Introduction
The NDT industry plays an essential role in various productive sectors by ensuring structural integrity, enhancing safety, and optimizing operational efficiency. These advanced non-destructive inspection techniques have proven fundamental for asset quality and reliability, significantly contributing to the profitability and sustainability of industrial operations.
Non-Destructive Testing methods are specialized techniques used to evaluate the properties of materials, components, or systems without causing damage. Unlike destructive methods, NDT allows continuous inspections without compromising the functionality of the inspected object. Common techniques include ultrasonics, radiography, magnetic particles, and liquid penetrants, each designed to detect different types of defects or irregularities. These techniques are essential to ensure that assets meet the strictest standards of structural integrity, quality, and safety, significantly contributing to industrial maintenance and production.
The relevance of the Ndt industry in major productive sectors is undeniable. In the aerospace industry, NDT is indispensable for ensuring the safety and reliability of aircraft, from fuselage inspections to the verification of critical components. In the energy sector, these techniques ensure the safe and efficient operation of nuclear plants, wind farms, and fossil fuel plants, preventing accidents and optimizing operations. In the automotive industry, NDT guarantees the quality and durability of vehicles by inspecting welds and key components. In construction and infrastructure, NDT is fundamental for evaluating the structural integrity of buildings, bridges, and other critical infrastructures, preventing structural failures and accidents.
The ability of the NDT industry to detect problems before they become catastrophic failures is vital for improving asset reliability and integrity, industrial safety, and operational efficiency. Implementing non-destructive inspection techniques allows companies to minimize risks, reduce operational costs, and extend the lifespan of their assets, resulting in a significant competitive advantage. The Ndt industry is an essential component for the modernization and sustainability of major productive sectors, ensuring that operations are safer, more efficient, and more profitable.
What is the NDT industry?
The NDT (Non-destructive testing) industry refers to a set of techniques used to evaluate the properties of materials, components, or systems without causing damage. These methods allow continuous inspection and evaluation of assets, ensuring their structural integrity and functionality without compromising them. Non-Destructive Testing is essential in various industries to guarantee the safety, quality, and efficiency of products and processes.
There are several types of NDT, each suitable for detecting different types of defects or irregularities:
- Ultrasonics (UT): Uses high-frequency sound waves to detect internal discontinuities. It is ideal for identifying defects in welds, laminations, and other metallic and non-metallic components.
- Radiography (RT): Uses X-rays or gamma rays to visualize the interior of an object. It is particularly useful for detecting internal defects in welds and complex structures.
- Magnetic Particles (MT): Involves applying a magnetic field and ferromagnetic particles to detect surface and subsurface discontinuities in ferromagnetic materials.
- Liquid Penetrants (PT): Consists of applying a high-capillary liquid to the material’s surface. The liquid infiltrates surface defects, which are revealed by applying a developer.
