Table of Contents
- From industry to the asset: Pipelines as the operational backbone
- What do we mean by pipeline integrity?
- Evolution of pipeline inspections
- What is a smart pipeline inspection?
- Smart pipeline inspection technologies
- Pipeline inspection technologies
- Eddyfi smart inspection success stories
- IoT and its contribution to pipeline integrity
- Strategic implementation in integrity programs
- Conclusions
- References
- Key questions about pipeline integrity
Pipeline integrity is one of the critical pillars of asset management for operational continuity in the energy and industrial sectors. Every pipeline section is a critical asset exposed to corrosion, mechanical stresses, and conditions that may compromise its performance. In this context, smart inspection technologies have transformed the way these systems are assessed and managed.
Among the most prominent actors is Eddyfi Technologies, an Inspenet partner company, whose solutions drive a new generation of precise, digital, and prediction-oriented diagnostics as an asset management system.
From industry to the asset: Pipelines as the operational backbone
In any process chain, whether oil, gas, petrochemical, or energy,pipelines function as the vital system that connects and sustains production. They operate under high pressures, flow variations, thermal fluctuations, and challenging environments that accelerate degradation mechanisms.
According to the ISO 55000 approach, these systems must be managed as strategic assets requiring a comprehensive vision:
- Periodic inspection
- Risk analysis
- Operational reliability
- Continuous monitoring
Pipeline integrity is not limited to identifying damage; it involves anticipating it and acting based on precise information.
What do we mean by pipeline integrity?
Pipeline integrity encompasses the set of methodologies, technologies, and processes designed to ensure that a pipeline can operate safely, reliably, and in compliance with technical standards. It considers factors such as internal and external corrosion, crack propagation, thickness loss, mechanical stresses, and remaining life analysis.
In essence, it refers to the system’s ability to perform its function without failing.
However, the current context demands more than occasional inspections: smart tools are needed to generate reliable and traceable data capable of feeding predictive models.
Evolution of pipeline inspections
The equipment inspection department, responsible for supervising asset condition and ensuring regulatory compliance, has seen a deep transformation in methodologies applied to pipeline assessment. Operational challenges, the need to reduce risks, and the adoption of new technologies have driven continuous evolution in how pipelines are inspected. This progress can be understood through four key stages:
- Early years: manual inspections, visual evaluations, and intrusive methods with limited capacity to detect hidden damage.
- Intermediate stage: incorporation of conventional ultrasound, radiography, and traditional NDT methods applied by qualified inspection personnel.
- Transition: arrival of automation, early geometric pigs, and mechanical systems for internal evaluation.
- Current stage: implementation of high-resolution smart pigs, online monitoring, advanced NDT, and predictive analytics integrated into integrity programs.
Standards such as API 1163 and ASME B31.8S formalize this advancement, establishing the need for standardized procedures, verifiable technical competencies, and risk-based assessments. Thanks to this, the Equipment Inspection Department has moved from reactive inspections to leading preventive programs based on data and smart technology.
What is a smart pipeline inspection?
An smart inspection combines technology, digitalization, and structured analysis to obtain deep information on pipeline condition without interrupting operation.
Its main characteristics include:
- Advanced sensors and digital acquisition
- Smart internal tools (smart pigs)
- Processing and interpretation software
- Integration with management platforms
- Predictive capability
Practical example:
A gas operator needed to evaluate an 18-km section without stopping the flow. A UT smart pig with digital acquisition traveled the entire line and detected a thickness-loss area near a support. The software correlated defect growth with historical data and recommended preventive repair for the next planned shutdown. This avoided a leak and enabled scheduled maintenance without surprises.
This represents the natural integration of advanced NDT, data analytics, and digital transformation.
Smart pipeline inspection technologies
Smart Pig Pipeline for pipelines
Smart pig pipeline tools perform internal inspections capable of recording geometry, corrosion, deformations, and cracks. They may use MFL, UT, EMAT, or combinations of high resolution.
