Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is square groove welding?
- Square groove welding process
- Symbols and representation of square groove welds
- Methods and techniques
- Inspection and problems of square groove welds
- Industry applications
- Advantages of square groove welding
- Disadvantages of square groove welding
- Safety considerations
- Security protocols
- Conclusions
- References
Introduction
Square groove weld is a very useful process in various industries, where high precision and strength are required in joining metals. This article provides a detailed overview of the concept of square groove weld joints, their applications, advantages, disadvantages, procedures and safety considerations.
What is square groove welding?
Square groove welding is a butt welding technique where the edges of the materials to be joined are prepared in the form of a square groove. This preparation allows an even distribution of the filler material, ensuring a strong and durable joint.
Square groove welding process
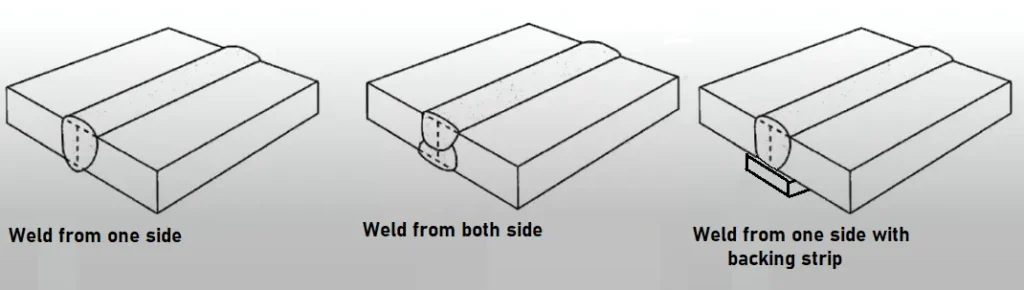
This process can be performed on one or both sides of the weld joint. Single-sided welding is generally used for thin sheet metal. When a weld joint is required for thicker sheet metal, welding must be done from both sides or welding from one side only using backing plates or welds1, as shown in figure1. Now, for square groove welds on very thick plates, automated systems such as Electrogas arc welding (EGW) are used for vertical welding.
Symbols and representation of square groove welds
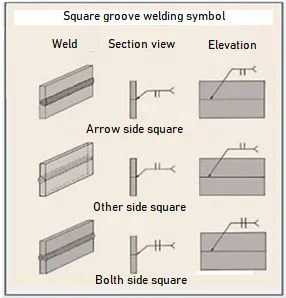
In the design and engineering of welds, correct nomenclature must be used. Groove names and symbols help to effectively communicate weld specifications. In the case of the square groove weld, the symbol mainly includes two parallel straight lines representing the edge of the groove and additional specifications with details on the size of the groove and weld parameters2. A general representation of this symbology is shown in figure 2.
Methods and techniques
- To perform this type of welding, the following should be considered:
- Material type: Select the appropriate materials (plate, pipe, electrode) for the application.
- Metal thickness: Ensure that the metal thickness is adequate for a square groove weld.
- Determine the proper groove width based on material thickness and welding process requirements.
- Cutting and machining: Metal parts are cut and machined to create square edges. It is critical that these edges are accurate and properly aligned.
- Contaminant removal: Clean the edges and adjacent surfaces of the parts to be welded to remove oils, oxides, dust, and other contaminants.
- Ensure that the groove is square and uniform along the joint.
- Use supports to keep parts in position and properly aligned during welding.
- Secure the parts in place with tack welds (Tack Welding).
- Choosing the appropriate welding process, e.g. Electrogas arc welding (EGW), Laser, MIG, MAG, TIG, SMAW, SAW, FSW based on material and application requirements. Taking as a special case the automated process.
- Set up the welding equipment.
- Adjust amperage and voltage according to material type and thickness.
- Apply proper joining technique to minimize distortion from thermal expansion and contraction. The use of dressers, fasteners, spot welding, and the application of controlled heat can help minimize this effect and ensure a high-quality joint.
Inspection and problems of square groove welds
Inspection is an essential part of the welding process to ensure joint quality and integrity. Inspection methods can include non-destructive testing (NDT) such as visual inspection methods, radiography, ultrasonic, and magnetic particle testing. Common problems in groove welding include porosity, cracks, inclusions, and lack of fusion, which can be detected and corrected by proper inspection.
Industry applications
In general, square groove welding is used in a wide variety of industrial applications, such as in the fabrication of storage tanks, pressure vessels, metal structures, bridges, and in particular in the following:
- Automotive industry: This sector is highly automated and robotized. These systems are used to join square groove joints in exterior body panels, pillars, frames and structural reinforcements, chassis, load-bearing and structural frames, and exhaust systems, among others.
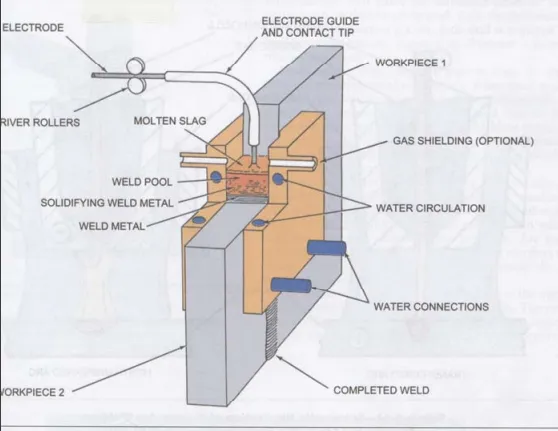
- Shipbuilding: For the construction of internal reinforcements, bulkheads, bridges, decks, hull plates, and mainly in the application of vertical welds in very thick plate, where automated systems such as Electrogas arc welding (EGW) are used, which allows high range deposition (between 7 to 13 kg/h.). This system is very high performance, also widely used in the manufacture of storage tanks3 and its process can be seen in figure 3.
Advantages of square groove welding
- High resistance.
- Low thermal distortion.
- Good penetration.
- Requires less filler material.
- Greater precision in alignment.
- Suitable for thin to moderate thicknesses.
- Uniform distribution of the filler material.
- Simplicity of the process.
Disadvantages of square groove welding
- Requires consistency on both sides of the material.
- Requires precise heat control.
- Difficult to weld.
Safety considerations
Square groove welding, like any welding process, requires the following strict safety measures to protect the operator and the work environment:
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Welding helmet: Use a welding helmet with appropriate shade filter to protect eyes and face from UV rays and spatter.
- Welding gloves: Wear heat-resistant gloves to protect hands.
- Protective clothing: Wear protective clothing, such as flame retardant jackets and pants, to prevent burns.
Security protocols
- Adequate ventilation: Ensure that the work area is well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of toxic fumes.
- Frequent inspection of equipment: Regularly inspect welding equipment for wear and tear.
- Training: Ensure that all operators are properly trained in welding techniques and safety measures.
Conclusions
Square groove welding is an essential process in metal joining, with applications ranging from structural metal fabrication to advanced industries such as automotive and aerospace. Understanding welding processes, joint preparation, inspection methods, and mechanical properties is crucial to ensure a high-quality, durable weld.
The continuous evolution of welding technologies promises to further improve the accuracy and efficiency of these processes, maintaining square groove welding as a vital technique in modern engineering and manufacturing.
References
- Soldaduras y estructuras. https://soldadurayestructuras.com/terminologia-de-juntas-soldadas/
- https://aqcinspection.com/types-of-weld-joints/
- Configuración para Soldadura Electrogas (EGW). https://es.triangleinnovationhub.com/setup-electrogas-welding

