Table of Contents
Gas in the oil industry has become a key element in driving operational efficiency and sustainability in this strategic sector. The oil industry has long been the main supplier of energy and the mainstay of the global economy.
However, the growing concern about climate change and the need for greater energy efficiency has led to the search for innovative solutions to maximize the value of gas and oil, reducing emissions. In this case, as emerging technologies are transforming industries around the world, oil and gas is no exception, this is because the oil and gas industry is currently in an environment of high risk and great opportunity. .
Oil price fluctuations in recent years have shown some volatility in the sector, but this situation has also led oil and gas companies to adopt new technologies to optimize inefficiencies and sustainability. It is clearer that modernizing processes with disruptive technology is an important step on the road to getting there.
Disruptive technology for gas processing in the oil industry
- Gasification
Gasification is a process with which transformations can be carried out, such as the methane present in natural gas, turning it into a synthesis gas through controlled chemical reactions. This gas can be used to produce a wide range of products, such as fuels, chemicals, fertilizers, and electricity. The ability to transform this raw material, giving it added value, makes it an attractive option to maximize the value of gas
Economic Benefits of Gasification
Gasification offers a number of significant economic benefits in the oil industry. First, it increases the flexibility and diversification of energy production, allowing companies to better adapt to fluctuations in the demand for fuel and electricity. In addition, gasification opens up new market opportunities by allowing the confession of high-value chemicals and materials from natural gas. This boosts the economy and creates jobs in industries with high growth potential.
2. Advanced processing
Advanced processing in the oil industry refers to the use of innovative technologies to improve efficiency at all stages of production. From exploration to distribution, advanced technologies are making it possible to reduce energy losses and optimize processes and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which translates into greater overall energy efficiency.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): CCS technologies hold great promise for making CO₂ emissions neutral, thus fulfilling an important part of the 2015 Paris Agreement conventions.
With the development of this technology, it will be possible to safely capture and store the captured CO₂ or use it for injection into oil wells to increase its performance.
- Reservoir Simulation and Modeling: Use of advanced software to simulate and model reservoir behavior, allowing for a better understanding of the geology and more informed decision making.
- Drilling and completion technologies: Improvements in drilling technology, such as directional drilling, measurement-while-drilling (MWD) systems, and completion techniques, which refers to the set of jobs performed on a well after or during drilling. repair, to leave them in a condition to efficiently produce fluids or to use it in water or gas injection.
- Renewable energy and electrification: Introduction of renewable energy sources in oil operations to reduce carbon footprint and improve sustainability.
3. Disruptive technological application
Disruptive technology is any technology or innovation that renders previous technology obsolete. It is disruptive because it produces a sudden rupture causing profound changes in the processes. In the oil industry, the following disruptive technologies are being applied with increasing emphasis:
Drones currently play a very important role in the oil industry, from improving safety in the field to increasing visibility at drilling sites, locating and controlling spills, fires and other emergencies. Giving a new level of confidence and security in this space.
Drone operators can deploy UAVs to assess emergencies before or instead of sending field personnel. The deployment of drones in this way keeps more people out of danger, inspections of facilities and equipment are carried out in high-risk sites and in areas that would require expensive access facilities, such as scaffolding, it also substantially reduces response times and costs .
