Low-VOC coatings represent a significant technical advancement in surface engineering, offering systems formulated to minimize the release of volatile organic compounds during application and curing. Due to their highly evaporative nature, these compounds actively contribute to atmospheric pollution and the degradation of indoor air quality, which has driven regulatory and operational pressure towards cleaner alternatives.
Low-VOC coatings address this challenge through optimized polymer matrices, reduced solvents, and resin technologies with greater transfer efficiency, achieving lower emissions without compromising mechanical performance or corrosion protection. Their adoption allows industries to align with sustainability strategies, improve working conditions, and reduce the environmental footprint associated with painting operations. In this context, low-VOC coatings are establishing themselves as a technical solution capable of combining durability, regulatory compliance, and environmental responsibility.
What are Low-VOC coatings?
A low-VOC coating is a protective system formulated to contain significantly reduced amounts of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), chemicals that evaporate at room temperature and, in traditional coatings, generate emissions responsible for indoor and outdoor air pollution. Its design seeks to minimize the release of these compounds during application, drying, and curing, reducing the environmental impact and risks associated with human exposure.
Low Volatile Organic Compound (Low VOC) paints and coatings have a molecular structure centered on high molecular weight polymers1 and binders that release few small molecules (VOCs) when drying, using water-based (aqueous) or 100% solid solvents. They represent more complex polymer structures and fewer volatile solvents to form a durable film with acrylic, polyurethane, or epoxy resins, prioritizing polymer and binder chemistry.
The “low-VOC” classification is determined by regulated thresholds in grams of VOC per liter, established by international environmental agencies. This type of coating reduces the odor and outgassing typical of conventional systems, improving air quality, increasing operational safety, and meeting strict environmental standards, representing an advanced alternative solution for contemporary construction and manufacturing.
Types of Low-VOC Coatings
Low-VOC technology includes several families:
- Water-based coatings: These replace solvents with water. They have minimal emissions, are easy to clean from equipment, and perform excellently indoors. Their durability can match solvent-based systems in corrosive categories C2–C5.
- Hybrid coatings (water + solvent): Combine the best of both worlds. They maintain low VOCs, but with robust curing and the typical manageability of traditional systems.
- High solids coatings: Increase the proportion of solids to very high levels, reducing the solvent without altering the application. They are common in two-component epoxies.
- Advanced technologies: Formulations with modified resins, nanostructured particles, and new-generation polymers that optimize chemical and mechanical resistance.
Benefits of Low-VOC Coatings
- Reduced environmental impact and pollutant emissions: The use of VOC coatings significantly reduces the release of chemicals that evaporate easily at room temperature. According to the documents, VOCs participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions that generate smog and damage air quality. By opting for solutions with low levels of these compounds or high-solids technologies, the carbon footprint is reduced and overall ecological damage is minimized.
- Improved occupational health and safety: The application of low-VOC coatings creates a much safer working environment for both applicators and occupants of treated spaces. By reducing the presence of organic solvents and thinners in the formulation, exposure to toxic vapors that can have a negative impact on human health is decreased. This not only makes workplaces and homes safer and more colorful places, but also reduces the risks associated with the flammability and explosiveness of traditional solvents, promoting overall well-being throughout the product’s life cycle.
- Strict compliance with legal regulations: Using low-VOC coatings ensures that companies comply with increasingly stringent federal and state regulations on emissions from stationary sources. The EPA and other regulatory agencies require constant monitoring to demonstrate that pollutant limits are being met. Adopting these technologies allows asset owners to align with approved “control techniques,” avoiding fines and legal penalties. It also facilitates adherence to international sustainability standards without the need to invest in costly additional filtering or combustion systems for emissions control at facilities.
- High performance and asset protection: Contrary to the belief that fewer solvents mean lower quality, modern low-VOC, high-solids coatings offer performance equal to or superior to solvent-based systems. These products are formulated to extend the service life of structures, equipment, and assets by providing robust and durable corrosion protection. By increasing the solids content in the applied film, coverage and efficiency are increased, reducing long-term maintenance costs and ensuring a favorable return on investment while maintaining the operational reliability of protected assets.
Environmental impact and sustainability of low-VOC coatings
The transition to coatings with low Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) content represents one of the most significant advances in the pursuit of industrial sustainability. The main driver of this change is the recognition of the ecological damage caused by traditional solvents. VOCs are carbon-containing chemicals that evaporate easily at room temperature; when released into the atmosphere, they participate in photochemical reactions that generate smog and ground-level ozone, deteriorating air quality and affecting the health of living beings2.
From a global sustainability perspective, the adoption of high-solids or water-based coatings directly mitigates these effects. By reducing dependence on solvents and thinners to control viscosity, pollutant emissions released during the drying and curing process are drastically reduced. This change is not just a matter of regulatory compliance; it represents a proactive decarbonization strategy.
The following video provides an overview of how Sheboygan Paint Company continues to develop low-VOC and water-reduced alkyd coatings, thereby helping to reduce environmental pollution.
