Table of Contents
- Risks and opportunities: keys to effective planning
- What does managing risks and opportunities according to ISO 9001:2015 involve?
- Benefits of risk management according to ISO 9001:2015
- Conclusions
- References
In a dynamic organizational context, companies striving for excellence and success need to anticipate potential events that could affect their performance. Within the framework of Risk Management according to ISO 9001, clause 6.1 of the standard introduces a risk-based approach as an essential principle for planning, implementing, and maintaining a robust and effective Quality Management System (QMS).
This proactive approach allows organizations to identify, evaluate, and address risks and opportunities that may affect performance, compliance with system objectives, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement. This article provides a clear and practical introduction to the principles of quality risk management, facilitating understanding of its key aspects for effective application.
Risks and opportunities: keys to effective planning
When an organization structures its activities in an organized, sequential, and methodical manner, it minimizes waste, reduces inefficiencies, and builds trust with its customers.
In this context, risk and opportunity management becomes a strategic practice that transforms the traditional reactive approach into a preventive and analytical culture.
According to ISO 9001:2015, risk is understood as the effect of uncertainty on objectives and is expressed in terms of probability and consequences.
An opportunity, on the other hand, is defined as a situation or condition that, if exploited, can generate a positive result for the organization, such as increased efficiency, innovation, or customer satisfaction.
Managing risks and opportunities therefore involves balancing the negative and positive aspects of the organizational context, planning to avoid failures and drive continuous improvement.
What does managing risks and opportunities according to ISO 9001:2015 involve?
Clause 6.1 of ISO 9001:2015 states that the organization must determine the risks and opportunities necessary to:
- Ensure that the QMS achieves the intended results.
- Prevent, avoid, or reduce unwanted effects.
- Promote continuous improvement.
This does not imply complying with a rigid procedure, but rather adopting a risk-based thinking approach that cuts across all activities and processes, from strategic planning to daily operations, considering resources, roles, and responsibilities.
Managing risks and opportunities is therefore a continuous, cyclical, and systematic process comprising the following stages: context definition, identification, analysis, evaluation, treatment, and monitoring.
Each of these stages is discussed below, according to the interpretation of Doria, López, Bonilla, and Parra (2019).
1. Definición del contexto
En esta etapa se determinan las condiciones, eventos, fenómenos, factores internos y externos que pueden incidir en la capacidad de la organización para alcanzar los objetivos del SGC.
- Contexto interno: cultura organizacional, estructura organizacional, recursos, procesos, tecnología, clima laboral, entre otros.
- Contexto externo: mercado, competencia, entorno político, regulaciones, factores ambientales, sociales y tecnológicos, proveedores y partes interesadas.
Una herramienta muy útil para desarrollar esta etapa es el análisis FODA, que permite reconocer las fortalezas, oportunidades, debilidades y amenazas que servirán de base para desarrollar un análisis estratégico.
El propósito es comprender el entorno en el que opera la organización, pues de allí surgen tanto los riesgos como las oportunidades.
2 Identification of risks and opportunities
This phase involves identifying events or situations that could have a positive or negative impact on the performance of the management system.
Common sources of information:
- Historical records, background information.
- Results of internal or external audits.
- Non-conformities and customer complaints.
- Performance indicators.
- Technological or regulatory changes.
- Staff experience and process analysis.
Guiding questions that can be answered to help describe the risks:
- What events or situations could occur that would pose a threat to the organization and its goals?
- What events or situations could occur that would represent an opportunity for the organization and its goals?
- What changes could represent competitive advantages or improvements?
The result of this stage is an initial list of potential risks and opportunities, which will then be analyzed in depth.
3. Risk analysis: The risk and opportunity matrix
In this stage, the identified risks and opportunities are examined to determine their level of significance.
Risk analysis considers two fundamental variables: the probability of an event occurring and the impact or severity of its consequences.
What is a risk and opportunity matrix?
