Currently, industries are adopting eco friendly corrosion control strategies as an alternative to traditional inhibitors. This transition responds to the need to replace conventional inhibitors made up of toxic compounds such as chromates and lead, whose low biodegradability and persistence pose significant risks to the environment and human health.
Conventional corrosion inhibitors act by forming a protective barrier or slowing down the electrochemical process, but regulatory and sustainability requirements have driven the use of plant extracts known as green corrosion inhibitors. Sectors such as oil and gas, petrochemicals, maritime, and water treatment are adopting these solutions to protect assets without compromising operational efficiency.
Green chemistry and advances in materials science have enabled the development of biodegradable plant-derived corrosion inhibitors, which have proven to be an effective and sustainable alternative. This article analyzes their fundamentals, adsorption mechanisms and action on metal surfaces, advantages, limitations, and experimental evaluation methods, highlighting how sustainable innovation is transforming corrosion management toward more responsible, efficient, and safer models.
What are eco friendly corrosion control methods?
Eco friendly corrosion control methods are defined as scientific and technological strategies based on synthesized inhibiting agents known as green inhibitors to mitigate or prevent the electrochemical degradation of metals using environmentally safe, biodegradable, and non-toxic compounds.
How do green inhibitors act on metal surfaces?
From an electrochemical point of view, eco-friendly methods act through physical or chemical adsorption mechanisms on the metal surface, forming passive organic layers. These processes reduce the corrosive current density, reduce the metal penetration rate, and stabilize the corrosion potential without altering the operating parameters of the system.
Mechanisms of action of green organic inhibitors
Plant-based corrosion inhibitors act by forming a protective layer on the metal surface, preventing corrosive species (such as H₃O⁺ or chloride ions) from coming into direct contact with the metal. Although the exact mechanism may vary depending on the type of plant, concentration, pH, and metal, in general, they follow three key processes:
- Adsorption on the metal surface: Organic molecules present in plant extracts adhere to the metal, occupying the sites where corrosion would normally occur. At this stage, natural compounds compete with aggressive ions and prevent them from binding to the metal. (Center stage of the image)
- Blocking of active sites and increased surface resistance: By covering the points where electrochemical reactions occur, the inhibitor reduces both metal loss (anodic reaction) and hydrogen generation (cathodic reaction). This slows down the rate of corrosion and increases the electrical resistance of the surface.
- Formation of a protective film: Finally, the organic molecules form a stable, continuous film, creating a physical barrier that limits the access of water, oxygen, and corrosive ions to the metal.
Green inhibitors function as a natural molecular shield, reducing electron transfer, preventing metal oxidation, and slowing down the corrosion process. The following figure shows the process of inhibitor adsorption until the surface is completely protected.
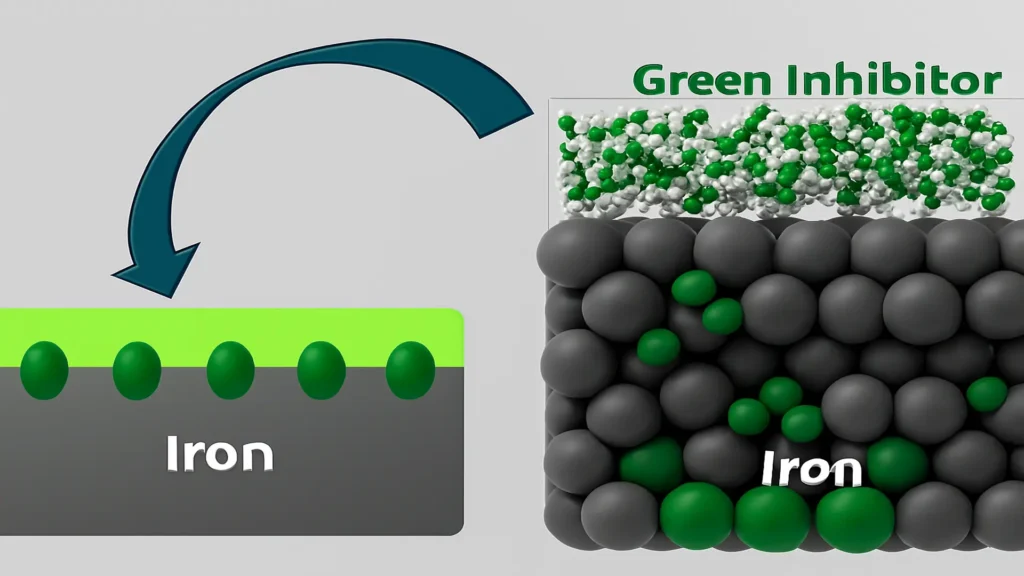
Organic inhibitors act mainly by adsorbing onto the metal surface, forming a hydrophobic barrier layer that limits access by corrosive species and delays the electrochemical reactions responsible for metal degradation. The process occurs in three main stages:
In the first stage, the exposed metal interacts directly with aggressive species such as H₃O⁺ ions, which promotes the release of metal ions (Fe²⁺) and the progression of the corrosion process. During the inhibitor adsorption stage, organic molecules from the plant extract migrate to the metal surface and begin to adhere physically or chemically, partially displacing the corrosive ions present at the metal/medium interface.
