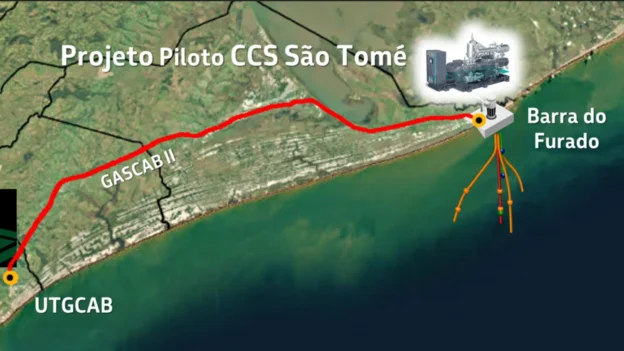
Petrobras announces the approval of a CCS project, a pilot carbon capture and storage development in Santo Tomé, Macaé. This strategic initiative will enable the capture of up to 100,000 tons of CO₂ annually starting in 2028, using technologies developed for offshore projects, now applied to the energy transition.
Integration of technologies for the CCS project
This project is structured on a total integration model: capture, transport and injection of CO₂ in a deep saline reservoir in the region of Barra do Furado, Quissamã. This configuration seeks to enhance Brazil’s strategy as a regional benchmark in the region in the geological carbon storagealigned with international standards and regulated by entities such as the ANP and INEA.
This development was designed as a learning and validation platform, a pilot scheme that will serve as a laboratory for testing under real conditions. The technologies employed will enable accurate monitoring of the CO₂ plume, generating essential information to establish reference standards and methodologies for future capture and storage centers.
The data obtained could drive new routes to exploit CO₂, such as its use in the production of synthetic fuels. This would expand the potential of CCS technologies beyond climate mitigation, opening up opportunities for industrial innovation in the country.
Petrobras proposes this pilot as part of a broader Research, Development and Innovation strategy, generating technical capabilities that can be replicated in both onshore and offshore CCS centers.
Source and photo: Petrobras