Online monitoring (industrial IoT)
Permanent systems capturing variables such as corrosion, pressure, vibration, or temperature in real time. This information enables detecting deterioration before it becomes a major problem.
Practical example:
In a multi-product pipeline exposed to mechanical vibrations, IoT sensors installed in critical points recorded an abnormal rise in acceleration. The early alert triggered a focused inspection that identified a loose clamp causing resonance. The immediate correction prevented fatigue damage and an unplanned shutdown.
Advanced Non-Destructive Testing
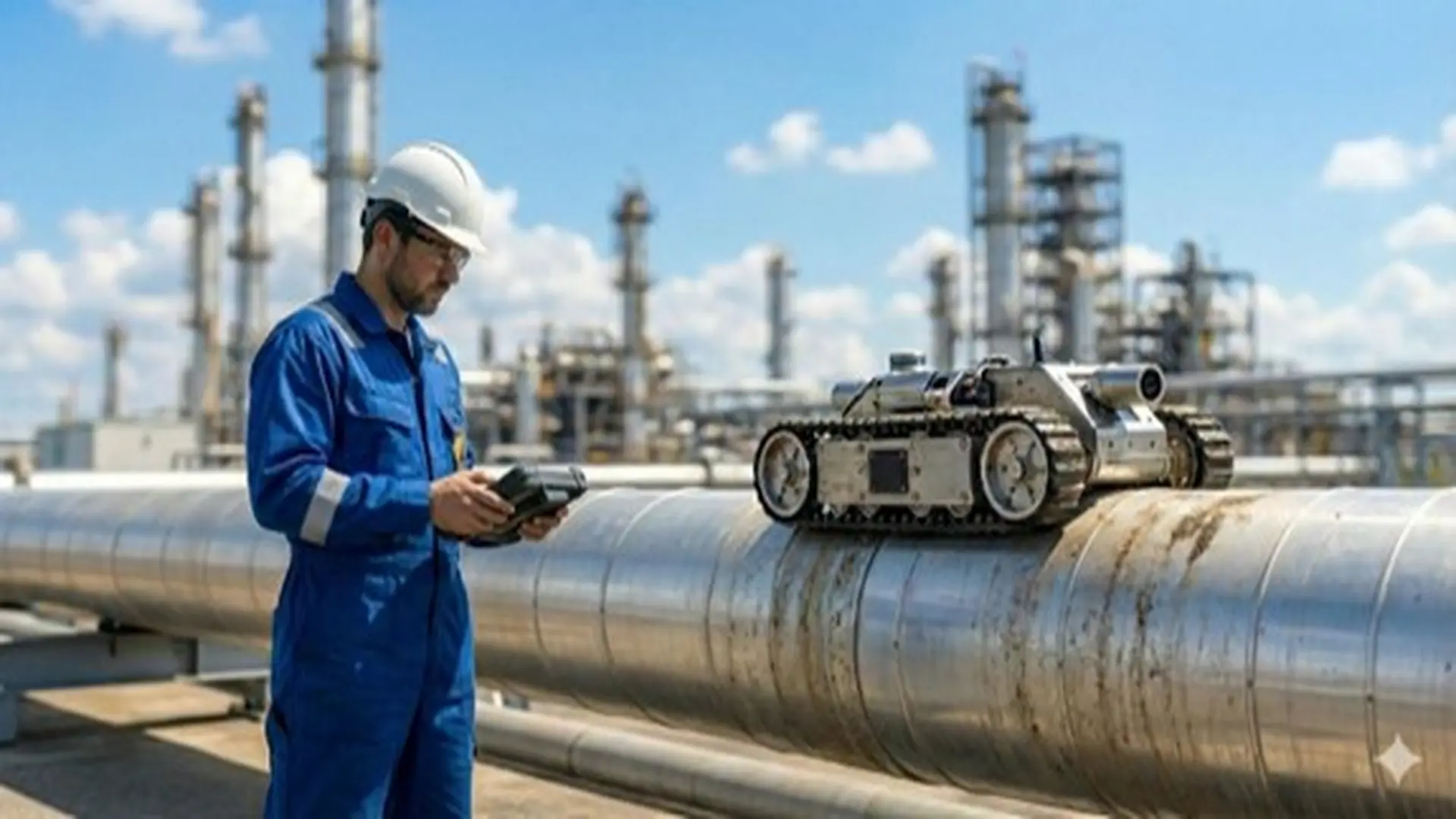

Applied externally, these methods assess integrity without needing internal access. Main technologies include:
- Pulsed Eddy Current (PEC): Ideal for detecting corrosion under insulation without removing it.
