Non-Destructive Testing are inspection methods to evaluate the integrity of materials and components in the industry. As technology advances, traditional testing techniques are evolving towards digital solutions supported by artificial intelligence 1 . This not only improves testing accuracy but also enables ongoing training for inspectors through the use of AI-backed applications.
This article presents the technological progress that digital Non-Destructive Testing represents in the industry, as well as its application in the technical training of professionals in the field of non-destructive inspections.
What are digital Non-Destructive Testing?
They are a set of methods that use digital technology to evaluate the quality and integrity of materials and components. These techniques go beyond traditional NDT methods, which often involved visual inspections, radiographs, ultrasonic testing, among others, and in an analog manner. Digital testing includes techniques such as digital radiography (DR), infrared thermography (IRT), advanced ultrasonic techniques such as phased array ultrasound (PAUT), time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD), and total focus method (TFM). ), and computed tomography (CT).
Advantages
Digital NDTs offer numerous advantages over traditional analog methods; which are reinforced today through the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI). Listed below are the main advantages that have led to increasing adoption of digitalization in the industry.
- Greater precision: One of the main advantages of digital NDT is its accuracy, it allows more precise data collection and interpretation of the results; Therefore, inspectors can identify smaller defects and evaluate the integrity of materials more efficiently.
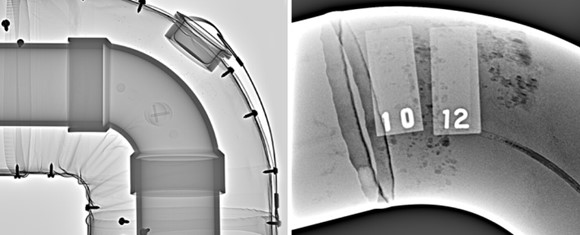
- Reducing radiation exposure: In the case of x-rays, the transition to digital radiography has significantly reduced radiation exposure for inspectors and other workers. Digital NDT uses more sensitive detectors (e.g., digital radiography, see Figure 1) and requires less exposure time, which decreases the risks associated with ionizing radiation.
- Greater efficiency: The incorporation of digital technologies in Non-Destructive Testing has optimized the effectiveness of the tests. Data collection and analysis are performed more quickly, reducing the time required to conduct an inspection 2 . In addition, results can be shared online (Figure 2), facilitating decision making and collaboration between work teams.

- Data Storage and Access: Inspection records can be archived digitally, making it easy to manage information and review previous inspections. This is essential for monitoring and evaluation over time.
Continuous training of inspectors
Below, various digital NDT applications are presented that contribute to the continuous training of professionals in this field.
- Simulations and virtual reality: The digitization of Non-Destructive Testing makes it possible to generate simulations and virtual reality experiences, using artificial intelligence for the training of inspectors 3 . This approach is especially beneficial in the initial training phase, allowing inspectors to practice identifying defects in a virtual environment before facing real situations.
- Automatic Defect Recognition (ADR): ADR can be used to show examples of digital radiographs with known defects. This allows beginning inspectors to become familiar with the types of defects they may encounter in real-world situations, making their initial training easier.
- Data-driven learning: Accurate data collection in digital testing allows inspectors to analyze and learn from the results. They can access an extensive data set from previous inspections to identify defect patterns and hone their detection skills. Machine Learning (ML), a sub-discipline of artificial intelligence, is very effective for this purpose.
- Distance training: Digital technology simplifies remote education, which is particularly beneficial in circumstances where inspectors cannot participate in face-to-face courses. Online training programs can encompass inspection demonstrations and interactive sessions to strengthen understanding of concepts and techniques.
- Continuous updating: Digital technology continues to advance, meaning inspectors need to constantly update their skills and knowledge. Experts can enroll in online training courses to stay informed on the latest techniques and technologies.
- Real-time assistance: During practical inspections, artificial intelligence can offer real-time support to inspectors 4 . For example, you can help interpret complicated data or point out potential issues.
Ethical challenges and considerations
- Cost: Implementing digital technologies may not be cost-effective, especially for small businesses. It is necessary to invest in state-of-the-art equipment and in the training and training of personnel.
- Ethics and privacy: The collection and storage of digital data raises ethical and privacy questions. It is essential to ensure compliance with privacy regulations and the safeguarding of sensitive information
- Training need: The transition to digital NDT requires adequate training for inspectors. The learning curve can be steep, and there is a need to ensure that professionals are prepared to use the technology effectively.
Conclusion
Digital Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) is transforming the performance of non-destructive inspections and inspector training. This technological progress is committed to raising quality and safety standards in the industry, while opening up possibilities for professional growth for those involved in the field of inspections.
References
- Hossein Taheri, Maria Gonzalez B, and Mohammad Taheri; “Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Smart Technologies for Nondestructive Evaluation”; Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun; 22(11): 4055.
- Siril Yella, NK Gupta, Dougherty; “Artificial Intelligence techniques for the automatic interpretation of data from non-destructive testing”; Volume 48, Number 1, 1 January 2006, pp. 10-20(11).
- Iikka Virkkunen, Tuomas Koskinen, Topias Tyystjärvi and Oskar Siljama; “AI will shape the future of NDE data analysis”; Accessed as of November 31, 2023. https://blog.asnt.org/ai-will-shape-the-future-of-nde-data-analysis/
- Maximilian Topp. How does Artificial Intelligence (AI) in NDT work; Accessed October 01, 2023. https://sentin.ai/en/ai-in-ndt/.