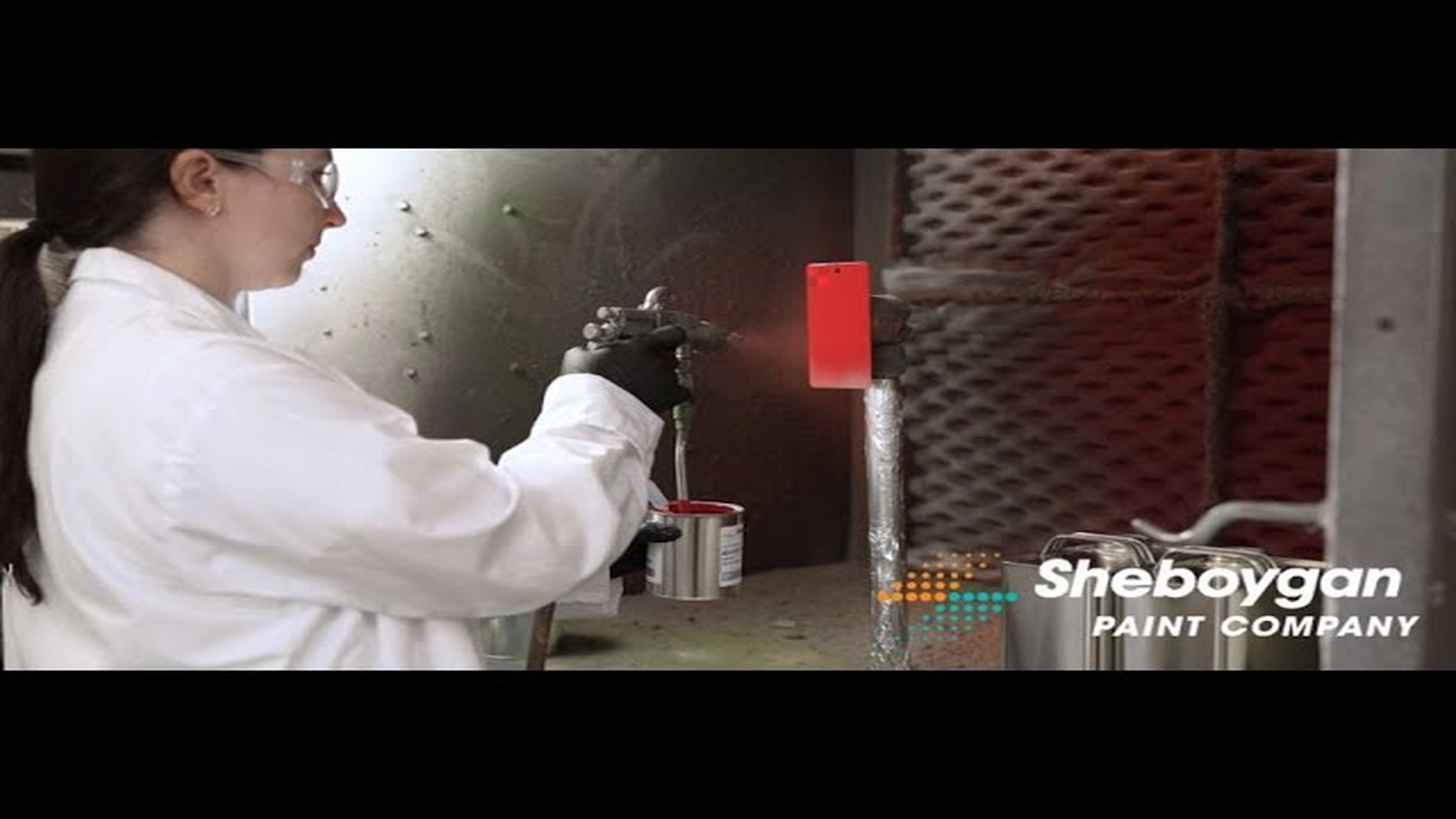

Low-VOC alkyd coatings.
The sustainability of these products is also evident in their operational efficiency and durability. There is a misconception that “green” products are less durable; however, today’s low-VOC technologies often outperform their solvent-based counterparts. By increasing the solids content in the applied film, greater coverage and robust corrosion protection are achieved, significantly extending the service life of assets, structures, and equipment. Extending the service life of assets is an act of sustainability, as it reduces the need for frequent repairs, the consumption of new materials, and the waste associated with maintenance.
Finally, the use of these technologies facilitates environmental compliance without requiring costly and complex infrastructure. Facilities using compliant coatings can meet strict EPA regulations and state standards for stationary source emissions without investing in additional control systems such as burners or vapor capture filters. This closes the circle of sustainability: cleaner processes, less energy wasted on pollution controls, and a safer, healthier environment for communities.
Conclusions
Low-VOC coatings represent an alternative solution for modern industry by integrating advanced technical performance with a significant reduction in environmental impact. Their ability to minimize the emission of volatile organic compounds improves indoor and outdoor air quality while reducing personnel exposure to hazardous vapors, thereby enhancing operational safety.
From a regulatory perspective, they enable compliance with increasingly stringent environmental standards without the need to install complex emission control systems, resulting in economic and operational efficiency. At the same time, high-solids, water-based, or hybrid technology formulations demonstrate that sustainability does not mean sacrificing durability: these coatings provide robust corrosion protection, extend asset life, and reduce maintenance costs. Taken together, low-VOC coatings represent a strategic innovation that aligns productivity, environmental responsibility, and industrial reliability.
References
- Jiang, X., & Luo, X. (2023). BC₆N monolayer as a potential VOC adsorbent in mitigation of environmental pollution: A theoretical perspective. ACS Omega, 8(49).
- Jiménez-López, A. M., & Hincapié-Llanos, G. A. (2022). Identification of factors affecting the reduction of VOC emissions in the paint industry: Systematic literature review (SLR). Progress in Organic Coatings, 170, 106945.

