Introduction
The Oil & Gas sector, as one of the world’s largest energy consumers, is facing increasing pressure to improve its energy efficiency, which is driven by the need to comply with stricter environmental regulations, respond to the increase in global energy demand and mitigate its ecological impact. Energy efficiency in the Oil & Gas sector has become a critical issue, reflecting a commitment to both environmental sustainability and operational optimization.
In this sense, energy efficiency in the Oil & Gas sector represents a strategy to reduce costs, greenhouse gas emissions and an opportunity to innovate in its processes and technologies. With increasing regulatory pressure and greater environmental awareness on the part of society, companies in the sector are called upon to adopt more efficient and sustainable practices, thus setting the direction for a more responsible and efficient energy future.
What is energy efficiency for the Oil & Gas sector?
Energy efficiency in the Oil & Gas sector refers to the optimization of energy use to maximize efficiency in the hydrocarbon value chain, from exploration to distribution, while minimizing the consumption of energy resources per unit of product. This translates into lower costs, lower emissions, greater competitiveness and more sustainable development. This sector must adopt the habit of responsible consumption and apply good practices to achieve a more rational consumption in its processes.
Energy consumption depends largely on the level of process complexity, but key areas for improving efficiency include process optimization, use of renewable energy, energy recovery and efficient transportation. There are worldwide initiatives that promote efficiency in this sector, which contributes to the fight against climate change and compliance with the most demanding environmental standards.
Current importance of energy efficiency in the Oil & Gas sector
Recently, energy efficiency in the oil industry has acquired great importance, motivated by the urgency of minimizing the environmental impact in all hydrocarbon processes. This sector, traditionally a major energy consumer and Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emitter, has undergone a substantial change in its approach to achieving maximum energy efficiency.
Historically, improvements focused on optimizing processes and reducing operating costs, but now extend to GHG reduction and reduced environmental impact, with technological advances in energy management and process optimization. Energy efficiency improvements range from optimizing combustion and refining to adopting digital technologies in operating processes. In addition, the integration of renewable energies in operations diversifies internal energy consumption.
Global climate change policies are forcing this sector to adopt efficient energy efficiency practices that additionally promote more sustainable economic development. Initiatives such as carbon pricing, carbon neutrality commitments and international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, are putting pressure on companies to improve their energy performance and reduce their carbon footprint. This underscores the importance of the transition to a more energy-efficient industry aligned with global environmental sustainability goals.
Optimizing the use of energy resources improves the security and sustainability of the world’s energy supply, strengthening the sector’s resilience to market fluctuations and changing energy policies.
Innovations to improve energy efficiency in this sector
Today, the Oil & Gas sector has multiple options to improve efficiency in the processes of its entire value chain. Among the most relevant are:
Process and plant optimization: It is possible to decrease energy consumption in plants and refineries; focusing on the improvement and installation of energy-efficient equipment and implementation of measures to prevent leaks and spills. This practice involves a continuous review and improvement of all stages of the supply chain, from extraction to distribution. The use of advanced technologies and monitoring systems makes it possible to identify and control the risks of energy inefficiency by locating the critical areas to be intervened.
Automation and advanced data analysis: The use of technologies such as AI, IoT and Big Data, are making it possible to optimize and stabilize operations, with predictive maintenance, automated condition monitoring and analysis of large data sets, reduce further interventions and improve the stability of operations and energy efficiency.
Sustainable design: Refers to the development of infrastructure and processes that minimize environmental impact and maximize energy efficiency. It involves the integration of advanced technologies and operating practices that reduce the consumption of natural resources and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable design in this sector seeks to balance energy demand with environmental preservation and social responsibility, preparing the industry for a sustainable energy future.
Improving equipment efficiency: The efficiency of the equipment involved in the processes is fundamental, modernizing equipment such as turbines, exchangers, compressors and ventilation systems, are necessary to minimize energy consumption. The integration of intelligent technologies in this equipment allows real-time monitoring and fine-tuning of operations, thus ensuring optimal energy management and reduced environmental impact.
Electrification of offshore operations: This strategy represents a significant reduction in energy consumption, electrifying offshore operations and using renewable energy on remote platforms are sustainable design options that improve energy efficiency and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. In addition, electrification facilitates the implementation of advanced energy management and control systems, further optimizing the use of resources and improving long-term operational sustainability.