- TECA™: For advanced detection of surface cracks.
- Advanced EMAT: Useful at extreme temperatures or without couplant.
- Automated UT: For high-resolution thickness mapping.
- Hybrid systems: Assisted by interpretation software.
When to use them? Ideal for sections where smart pigs cannot enter the line (“unpiggable pipelines”) or when pipeline geometry is complex.
Predictive analysis based on data
Models that integrate historical information, corrosion maps, probability of failure (POF), and remaining life calculation to guide maintenance decisions.
Pipeline inspection technologies
To select the appropriate inspection technique, it is necessary to understand what each technology detects, in which scenarios it excels, and what its limitations are. The following table summarizes the most commonly used solutions in integrity programs, including advanced tools such as PEC, TECA™, and robotic systems applied by Eddyfi Technologies.
Comparative table of pipeline inspection technologies.
| Technology | Detect | When to use it | Key advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smart Pig (ILI) | Internal corrosion, loss of thickness, cracks, ovalization | Piggable pipelines in continuous operation | Complete inspection without stopping flow; high precision; digital traceability | Does not work in non-piggable pipelines; requires launch and receive traps |
| PEC (Lyft®) | Corrosion under insulation (CUI), loss of thickness | Insulated, buried, or hard-to-reach pipelines | No insulation removal required; fast; safe; ideal for CUI | Lower resolution than direct UT; sensitivity to multilayer materials |
| TECA™ / Sharck™ | Surface cracks and welding cracking | Critical welded joints, aged lines | High sensitivity; ideal for complex geometries and limited access | Superficial reach; requires proximity to the cord |
| Advanced EMAT | Corrosion, cracks, loss of thickness | Areas with high temperatures or where couplings cannot be used | Works without contact; ideal for hot surfaces | Weaker signal; greater dependence on surface conditions |
| Automated UT | Full volume, localized corrosion, laminations | Accessible ducts without insulation | High resolution; detailed corrosion mapping | Requires direct access and surface preparation |
| Hybrid UT/PEC robotics | Thinning, internal and external corrosion | Non-piggable pipelines, complex routes, and irregular geometries | Allows inspection of previously inaccessible areas; digital integration | Requires minimal space and specialized logistics |
Smar inspection
Smart technologies not only transform pipeline analysis; they are also redefining the speed and efficiency of field inspections. A clear example is the Inspenet interview on WeldXPRT, a digital solution capable of evaluating welds in under five minutes, integrating advanced processing, immediate visualization, and automated acceptance criteria.

These tools represent the future of inspections: fast, reproducible, digitally based, and fully aligned with the concept of smart inspection, where technology shortens decision times and increases operational reliability.
Key benefits of using smart pigs
Implementing internal inspection tools (Smart Pigs) provides highly strategic advantages:
- Operational continuity: Full inspection while maintaining flow, avoiding losses by downtime.
- Diagnostic precision: Quantifies wall loss, corrosion, cracks, and geometric anomalies with high resolution.
- Digital traceability: Generates auditable digital reports for asset management systems.
- Massive coverage: Can inspect hundreds of kilometers in a single run.
In summary, Smart pigs are the undisputed standard tool for transmission and distribution lines in continuous service.
Eddyfi smart inspection success stories
Aluminum industry – CUI inspection with Lyft® PEC
An aluminum plant needed to evaluate pipelines with thick insulation, where conventional inspection required removing large areas and shutting down operations. With Lyft® PEC, Eddyfi inspected the entire line without removing insulation.
