Rumours about the arrival of a new geological era known as the Anthropocene have caused concern in recent months. Do you know what it is, when it started and what consequences it will bring? In this analysis you will understand what it means for humanity, what its characteristics are and if we still have time to do something to mitigate its impact.
What is the Anthropocene?
The term Anthropocene comes from the Greek anthropos , meaning “human,” and kainos , meaning “new.” It was proposed by the scientific community as a new geological epoch that could replace or succeed the Holocene and arises due to the significant impact that human activities have had on terrestrial ecosystems. In other words, the Anthropocene refers to the period in which human actions have left a deep mark on the planet.

Although the term has been suggested as a new geological epoch due to the notable effect of human activities on the environment , there is still no consensus on its exact start date. However, it is important to clarify that the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) and the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) – which is a subcommittee of the IUGS – issued a joint statement where they formally rejected the Anthropocene as a geological era .
It is with the delegated authority of the President and Secretary General of IUGS and on behalf of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) that the vote of the ICS Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy (SQS) to reject the proposal for an Anthropocene Epoch as a formal unit of the Geologic Time Scale is approved. 26 March 2024.
In the following image from the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) you can see the geological stages of the planet, with the Holocene being the current era.
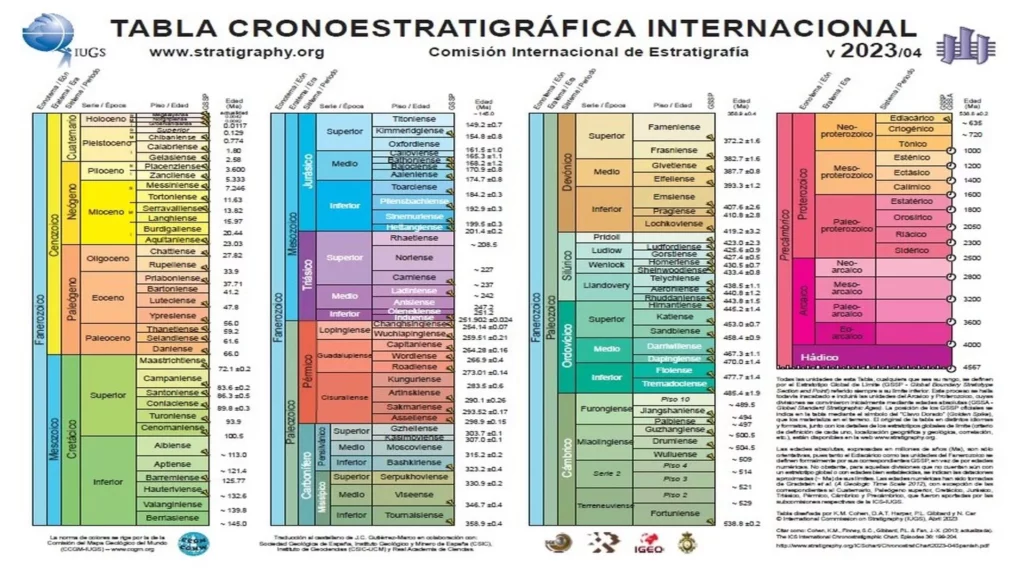
Despite this, the ICS clarifies that the term “will continue to be an invaluable description of human impact on Earth.” This means that until now the word Anthropocene is only a symbolic expression used to refer to this current period where the consequences of polluting activities that have greatly contributed to global warming and climate change are already visible.
It is worth noting that these organizations have not been the only ones to talk about the Anthropocene, as UNESCO published a digital publication in 2018 that encompasses aspects that have increased their relevance to the point that to date they remain more relevant than ever.
Holocene and Anthropocene: A time of transition?
According to science, it is argued that the most direct consequence of human activities on the environment is global warming of anthropogenic origin , caused by carbon dioxide emissions derived from the burning of fossil fuels, such as oil, coal and gas, as well as deforestation and, to a lesser extent, cement production.
However, an article published in the National Library of Medicine explains that although the definition of anthropogenic contaminants is not entirely clear, anthropogenic contamination dates back to the time when humans learned to master fire.
On the other hand, there is other evidence of contamination that is confirmed by the presence of rocks called plastiglomerates , which consist of a mixture of plastics, sand, rocks and human waste. Scientists say that in the future, these rocks will constitute some of the strongest evidence of human impact on the planet.
A known case is from the island of Trindade located in Brazil, where a team of geologists found this type of rock, setting off concern alarms.

Geologist Fernanda Avelar Santos explains the disturbing discovery Source: UnoTV.
Likewise, other scientists have found evidence that supports their hypotheses and an example is what happens in Lake Crawford, located in Ontario, Canada. Although this lake is a popular tourist destination, microplastics and traces of nuclear explosions have been found in its sediments, demonstrating that we have entered a new stage beyond the Holocene.
Is there still time to do something?
One way to protect the planet from this deterioration that could be irreversible is to adopt a more responsible attitude towards the impact that our activities have on the Earth’s ecosystem. Some measures we can take to stop the advance towards an environmental catastrophe that affects everyone include the conservation and care of biodiversity, the use of renewable energy sources, more sustainable agricultural and industry practices, the care and responsible use of water. , reducing deforestation and adopting more ecological means of transport.
Follow us on social media and don’t miss any of our posts!
Inspenet.com YouTube LinkedIn Facebook Instagram X
Source: ensedeciencia.com
Photos: Inspenet

