Productivity is a key factor in the competitiveness of any company, it indicates the efficiency to generate goods and services in relation to the resources used, such as labor, materials, energy and machinery, that is, it shows what is produced by a system in terms of the inputs used.
In this sense, engineering plays a fundamental role in the optimization of industrial and service processes, due to its ability to develop innovative solutions based on knowledge, skills and technical competencies. In this context, the analysis of the processes, procedures, techniques and products generated plays a significant role in systematically understanding the improvements to be achieved through innovation.
This article focuses on the generalities of the intersection between engineering, productivity and the evolution towards Industry 5.0, highlighting how digital transformation is redefining production processes in the business environment. It discusses the fundamental role of engineering as a driver of optimization, capable of integrating theoretical knowledge and advanced technological tools to improve efficiency and quality in manufacturing and services.
Throughout the text, the reader will discover how the convergence of emerging technologies has driven the transition from Industry 4.0 to a more collaborative and human-centered paradigm, enabling higher levels of productivity and competitiveness.
Engineering as a productivity developer
Over time, engineering has evolved significantly, driven by innovation and technological advances. From its initial foundations to the implementation of advanced models in Industry 5.0, its development has been aimed at improving efficiency and quality in production processes. The constant evolution of tools, methodologies and strategies in engineering has allowed a sustained growth in productivity, achieving a greater optimization of resources, cost reduction and improvement in business competitiveness.
This progress has not occurred in isolation, but in close relationship with technology. Engineering, as an applied discipline, finds in technology the vehicle to materialize its innovations and transform production systems. In fact, technology is the bridge that makes it possible to convert theoretical knowledge into practical, scalable and efficient solutions.
Etymologically, the term technology comes from the Greek téchne, which refers to techniques or trades, and logos, which means knowledge. From this perspective, technology is understood as the set of knowledge that makes possible the application of techniques to develop a trade or solve a problem. In addition, its scope extends to the use of industrial techniques that facilitate the efficient production of goods and services. Along these lines, (Saavedra, Figueroa and Sanchez, 2021) point out that the American Association for the Advancement of Science defined technology as “the application of knowledge, tools and skills to solve practical problems and expand human capabilities”.
In line with this vision, UNESCO stresses that technology not only uses knowledge and tools to increase human potential, but also transforms our environment by solving practical problems. Thus, technology becomes a fundamental pillar within industrial production, articulating scientific knowledge with its technical application to generate efficient and sustainable processes.
In this context, the convergence of engineering and technology has revolutionized industrial production. Engineering designs and optimizes processes based on scientific and mathematical principles, and drives the adoption and improvement of new technologies. This process is bidirectional: while engineering finds in technology the means to innovate, technological advances open up new possibilities for engineering, generating a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement.
The integration of theoretical knowledge with advanced tools has given rise to an ecosystem of constant innovation, where each technological advance redefines the limits of what is possible. This synergy has driven the development of intelligent automation systems, flexible manufacturing processes and predictive maintenance strategies, optimizing resource management and enabling agile adaptation to changing global market conditions.
In short, engineering and technology have optimized the production of goods and services, and have enhanced the human capacity to innovate, solve complex problems and transform the industrial environment in a sustainable manner.
Beyond Industry 4.0
Let’s start by defining the term Industry 4.0, according to Peralta, Martinez and Enriquez (2020), this term represents the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) in an environment where devices, sensors and machines are connected, facilitating a connectivity that merges the virtual and physical worlds.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, originates in 2011, as cited by Xun Xu, Yuqian Lu, Birgit Vogel-Heuser, Lihui Wang (2021), in their article “Industry 4.0 and Industrial 5. 0: origin, conception and perception”; in this industrial era production systems, in the form of Cyber-Physical Production Systems (CPPS), achieve intelligent decision making through real-time communication and collaboration between makers of things, enabling flexible production of high quality customized products with massive efficiency.
This transformation is based on fundamental pillars that make it possible to optimize production processes and increase manufacturing efficiency. These pillars include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connects devices, sensors and machines in an intelligent network, enabling real-time collection and analysis for proactive process management.
- Big Data and analytics: They allow processing and interpreting large volumes of information, enabling strategic decision making based on accurate insights.
- Cyber-physical systems: Integrate the physical and digital worlds, creating intelligent production environments that operate autonomously and adaptively.
- Robotics and advanced automation: Automate complex and repetitive tasks, increasing accuracy, reducing errors and improving operational efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: Facilitate the anticipation of trends, optimize processes and improve decision making through algorithms that learn and adapt.
- Additive manufacturing: Revolutionizes production through techniques such as 3D printing, enabling the manufacture of customized and complex components.
- Cloud Computing and Cybersecurity: Provide the essential infrastructure to securely manage and protect data and digital systems, ensuring the continuity and reliability of processes.
These pillars of Industry 4.0, together, have enabled the digital transformation of production processes, integrating management tools and strategies that automate and optimize workflow, maximizing production efficiency. The adoption of smart factories has generated significant improvements in manufacturing, highlighting the real-time monitoring of equipment, the automation of supply chains and the strategic use of Big Data, which translates into more agile decision-making and a direct increase in productivity.
