Success stories in the application of Non-Destructive Testing
- Ethical and environmental considerations
- Conclusions
- References
Introduction
Composite materials have revolutionized numerous industries, from aerospace to automotive, due to their strength and lightness properties. However, ensuring the structural integrity of these materials is necessary for their long-term performance. In this context, Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) has become important tools to evaluate quality and detect possible defects without compromising the integrity of the material.
This article highlights “Advances in the evaluation of composite materials”, focusing attention on “Non-Destructive Testing”. It addresses the following technologies: advanced ultrasound, digital radiography, active thermography and artificial intelligence, in order to understand how these tools ensure the excellence and reliability of the materials that drive the technological era.
The Importance of composite materials
Before discussing Non-Destructive Testing , it is necessary to understand the importance of composite materials in various applications. From structural components in aircraft to automotive parts, these materials offer a unique combination of strength and lightness, optimizing performance and efficiency across multiple industries.
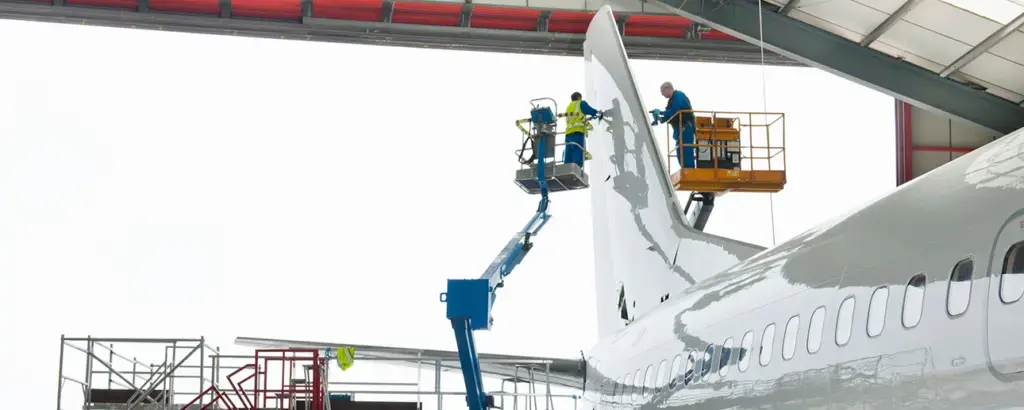

Challenges in evaluating composite materials
Despite their advantages, the evaluation of these materials presents significant challenges. Internal defects, such as air inclusions or delimitations, can be difficult to detect without damaging the material. This non-destructive testing provides solutions to evaluate integrity without compromising material quality.
Types of Non-Destructive Testing for composite materials
Among the most used testing methods are:
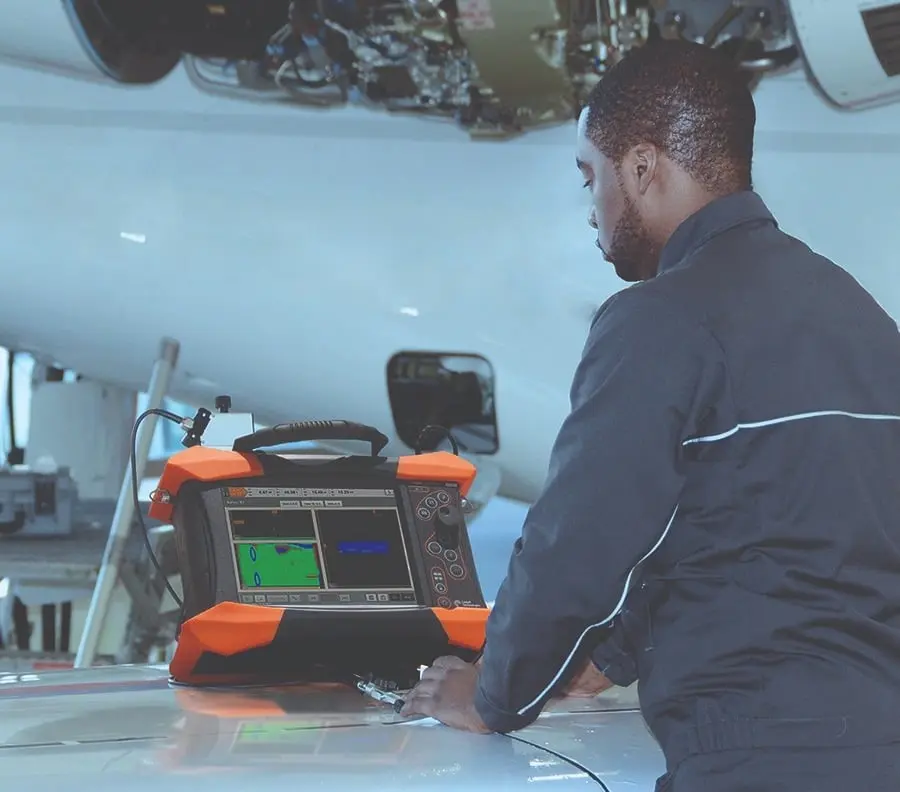
Ultrasound: This method uses ultrasonic waves to detect imperfections in the material. Variations in wave speed can indicate the presence of defects, allowing accurate assessment of material integrity.