The following video focuses on the topic: Supplying electricity to an oil and gas facility using a floating wind and hydrogen power plant. (Source: Courtesy of Floating Power Plant).
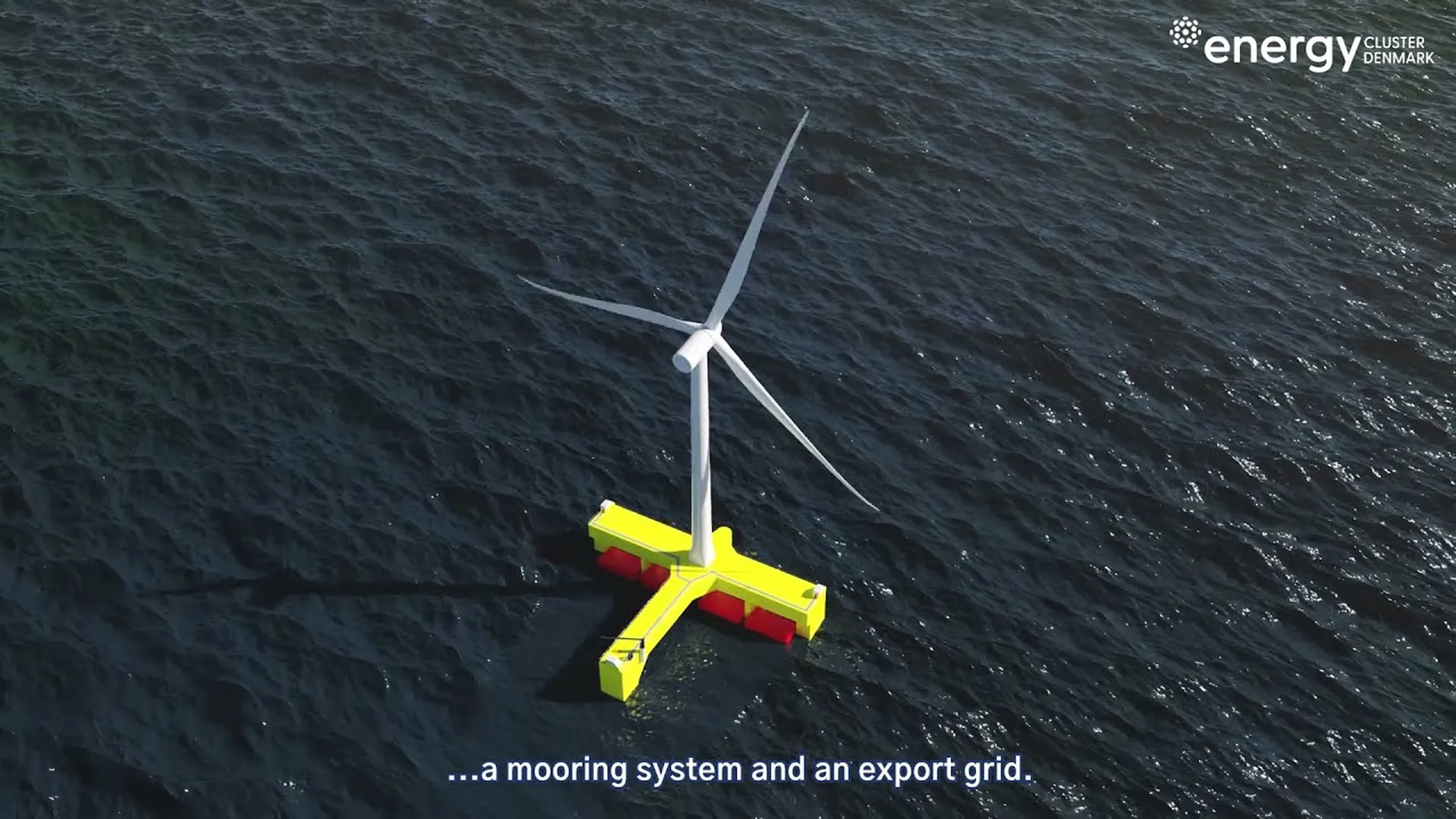

Planta de energía flotante: Petróleo y gas más ecológico.
Advanced heat management and energy recovery: In addition, technologies such as combined heat and power (CHP) and waste heat recovery (WHP) are gaining ground, providing practical and efficient solutions for recycling wasted heat and converting it into electricity or other forms of useful energy, thereby reducing energy use and costs.