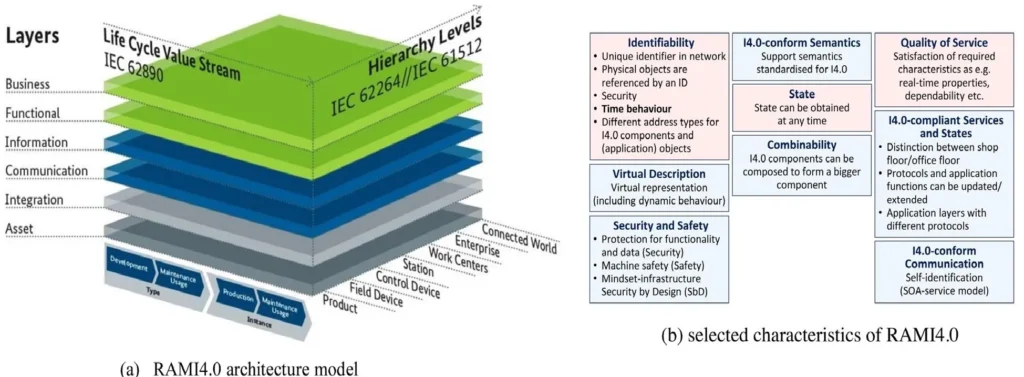
As described by Xun Xu, Yuqian Lu, Birgit Vogel-Heuser, Lihui Wang (2021), one way to understand Industry 4.0 is through the RAMI 4.0 model, which is a three-dimensional coordinate system representing the systems this industry exemplified in Figure 1. The “Hierarchy Levels” axis is derived from the automation information model and represents the different functionalities within factories or facilities; the “Layers” axis describes the decomposition of a machine into its properties and the “Life Cycle Value Stream” axis represents the life cycle of facilities and products. The latter also includes the business models and benefits of using Industry 4.0.
In this context, it is worth noting the evolution towards Industry 5.0, an emerging concept that, from 2020, thanks to the call of the European Commission, in the quest for a more sustainable, human-centered and resilient industry, proposes a more collaborative approach between humans and machines.
While Industry 4.0 focuses on automation and optimization through advanced technologies, Industry 5.0 seeks to enhance the value of human input, integrating artificial intelligence and collaborative robotics to personalize processes, improve sustainability and increase the resilience of production systems. This new paradigm recognizes that, while technology drives efficiency, the experience and critical judgment of the human factor remain irreplaceable in interpreting data, adapting processes and making strategic decisions, ensuring the optimal use of resources and materials.
The Industry 5.0 approach is based on emphasizing the importance of research and innovation to support industry in its long-term service to humanity within planetary boundaries and placing worker welfare at the center of the production process.
In short, the convergence between engineering, technology and the evolution from Industry 4.0 to 5.0 drives the automation and optimization of production processes, and reinforces the role of the human being in the digital transformation. This synergy enables new levels of productivity, where technological innovation and human analysis combine to comprehensively address the challenges of the modern industrial environment.
When analyzing these perspectives, an important evolution is evident in the incorporation of pillars that redefine the very fabric of our society. Looking to the future, greater adaptability and agility will be required in the face of constant changes in industries; however, this should not imply neglecting the individual or the environment. In line with the principles of Industry 5.0, it is imperative to build a resilient industry that places the human being at the center, fosters sustainable practices and ensures a robust response to emerging challenges.
Challenges and opportunities in the digital era: Towards sustainable productivity
Digital transformation presents both challenges and opportunities for companies seeking to achieve sustainable productivity in an increasingly competitive environment. The integration of advanced technologies has made it possible to optimize processes and significantly reduce costs. However, to take advantage of these benefits, it is essential to carry out strategic management, involving the adoption of new technologies, continuous training of human talent, the implementation of sustainable practices in the use of resources, robust cybersecurity and constant innovation.
A fundamental pillar of this transformation is the training and adaptation of human talent. Recognizing this challenge, Inspenet Academy offers a series of training programs in technical and management areas, focused on the energy and industrial sectors. If you wish to reinforce your knowledge and keep up to date, do not hesitate to explore its range of courses and diplomas designed to accompany professional growth in times of change.
Accelerated technological advancement requires professionals to constantly update and strengthen their skills to interpret and manage the vast amount of data generated by digital platforms and automated systems. Investing in the development of digital competencies improves the operational efficiency of organizations, and enhances the capacity for innovation, allowing companies to respond quickly to the changes and challenges of the global market.
At the same time, cybersecurity is an essential challenge in the digital era. The interconnection of systems and the handling of critical information require robust protection and risk management strategies. Ensuring the security of digital assets is essential to maintain operational continuity and data integrity, key elements to sustain and enhance productivity in an environment increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats.
Finally, continuous innovation and organizational transformation are essential drivers to face digital disruption. Companies must be willing to restructure their processes, adopt new business models and reinvent their strategies to remain competitive. This adaptation, combined with effective technology integration, translates into a competitive advantage that drives sustainable growth and positions the organization at the forefront of the industry.
Conclusion
The fusion between engineering, productivity and Industry 5.0 shows that digital transformation is an integral process where technology and human talent complement each other to drive innovation and sustainability. The adoption of automated systems and advanced analytics strategies optimizes resources and reduces costs, thus strengthening the ability of companies to adapt to an ever-changing global market. This analysis reaffirms the importance of investing in training, cybersecurity and sustainable practices, essential elements to consolidate a lasting competitive advantage and build a more efficient and resilient industrial future.
The 5.0 industrial revolution is here, and technology is its main driver of change!
References
- Peralta, J; Martínez, B; Enríquez, J; (2020). Industria 4.0. Inventio. Año 16; núm.39, julio-octubre. DOI: 10.30973/inventio/2020.16.39/4
- Saavedra, C; Figueroa, C: Sánchez, P. (2021). Acercamiento teórico al concepto de tecnología desde la educación en tecnología. Revista Boletín REDIPE 10 (5): 110-120.
- Xun Xu, Yuqian Lu, Birgit Vogel-Heuser, Lihui Wang, (2021). Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0—Inception, conception and perception. Journal of Manufacturing Systems. Volume 61, Pages 530-535. ISSN 0278-6125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmsy.2021.10.006. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0278612521002119