- Eddy Current Testing (ECT): Uses induced electrical currents to detect surface and subsurface defects in conductive materials. It is particularly useful in inspecting aircraft components and pipelines, where precise detection of cracks and discontinuities is crucial.
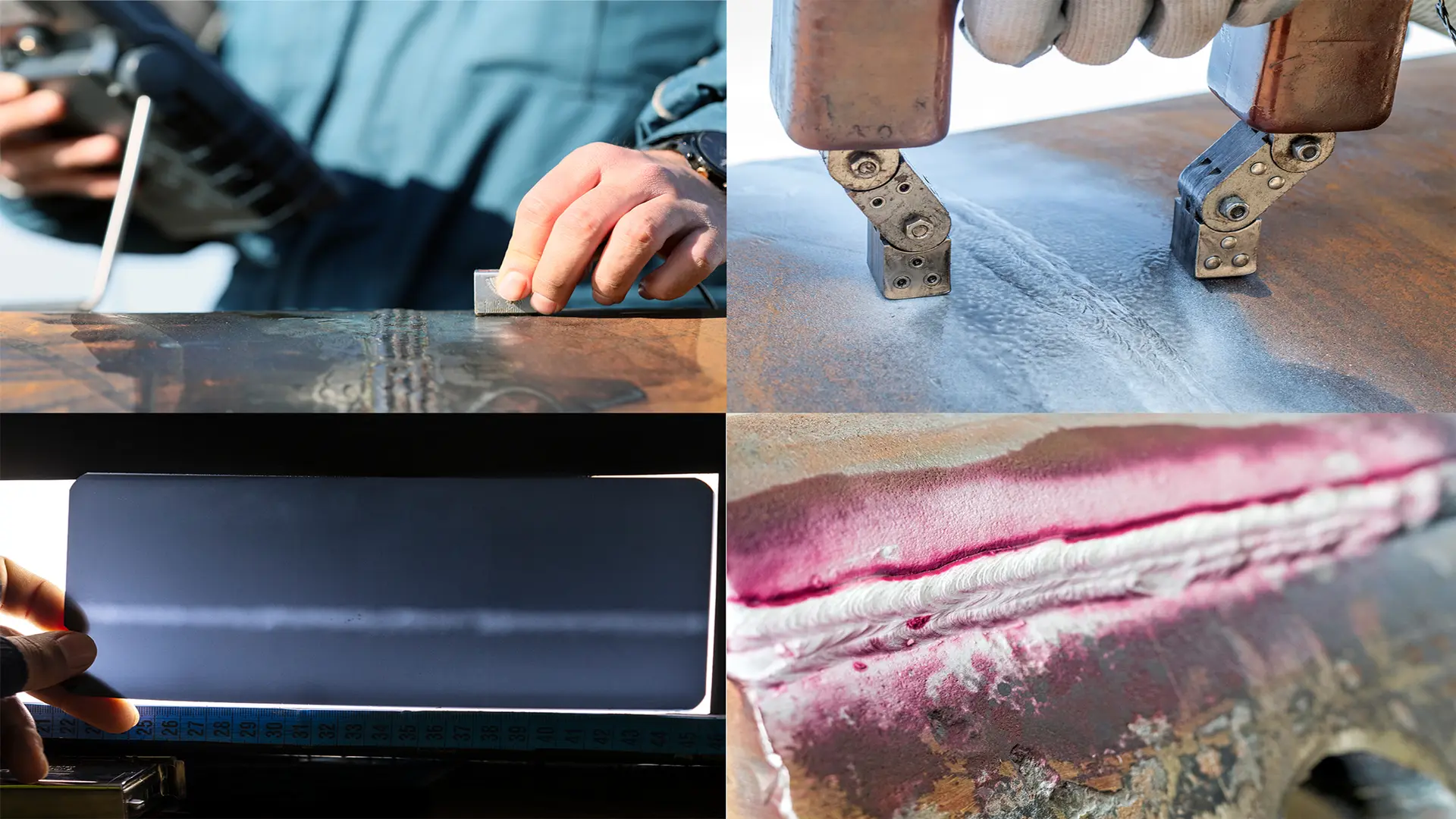

The general benefits of the Ndt industry are numerous. Firstly, they allow early detection of defects, preventing catastrophic failures and reducing accident risk. Additionally, they improve product quality by ensuring compliance with the highest standards of structural integrity. NDT techniques also contribute to operational efficiency by enabling predictive and preventive maintenance, extending asset lifespan, and reducing operational costs. Non-destructive testing is a vital tool for industrial inspection, ensuring the safety, quality, and efficiency of productive processes.
Applications of the NDT industry in productive sectors
Aerospace industry
In the aerospace industry, applying
(NDT) is import for ensuring aircraft safety and reliability. Its allows detailed inspection of fuselages and critical components such as wings, engines, and landing gear systems without compromising their structural integrity. Among the most used techniques are ultrasonics, which detects internal cracks and discontinuities in wings, and radiography, which visualizes internal defects in complex components.
Magnetic particles and liquid penetrants identify surface defects in ferromagnetic and non-ferromagnetic parts, respectively. Additionally, eddy current testing (ECT) is employed to inspect conductive surfaces and detect surface and subsurface cracks, especially in non-ferromagnetic materials such as aluminum. These techniques ensure that any anomaly is detected and corrected before compromising flight safety, thus improving the quality and structural integrity of aircraft.
Energy sector
In the energy sector, NDT is applied in nuclear plants, wind farms, and fossil fuel plants to ensure the safe and efficient operation of these systems. In nuclear plants, ultrasonics and radiography are essential for inspecting critical components such as pressure vessels and pipes, ensuring no defects that could cause radioactive leaks.
In wind farms, NDT techniques are used to inspect the blades of wind turbines and mechanical components, ensuring their integrity and operational efficiency. In fossil fuel plants, boiler and pipe inspections using NDT prevent accidents and optimize operation. Case studies have shown that implementing NDT in these environments not only improves industrial safety but also increases operational efficiency and reduces maintenance costs.
Automotive industry
The automotive industry uses NDT in vehicle production and maintenance to ensure the quality and efficiency of operations. Techniques such as ultrasonics and radiography are employed to inspect welds and critical components such as chassis and engines, ensuring compliance with the highest quality standards.
Magnetic particle and liquid penetrant inspection identify surface defects in metallic and non-metallic parts. These methods not only ensure vehicle quality but also increase production line efficiency and extend component lifespan, reducing operational costs and improving customer satisfaction.
Construction and infrastructure
In construction and infrastructure, NDT is crucial for evaluating the structural integrity of buildings, bridges, and other critical infrastructures. Ultrasonics and radiography are used to inspect beams, columns, and other structural elements, detecting internal cracks and defects that could compromise stability. Magnetic particle and liquid penetrant application detect surface defects in ferromagnetic and non-ferromagnetic materials.
