The aerospace industry is a sector where quality and safety standards are extremely demanding, influencing technical disciplines such as Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) to more and better developments to detect the smallest defect. This has led in the case of Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing (UT) to continue evolving with tools such as “time reversal” for inspection of parts with composite materials and complex geometries, on the other hand, for comprehensive evaluations, the combination with Eddy currents make this pair of techniques the most used in terms of inspection of aircraft parts and components.
For both civil and military purposes, aerospace manufacturing is subject to strict design specifications and quality standards. In addition, they must also strictly check the quality of the aircraft’s engine, fuselage and all related components before operation and frequently during service. In order to protect human lives associated with this type of activity.
NDTs have been a routine practice in the inspection and quality assessment of components associated with this industry for decades. Ensuring the safety of a wide range of components quickly, efficiently and volumetrically.
NDT inspection of composite elements, vital for aircraft.
Composite materials or “composites” are widely used in the aerospace industry to manufacture components such as the body structure, engine blades, wings and fuselage (Figure 1). It is a viable alternative due to its light weight while providing similar structural strength to other metals. The defects induced in these composite materials can come from manufacturing and can be detected by scanning with Phase Array Ultrasound (PAUT) instruments with an appropriate inspection technique.
Modern PAUT scanners and probes provide flexibility, accuracy, and reliability when detecting damage to composite materials that can include delamination, cracking, inclusions, and porosity . Skilled technicians coupled with powerful inspection solutions can help maintain quality standards with various NDT techniques in the aerospace industry.
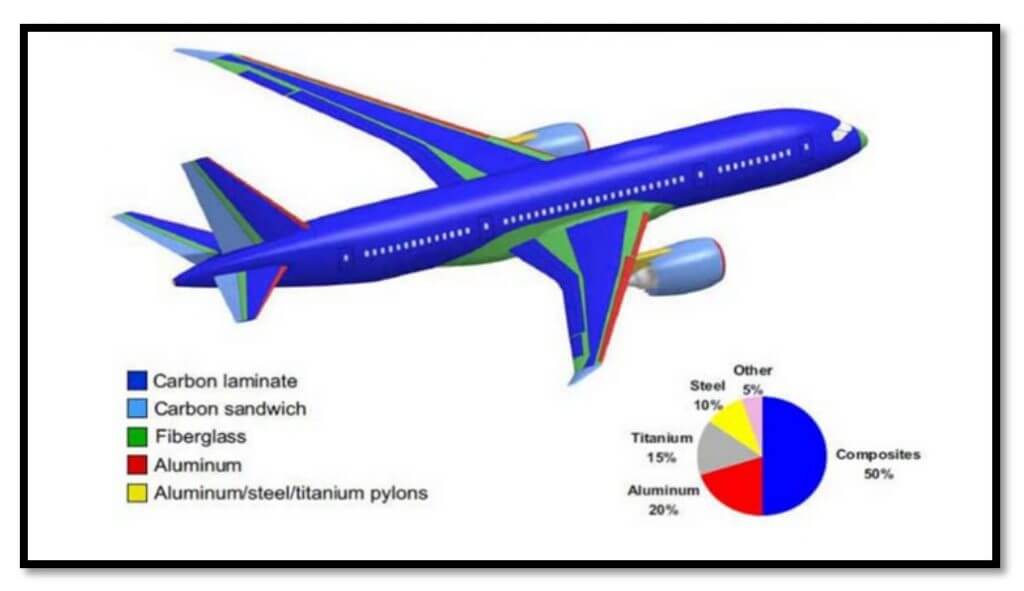
One of the most widely used composite materials in this type of industry is carbon fiber. The NDT inspection of carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) composites for the aerospace industry benefits from the PAUT technique and specifically from the Time Reversal (Time reversal in English) , which provides better signal quality, coverage and probability of defect detection (Figure 2).
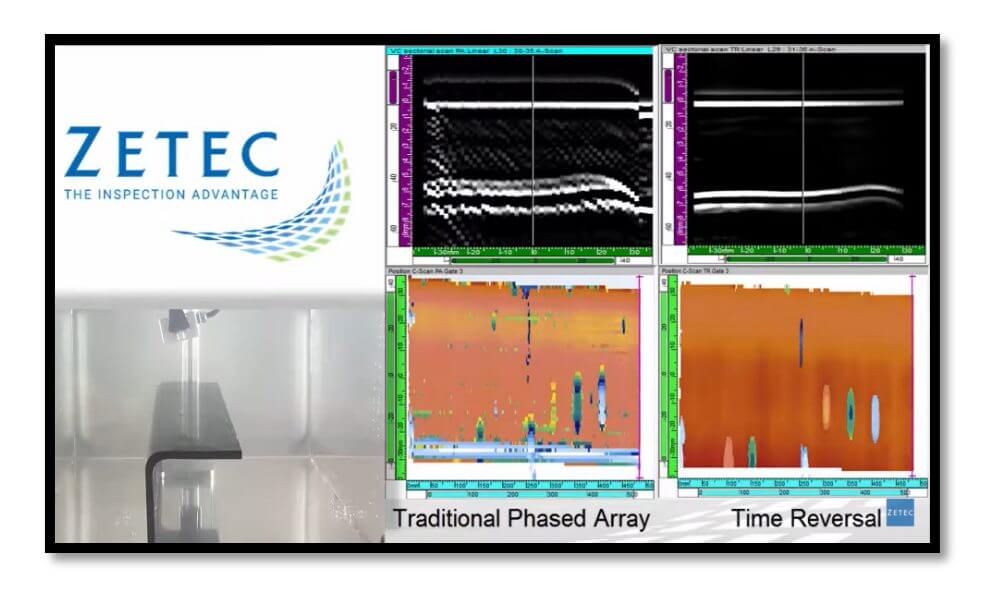
Effect of the evaluation with the “Time Reversal” function in parts with complex geometry
Using PAUT probes with the time reversal feature can overcome the challenges of complex geometries and variable thickness inspection problems faced by a standard PAUT in composite material inspections. Through the improved ability of the probes to align the UT beams according to the profile of the inspected part, the automatic inspection system facilitates efficient surface profiling, data capture and analysis, the PAUT with the function investment of time can produce faster and more accurate results.
Inspection of critical components of the aircraft.
Every takeoff and landing takes a toll on the aircraft’s landing gear due to extreme heat and braking force. As an important part of the aircraft, the wheels must be inspected for possible defects such as cracks (Figure 3). For improved accuracy, faster inspection, and cost effectiveness, many technicians rely on eddy current testing (ECT).

Defects induced in the helices due to heat or stress can be difficult to visualize manually (Figure 4). Since the propellers are mostly made of composite materials, most of the flaws can be underlying. To identify flaws, quality inspectors can use NDT techniques such as ECT and UT. ECT is favorable for identifying surface defects, especially on conductive alloys. UT is suitable for locating sub-surface defects and is a perfect solution for inspection of composite materials.

NDT for commercial and military aerospace use require compliance with standards established by government and international organizations. For example, in the US, the Federal Aviation Administration recommends obtaining an annual inspection certification. Compliance with federal and international regulations during manufacturing and maintenance helps keep crew and passengers safe and ensures aircraft durability.
Conclution.
The value of commercial flights is associated with their excellent performance and at the same time guaranteeing the safety of the crew and passengers. This can be accomplished by identifying underlying defects that may affect the integrity of aircraft components. UT and ECT can produce inspections with high-quality results in less time, facilitating quality control with less downtime.
References
Own source.