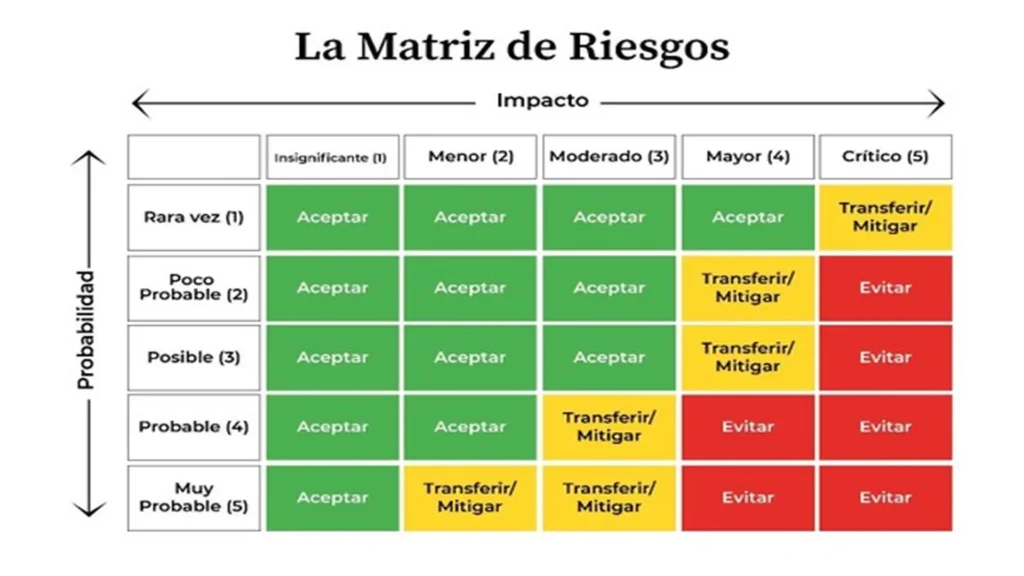
The risk and opportunity matrix is a structured tool that allows risks to be visually represented and classified according to their probability and impact. In simple terms, it is a table that crosses both factors (probability × impact) to determine a level of risk and thus prioritize the actions to be taken.
Its purpose is to convert complex information into a clear and visual format, facilitating understanding and decision-making within the organization. In addition, the matrix helps to comply with clause 6.1 of the ISO 9001:2015 standard by demonstrating that risks and opportunities have been determined, analyzed, and prioritized based on objective criteria.
How to create a risk and opportunity matrix step by step
- Define the probability and impact scales
The first step is to define the rating scales that will represent the degree of probability and impact of each event.
For example, when using a 5×5 matrix, the values can range from 1 to 5, from lowest to highest severity.
Example scales:
- Probability: rarely, unlikely, possible, likely, almost certain.
- Impact: insignificant, minor, moderate, major, critical.
Where are probability values obtained?
Probability values are determined from objective, specialized sources, such as historical records of incidents, failures, or non-conformities, failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA), expert judgments, among others. When no numerical data is available, qualitative scales agreed upon by the management team can be used, ensuring consistency in the assessment.
- Calculate the risk level
Once the scales have been defined, the risk level is calculated using the formula:
Risk level = Probability × Impact
This result allows the severity or relevance of the risk to be quantified, classifying it as low, medium, or high according to the values obtained. This stage is key to prioritizing actions within the strategic planning of the QMS.
- Build the heat map
The information is represented graphically on a heat map, where each cell combines a probability level with an impact level.
The colors indicate the priority of risk treatment:
- Green: low or acceptable risk.
- Yellow: moderate risk (requires monitoring).
- Red: high or critical risk (requires immediate action).
The heat map facilitates the interpretation and visual communication of risks throughout the organization.
4. Risk assessment
Risk assessment consists of comparing the results of the analysis with the acceptability criteria defined by the organization, thus determining which risks require immediate treatment, which can be accepted, and which opportunities should be leveraged.
The evaluation criteria are predefined levels of risk acceptability, usually classified as:
- Unacceptable (critical): requires immediate action.