Thermography: Infrared thermography detects temperature variations on the surface of the material, revealing internal defects. This method is especially useful for identifying deliminations and bonding problems.
Radiography: Industrial radiography uses x-rays or gamma rays to penetrate the material and reveal possible internal defects. This method is effective for identifying air inclusions or density problems.
Remote Visual Inspection: The use of cameras and visual inspection systems allows a superficial evaluation of the material. Although less penetrating, this technique is valuable for identifying visible surface defects.
Advantages of Non-Destructive Testing on composite materials
Through these tests, the evaluation can be carried out without affecting the physical integrity of the material. This is important, especially in industries where safety and reliability are a priority. In addition, these tests allow the early detection of defects, which facilitates the implementation of corrective measures before problems worsen.
Recent technological developments
Technology does not stand still, and Non-Destructive Testing is no exception. Recent advances have improved the accuracy and efficiency of these methods in the inspection of composite materials. Among these are:
Advanced Ultrasound Techniques
Although it has been applied for decades, new technological advances have been integrated in recent years that have facilitated the inspection of these materials with an increase in the probability of defect detection (POD).
Among these advances we can mention: Phase Array Ultrasound (PAUT), the Total Focusing Method (TFM) and more recently Phase Coherence Imaging (PCI), the latter special for the detection of faults close to surfaces and inspection of thin components, because start and background echoes are eliminated. Likewise, new transducer designs have been developed to facilitate the inspection tasks of these types of components.
digital x-ray
Digital radiography has also shown great advances in the inspection of composite materials , such as providing high-resolution images more quickly and efficiently.
With advances in automation, image analysis is performed quickly and accurately using advanced algorithms, accelerating the inspection process and facilitating the identification of potential defects with a high probability of detection (POD) and greater data storage capacity. . Furthermore, in the near future, emerging technologies such as backscatter tomography present encouraging prospects.
Microwave test
Although its application has not yet become widespread, research has shown great progress in recent years in the inspection of composite materials with non-destructive testing such as microwave through its dielectric nature and its penetration capacity, which allows the detection of failures inside the component.
Active thermography
In the active thermography technique, controlled heat generation technologies have been improved, allowing greater precision by focusing heat on specific areas, facilitating the identification of microscopic defects. Furthermore, the incorporation of advanced image processing algorithms has optimized data interpretation, allowing automatic detection of anomalies.
Remote Visual Inspection
The latest developments in Remote Visual Inspection in obtaining higher quality images and improvements in stereoscopic measurements have facilitated the generation of more efficient quality controls, more precise sizing and an increase in the probability of detection (POD).
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence has been integrated into the interpretation of data, allowing a faster and more accurate identification of possible defects, and its integration into robotization and automated learning (machine learning, ML), has enabled the most efficient application with continuous improvement in inspection of composite materials.
Success stories in the application of Non-Destructive Testing
Several cases demonstrate the effectiveness of these tests in the evaluation of this type of material. For example, in the aerospace industry, where safety is paramount, the use of ultrasound has made it possible to identify internal defects in critical components without affecting their performance. These cases highlight the importance of the systematic application of Non-Destructive Testing in the manufacturing and maintenance of products based on composite materials.
Ethical and environmental considerations
As we advance the use of technologies to evaluate materials, it is essential to address ethical and environmental considerations. The waste generation associated with some traditional methods, such as radiography, poses environmental challenges. The industry is responding with more sustainable approaches and methods that minimize environmental impact.
Conclusions
In the era of composite materials , assessing structural integrity is key to ensuring safety and performance. Non-destructive testing has emerged as important tools in this process, offering accurate evaluation without compromising material quality.
With continued technological advances, these inspection methods will continue to play a valuable role in the manufacturing and maintenance of products that depend on the strength and lightness of these materials. The systematic application of non-destructive testing not only ensures product quality, but also drives innovation and sustainability in key industries.
References
- EVIDENT. Non-destructive adhesion control for aircraft composite materials; Consulted on November 24, 2023; https://www.olympus-ims.com/en/applications/non-destructive-bond-testing-aircraft-composites/
- AJAY KAPADIA . Non-Destructive Testing of Composite Materials; Consulted on November 25, 2023; https://avaloncsl.files.wordpress.com/2013/01/ncn-best-practice-ndt.pdf
- B. BORO DJORDJEVIC . Nondestructive Test Technology for the Composites; Consulted on November 27, 2023; https://www.ndt.net/article/ndt-slovenia2009/PDF/P28.pdf .
- ADDCOMPOSITES . What are the Different Inspection Methods of Non-destructive Testing for Composites?; Consulted on November 14, 2023; https://www.addcomposites.com/post/non-destructive-testing-for-composites-different-inspection-methods
About the Author.

Carlos Alvarez. Mechanical Engineer, with Level III certification by the American Society for Nondestructive Testing (ASNT) in Ultrasound and Industrial Radiography testing. He has more than 29 years of experience in the oil and gas industry, especially with Petróleos de Venezuela SA (PDVSA) and inspection service companies related to the oil sector. He has an extensive academic career as a University Professor and Facilitator of Specialized Training Programs for professionals in the inspection area. E-mail: carlos alvarez@inspenet.com