These non-destructive tests are essential for preventing structural failures and accidents, ensuring that infrastructures are safe and durable. Practical cases of Non-Destructive Inspection in bridges and buildings have shown that implementing NDT can identify problems before they become serious failures, thus improving public safety and maintenance efficiency.
Watch the following video about NDT applications in different industries. Source: TWI Ltd.

Non-Destructive Testing (NDT).
Benefits of the NDT industry
Quality, efficiency, and profitability of operations
The NDT (Non-destructive testing) industry plays a crucial role in improving the quality of industrial products and processes. NDT techniques allow the early detection of defects and discontinuities, ensuring that materials and components meet the most rigorous quality standards before their use or implementation in productive processes. This not only improves the final quality of the products but also increases efficiency by reducing the need for rework and waste.
Operational efficiency is also increased thanks to NDT, as it allows rapid and precise evaluation of components without needing to dismantle or interrupt operations. This approach minimizes downtime and optimizes resource use. For example, in the automotive industry, inspecting welds using ultrasonics or radiography can identify defects that could cause future failures, allowing their correction before the vehicles hit the market. This not only improves the final product quality but also reduces costs associated with repairs and warranty claims.
Reliability and integrity of assets
The reliability and integrity of assets in the long term are fundamental for any industrial operation. Non-Destructive Testing allows predictive and preventive maintenance, identifying potential problems before they become catastrophic failures. This proactive approach ensures that assets maintain their functionality and safety for longer, extending their lifespan and optimizing their performance.
Success stories in various industries demonstrate how NDT has been key in extending the life of assets. For example, in the energy sector, regular inspection of pipes and pressure vessels in nuclear plants using NDT techniques has allowed the detection and correction of small cracks before they become leaks, ensuring operational reliability and long-term safety.
Industrial safety
Industrial safety is another vital aspect benefited by NDT. By allowing the early detection of defects and discontinuities, non-destructive tests significantly reduce occupational risks and the possibility of accidents. This has a direct impact on the health and safety of workers by minimizing exposure to hazardous situations and ensuring that equipment and structures are safe for use.
There are numerous examples of how NDT has prevented serious accidents in various industries. In construction, inspecting cranes and other elevated structures using NDT techniques has identified cracks and defects that, if undetected, could have caused catastrophic collapses. In the petrochemical industry, inspecting pipes and pressure vessels has prevented explosions and hazardous leaks, protecting both workers and the environment.
Challenges and future of the NDT Industry
Current challenges
The NDT industry faces several challenges in its development and application. Technological and operational limitations are one of the main obstacles. Some NDT techniques, although effective, can be costly and complex to implement in various industrial environments. Additionally, the precision and resolution of certain methods may be insufficient to detect very small defects or defects in complex materials, limiting their effectiveness.
The need for trained and specialized personnel is another critical challenge. Non-Destructive Testing requires advanced technical knowledge and experience to correctly interpret results and perform precise inspections. Training and retaining these specialized professionals can be costly and difficult, especially in regions with a shortage of skilled personnel.
The associated costs and implementation barriers also represent significant challenges. The initial investment in NDT equipment and technologies can be high, and companies must weigh these costs against long-term benefits. Additionally, adopting new technologies may encounter organizational and cultural resistance within industries.
Innovations and future trends
Despite these challenges, the NDT industry is experiencing technological advancements that promise to transform its future. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics in non-destructive testing is revolutionizing the precision and efficiency of inspections. Automated systems equipped with AI can quickly analyze large volumes of data, identifying patterns and anomalies with greater accuracy than traditional methods.
Digitalization and incorporating advanced technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) enable continuous and real-time monitoring of assets, facilitating predictive and preventive maintenance. These innovations not only improve the precision and efficiency of inspections but also reduce long-term operational costs.
The potential of new techniques and methodologies, such as industrial computed tomography and infrared thermography, is expanding NDT capabilities to detect defects in increasingly complex materials and structures. These emerging technologies position NDT as a key component in the digital transformation of industries, improving the reliability, safety, and efficiency of industrial operations in the future.
Conclusions
The NDT industry, through its advanced non-destructive inspection techniques, has proven to be an essential pillar in the modernization and sustainability of major productive sectors. Its ability to detect problems before they become catastrophic failures is vital to ensure the reliability, integrity, and safety of industrial assets. In the aerospace industry, NDT guarantees the safety of aircraft; in the energy sector, it optimizes the safe operation of nuclear plants and wind farms; in the automotive industry, it ensures vehicle quality; and in construction, it prevents structural failures.
Additionally, NDT not only improves the quality and efficiency of operations but also facilitates predictive and preventive maintenance, extending asset lifespan and reducing operational costs. With continuous technological advancements, including AI and robotics integration, the Ndt industry is prepared to face future challenges and continue being a crucial component in the digital transformation of industries, ensuring safer, more efficient, and more profitable operations.
References
Own source