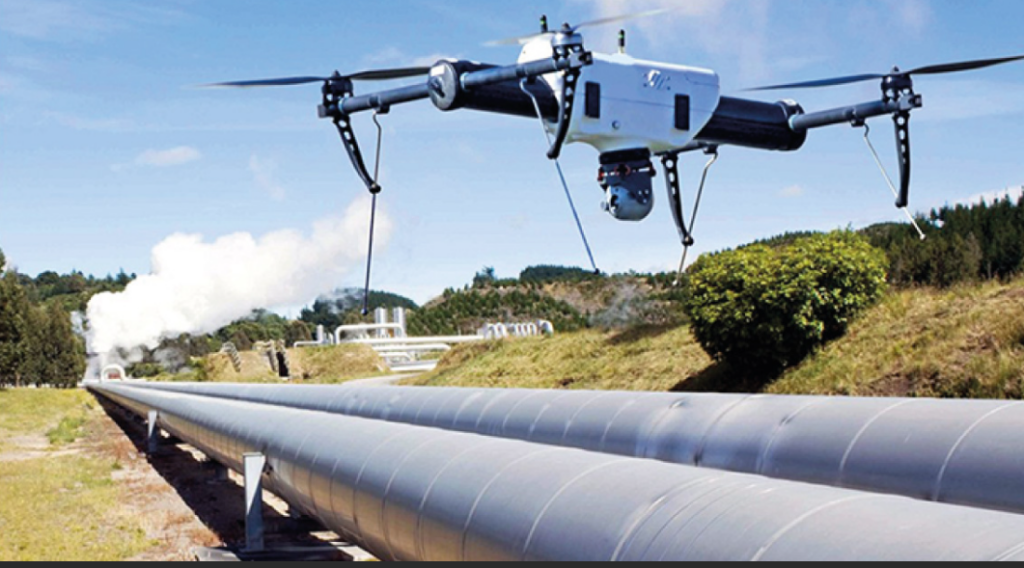

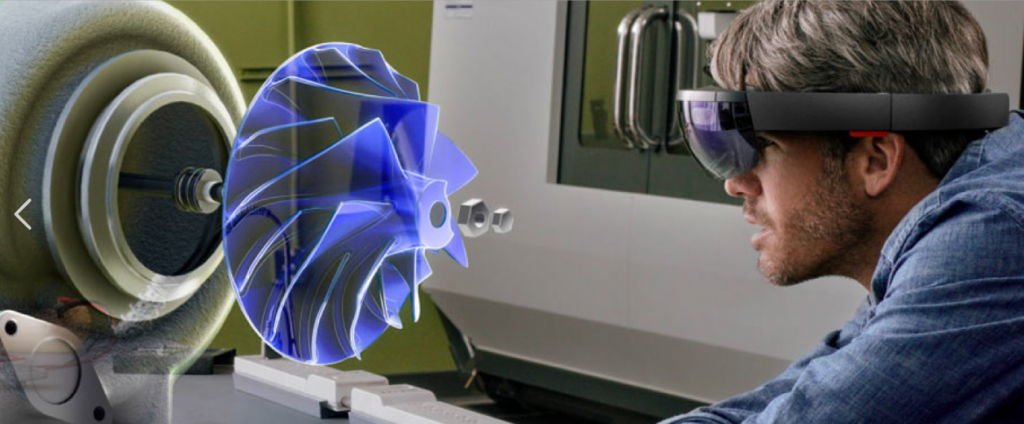
- Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented reality (AR) places digital images on top of the real world using headsets, smart glasses, phones or tablets, although it’s better known as a gaming technology (think Pokémon Go), it’s becoming more popular in professional industries, such as that of oil and gas. In fact, AR revenue in the energy and utilities sector is estimated to be $18 billion by 2022, with industry leaders like BP and GE already using the technology.
For one, on-site technicians can use AR to instantly connect with off-site specialists, significantly reducing travel costs to get experts to remote facilities. With this use of that technology, experts can guide technicians through tasks with audio and video, which reduces the chance of costly or dangerous errors on site and can also be used to overlay relevant data in the field. Using a headset, a field technician can see exactly where an underground pipe is located to prevent any type of break or accident during the excavation process.
- Blockchain
Another recent innovation that is revolutionizing the oil and gas industry today is blockchain, a technology that allows digital information to be distributed, but not copied.
One use case for blockchain is the tracking and trading of commodities. Given that crude oil is one of the most traded commodities globally, it is not surprising that the industry requires infrastructure to track these exchanges.
On the other hand, blockchain ledgers are cheap and secure, and don’t require the time-consuming maintenance needed with older solutions.
Demonstrating the potential of this use case, companies such as ENI, BP, and Wien Energie collaborate with to track transactions using enterprise blockchain technology and found that they could reduce overall transaction tracking costs by 30-40%.
- Artificial intelligence (AI):
Using AI to automate drilling operations and its ability to eventually reduce the number of wells needed for oil and gas operations. AI can also help prevent incidents and improve environmental performance by predicting leaks and identifying them in real time.
- The internet of things (IoT):
The oil and gas industry has been an early adopter of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, and for good reason. Energy providers employ many of the same IoT components used in other industries, including remote sensing, machine learning, and the cloud. When connected and combined with business processes such as alerts, the IoT enables operators to monitor systems and react, securely and in real time, to issues that arise in production.

Conclusion
Gasification and advanced processing, augmented reality, drones and blockchain are disruptive technologies, AI and IoT that are transforming the oil industry by enabling greater energy efficiency, reducing emissions and maximizing the value of gas. These innovations are paving the way to a more sustainable and prosperous future, where natural gas and other energy resources can be used more intelligently and responsibly. To achieve a successful transition to a cleaner energy system, it is essential that the oil industry continue to apply and invest in research and development of these technologies.