Results:
- Precise detection of wall loss under insulation
- Elimination of large-scale insulation removal
- Digital maps ready for predictive analysis
Hydrocarbon transport – Crack detection with TECA™ / Sharck™
In a hydrocarbon transport system, evaluating critical welds was challenging due to low sensitivity of conventional techniques. With Sharck™ (TECA™-based), surface cracks previously undetectable were identified.
Results:
- Higher weld inspection resolution
- Reduction of false indications
- Improved analysis under API 1163 guidelines
Source: Pipeline Integrity Solutions
Petrochemical plant – Advanced robotics for unpiggable pipelines
A pipeline classified as “unpiggable” had complex geometries, diameter changes, and multiple valves. Eddyfi deployed a robotic platform with hybrid UT/PEC sensors capable of scanning the entire line.
Results:
- Inspection of previously inaccessible areas
- Identification of internal thinning zones
- Integration of data into client digital systems
Source: Semi-Automated Condition Monitoring of Pipelines Made Possible
IoT and its contribution to pipeline integrity
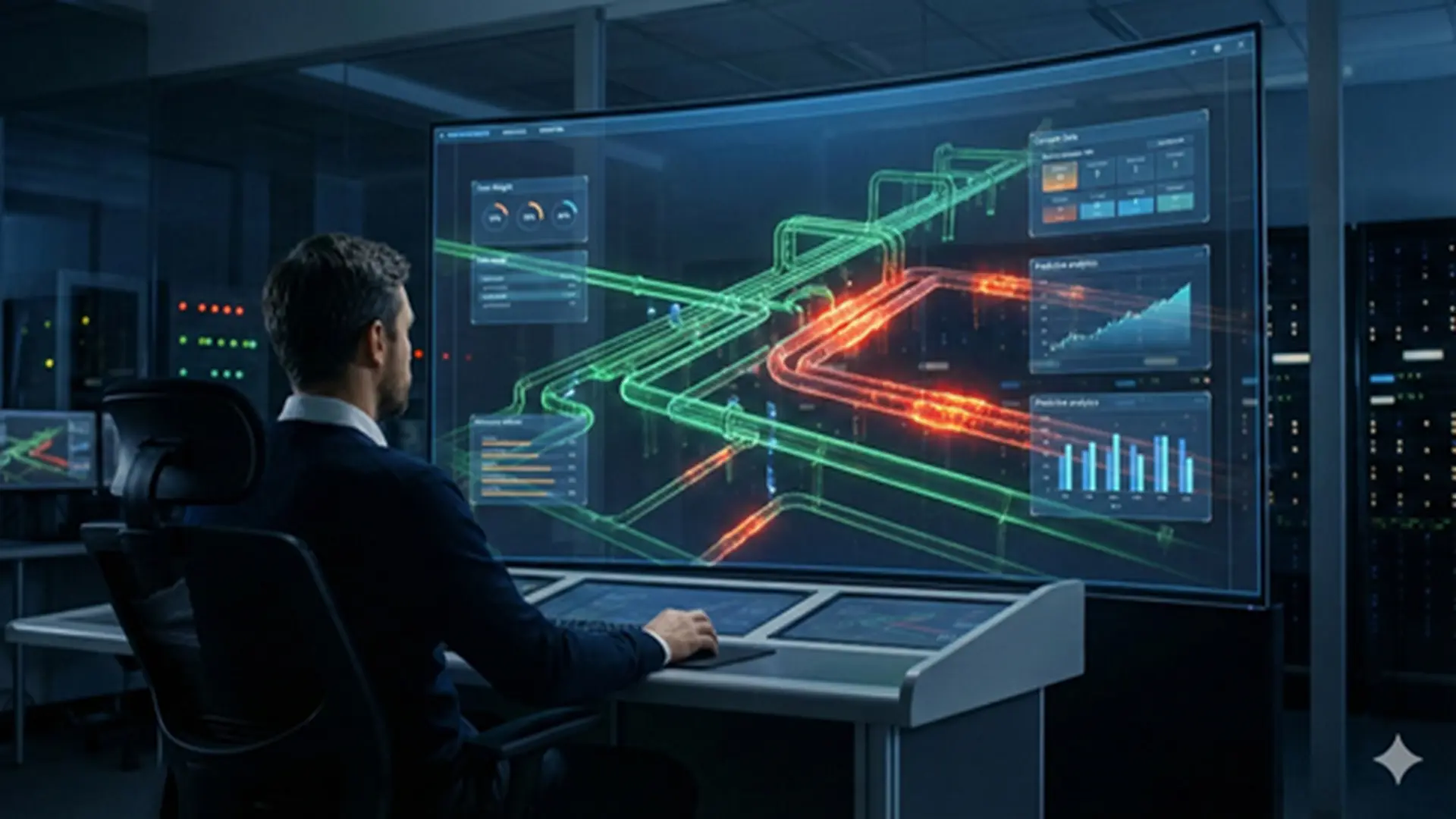

The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) transforms traditional monitoring, shifting from periodic checks to continuous surveillance. By integrating sensors and connectivity, pipeline integrity is enhanced through:
- Permanent sensors: Installed at critical points measuring thickness, vibration, or temperature 24/7.
- Real-time alarms: Instant detection of anomalies enabling immediate action.
- Total integration: Automatic synchronization with SCADA and asset management platforms.
- Dynamic modeling: Algorithms updating corrosion rates based on real operating conditions.
The result: the pipeline becomes an smart asset that communicates its own health state.
Strategic implementation in integrity programs
An effective integrity strategy requires:
- Identifying critical lines
- Selecting the right technique based on risk
- Applying smart tools (smart pigs, PEC, TECA, UT)
- Analyzing data and projecting remaining life
- Integrating information into ISO 55000-compatible systems
- Executing mitigation actions
Practical example:
