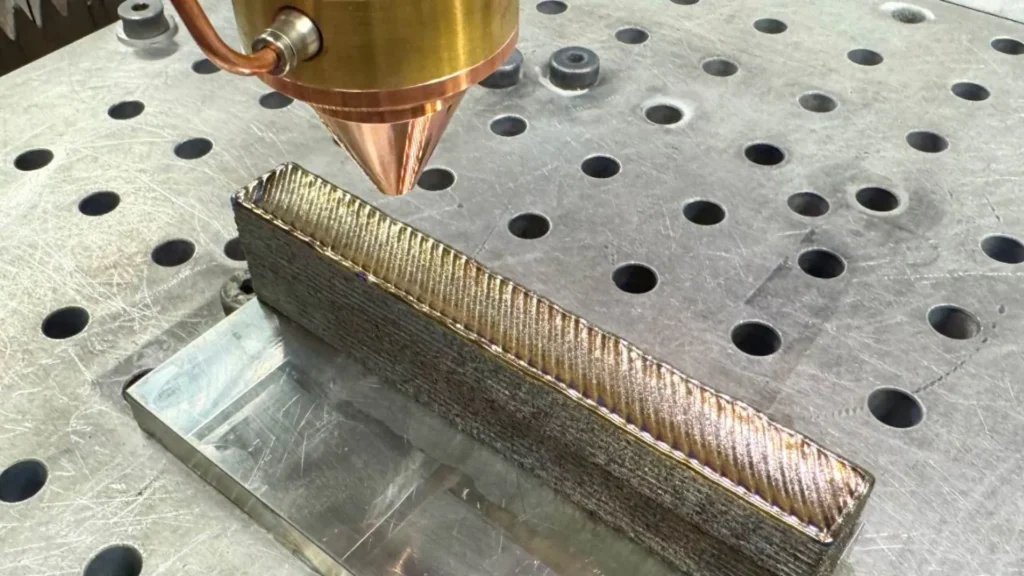
Engineers at RMIT University in Melbourne have developed a 3D printed titanium alloy that promises to significantly reduce costs and improve mechanical performance in a variety of industries. The team succeeded in producing a cheaper alternative to traditional Ti-6Al-4V, one of the most commonly used materials in additive manufacturing.
Can a titanium alloy without vanadium be more efficient?
The new approach replaces increasingly expensive vanadium with more affordable alternative elements. In addition, the developed formulation has been designed to generate a more uniform equiaxial grain structure during printing, overcoming the common columnar pattern that tends to weaken certain areas of the printed metal.
Thanks to this new design framework, as detailed in a recent publication in Nature Communicationsthe researchers were able to reduce the alloy’s production cost by 29%, while maintaining superior strength and ductility over conventional alloys. conventional alloys used in 3D used in 3D printing. Tests showed superior performance in both load and toughness, critical factors for aerospace and medical applications.
Ongoing commercialization and industrial validation
Ryan Brooke, PhD candidate and lead author of the study, is exploring commercialization avenues through an RMIT research translation grant. Following interviews with stakeholders in the aerospace, automotive and medical technology industries, the team identified a clear demand for new alloys with substantial cost and performance advantages.
The published methodology provides predictive criteria for the design of new alloys with 3D printing. Beyond the development of this particular alloy, RMIT has laid the foundation for future innovations in advanced metallic materials that can be adapted to more sustainable and efficient production.
Follow us on social networks and don’t miss any of our publications!
YouTube LinkedIn Facebook Instagram X (Twitter) TikTok
Source and photo: RMIT