- Moderate (tolerable): requires control or monitoring.
- Acceptable: can be assumed or monitored.
This phase seeks to prioritize the risks and opportunities that require intervention, establishing the order of attention. The risk and opportunity matrix becomes a visual tool that facilitates this prioritization: risks located in the red zones represent critical conditions that must be addressed as a priority or avoided; those in the yellow zones require the application of transfer or mitigation strategies, and those in the green zones can be considered acceptable or monitored, depending on the organization’s policy. (See Figure 1. The Risk Matrix).
The result of this assessment will serve as input for the next phase: the treatment of risks and opportunities, in which specific response measures and their integration into the QMS plans will be defined.
Recommended criteria for prioritization:
- Impact on quality objectives.
- Mitigation cost or effort.
- Expected frequency or recurrence.
- Effect on customer satisfaction.
5. Treatment of risks and opportunities
Once risks and opportunities have been identified, analyzed, and evaluated, the organization must plan and implement specific actions to address them.
Common treatment options:
- Avoid risk: eliminate its cause.
- Reduce/mitigate risk: decrease its probability or impact through controls.
- Transfer risk: delegate its management (e.g., insurance or partnerships).
- Accept risk: when it is tolerable and treatment is not feasible.
In the case of opportunities, the strategy is aimed at taking advantage of or enhancing the benefits they offer.
Each action must be documented, assigning responsibilities, resources, deadlines, and monitoring methods.
6. Monitoring and review
Risks and opportunities must be monitored and reviewed on an ongoing basis, as internal and external conditions change over time.
This monitoring allows you to:
- Verify the effectiveness of the actions implemented.
- Detect new emerging risks.
- Adjust the matrix and mitigation plans.
In this way, risk management becomes a dynamic process, aligned with the philosophy of continuous improvement of ISO 9001:2015.
Benefits of risk management according to ISO 9001:2015
Each organization manages risks according to its own characteristics, risks inherent to its nature and operations, as well as according to the sector in which it operates.
In general, managing risks within the framework of ISO 9001:2015 will contribute to a greater or lesser extent, depending on the impact these risks represent, to aspects such as:
- Greater customer satisfaction and compliance with ISO requirements.
- Reduction of financial and operational losses.
- Analysis of the production system, optimizing processes and response times.
- Selection of more reliable suppliers.
- Increased organizational reliability and reputation.
- Promotion of innovation by turning risks into opportunities.
- Preventive culture that strengthens decision-making and continuous improveme
Conclusions
Risk and opportunity management within the framework of ISO 9001:2015 is not a documentary requirement, but rather a strategic management principle that drives organizational excellence.
The use of tools such as the risk and opportunity matrix, in accordance with clause 6.1, allows organizations to prevent deviations, take advantage of opportunities, and ensure compliance with QMS objectives.
Adopting a risk-based approach means deciding in advance, acting with knowledge, and maintaining a system that is resilient to changes in the environment.
If you want to strengthen your skills in this area and master the practical application of the ISO 9001:2015 requirements, explore the courses and diplomas offered by Inspenet Academy, designed for professionals in the industrial and energy sectors who seek to lead quality with an analytical and strategic vision.
You can learn more about the risk matrix by consulting the following article: Development of the risk and opportunity matrix in ISO 9001.
References
- Pirani Academy (2024). Guide to implement a risk management system, according to ISO 31000. https://www.piranirisk.com/es/academia/especiales/guia-del-sistema-de-gestion-de-riesgos-iso-31000
- Doria-Parra, A., López-Benavidez, L., Bonilla-Ferrer, M. & Parra-Cera, G. (2019). Methodology for the implementation of risk management in a quality management system. Signos. Research in
- Management Systems, 12(1), 123-135. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15332/24631140.5424
ISOTOOLS. ISO Standards for Enterprise Risk Management. https://www.isotools.us/2022/02/17/normas-iso-para-la-gestion-de-riesgos-corporativos/