During the annual evaluation, the predictive platform identified a section with increasing failure probability due to accelerated internal corrosion. Instead of replacing the entire line, the model recommended intervening only 12 meters. This reduced repair costs by 70% and extended the remaining life.
This process shifts maintenance from corrective to predictive.
Conclusions
Pipeline mechanical integrity is essential for safety, sustainability, and industrial productivity. The adoption of smart inspection technologies enables more precise, less intrusive diagnostics fully connected to modern asset management.
With solutions such as Lyft® PEC, TECA™, and advanced robotic platforms, Eddyfi Technologies confirms that the future of pipelines is not reactive but predictive, digital, and highly reliable.
From the energy sector to the last pipeline segment, smart inspection redefines industrial integrity standards.
“Continue exploring at Inspenet how technology, data, and engineering come together to elevate industrial integrity standards.”
This article is part of Inspenet’s editorial line, official media partner of global events such as GASTECH, API, AMPP, SLOM, and others.
References
- Eddyfi Technologies. (2023). Lyft® PEC Applications and Field Case Studies.
- ASME. (2020). ASME B31.8S: Managing System Integrity of Gas Pipelines.
- API. (2022). API 1163: In-line Inspection Systems Qualification Standard.
- Fernandes, F., & Mukherjee, R. (2021). Advances in Non-Invasive Pipeline Inspection Using Eddy Current and Emerging Sensor Technologies. Journal of Pipeline Engineering, 20(3), 145–162.
- Skolnik, A., & Thomas, K. (2020). Digital Monitoring and IoT Integration for Pipeline Integrity Management. International Journal of Industrial Asset Management, 12(2), 89–103.
Key questions about pipeline integrity
What is pipeline integrity?
The practice that ensures safe and reliable pipeline operation throughout its service life.
What is a smart inspection?
A process combining sensors, digitalization, and advanced analytics to determine the pipeline’s actual condition without interrupting operation.
What benefits does a Smart Pig offer?
Higher precision, traceability, and comprehensive inspection capability without stopping flow.
How does IoT help?
It enables continuous monitoring, early failure detection, and efficient management through real-time data.