Integration of renewable energies: The use of energies such as solar, wind and geothermal for operations in remote sites or for auxiliary processes is a great contribution to reducing dependence on fossil fuels and reducing emissions. The implementation of cogeneration and trigeneration systems for the simultaneous generation of electricity, heat and/or cold increases energy efficiency in various processes.
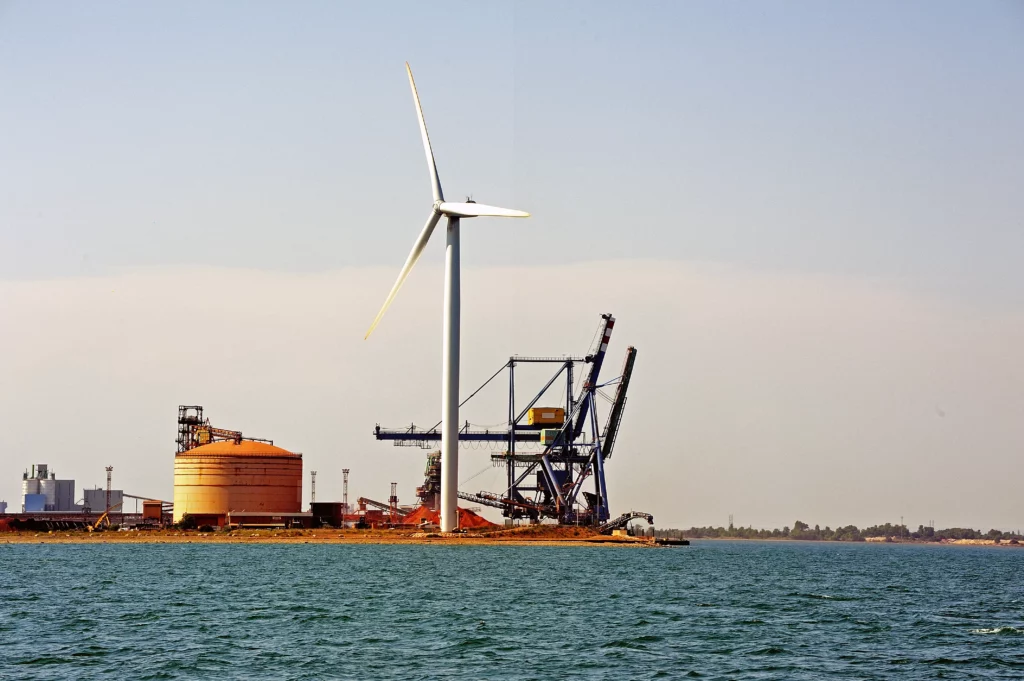

Circular economy models: The Oil & Gas sector is increasingly joining the circular economy, developing different ways of making sustainable use of its resources. In search of making the most of energy resources, they focus on waste reduction and control, in order to find usefulness and application of industrial waste and turn it into a value-added resource, thus generating security for future energy needs.
Efficient transportation: Focuses on optimizing transportation routes to minimize fuel consumption and reduce CO2 emissions. This is achieved through the use of electric, hybrid or energy-efficient vehicles, along with the implementation of advanced traffic management systems that improve vehicle flow.
Enhanced Oil Recovery (EOR): EOR techniques use advanced methods, such asCO2 injection, to optimize oil extraction while reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions. This method improves production in a sustainable manner, integrating efficient management of energy resources and environmental mitigation.
These innovations reflect the Oil & Gas sector’s commitment to continuous improvement in energy efficiency, seeking not only an economic benefit, but also a smaller environmental footprint and a move towards more sustainable operations.
Conclusion
Energy efficiency in the Oil & Gas sector is advancing significantly, driven by the need to meet environmental sustainability demands and the urgency to transition to clean energy sources. Initiatives to improve energy efficiency are focused on operations optimization, automation, and the implementation of advanced data analytics, reflecting an effort to reduce the carbon footprint and improve the management of energy resources.
The integration of sustainable technologies such as efficient design, electrification of offshore operations, and adoption of renewable energy, along with advanced heat management and a focus on efficient transportation, underscores the industry’s transformation towards more energy-efficient and energy-saving practices. These changes are not only aimed at an economic benefit, but are also aligned with the overall objective of achieving greater energy efficiency in the Oil & Gas sector. There are several opportunities for energy efficiency savings in each area and process.
Reference
Own source