Finally, once the continuous protective film is established, the inhibitor forms a compact, hydrophobic molecular barrier that hinders the transfer of ions and electrons between the metal and the corrosive medium. This layer prevents the diffusion of species such as H₃O⁺ and limits the dissolution of iron, thus reducing the corrosion rate.
Together, this mechanism protects the metallic material by blocking active sites, reducing the transport of aggressive species, and mitigating both anodic and cathodic electrochemical reactions, significantly increasing corrosion resistance in aqueous systems and aggressive media.
Science and efficiency in eco-friendly corrosion control
The science behind eco friendly corrosion control focuses on minimizing environmental impact by using sustainable materials and processes1, avoiding hazardous chemicals. The main objective is to protect metal surfaces without compromising the health of the environment, using “green” inhibitors, biodegradable coatings, or efficient cathodic protection systems.
In this context, scientific research has focused on the study of plant-based corrosion inhibitors or green inhibitors from natural compounds capable of adsorbing onto metal surfaces, forming biodegradable protective films. Among the most studied compounds are polyphenols, tannins, flavonoids, and terpenoids, present in various plant species, especially xerophytic plants.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of these natural organic compounds in protecting steel from various corrosive environments. The results of this research, compiled from different sources, are presented below in Table 1, showing the efficiency of various plant extracts as corrosion inhibitors on different types of steel.
Table 1. Results of plant extracts evaluated as corrosion inhibitors for steel2
| Plant (Scientific Name) | Extraction Solvent | Metal | Corrosive Medium | Inhibition Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pineapple (Ananas comosus) | Water | Carbon steel | Hydrochloric acid | 98 |
| Canary Wormwood (Artemisia herba-alba) | Water | Stainless steel | Phosphoric acid | 88 |
| Brahmi / Henna (Bacopa monnieri / Lawsonia inermis) | Water | Low-carbon steel | Sodium hydroxide | 80 |
| Green tea (Camellia sinensis) | Water | Carbon steel | Sodium chloride | 80 |
| Peumo (Cryptocarya nigra) | Hexane, methanol | Mild steel | Hydrochloric acid | 91 |
| Blue Gum Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus) | Water | Low-carbon steel | Sulfuric acid | 88 |
| Milk Spurge (Euphorbia heterophylla Linnaeus) | Water | Mild steel | Hydrochloric acid | 93 |
| Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) | Water | Q235 steel | Sodium hydroxide | 88 |
| Wild Rose (Rosa canina) | Water | Mild steel | Hydrochloric acid | 90 |
| Ashoka Tree (Saraca ashoka) | Water | Mild steel | Sulfuric acid | 93 |
| Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) | Water | Mild steel | Sodium chloride | 96 |
Traditional inhibitors vs. ecological inhibitors
Green inhibitors, compared to traditional inhibitors, represent an ecological option that helps reduce environmental problems associated with the excessive use of chemicals in the manufacture of conventional inhibitors.
Eco-friendly inhibitors are obtained from natural sources, are biodegradable, and have low toxicity, while conventional inhibitors are usually made up of synthetic chemical compounds containing heteroatoms such as N, S, P, and O, which can have negative environmental impacts. Although conventional inhibitors have historically been more effective, the use of eco-friendly inhibitors is increasing due to their environmental advantages and growing efficiency in protecting against corrosion.
Table 2 presents a comparative summary of traditional and eco-friendly inhibitors, highlighting their main characteristics, mechanisms of action, and performance in different corrosive environments.
Table 2. Comparison: Traditional Inhibitors vs. Green Inhibitors
| Characteristic | Traditional Inhibitors | Green Inhibitors |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | High (Cr, Zn, phosphates) | Low / Zero |
| Environmental Impact | Eutrophication / Hazardous residues | Biodegradable |
| Cost | Moderate–High | Low (plant extracts) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Increasingly restricted | Aligned with green regulations |
Industrial applications
The adoption of environmentally friendly inhibitors has gained relevance in various industries due to their effectiveness in protecting against corrosion and their lower environmental impact.
- In the oil and gas industry, these natural compounds are mainly used for the internal protection of pipelines, mitigating corrosion induced by corrosive gases such as CO₂, H₂S, and O₂, thus extending the useful life of transport systems and avoiding costly operational interruptions.
- In the maritime sector, green inhibitors are applied to reduce corrosion in structures and components exposed to salt water, where the effects of salinity and the action of marine microorganisms accelerate corrosive processes.
- In water treatment, these inhibitors help prevent deposits and corrosion in closed systems, improving the efficiency of heat exchangers, boilers, and industrial piping networks, while minimizing the need for aggressive chemicals.
- In the chemical industry, eco-friendly inhibitors allow the replacement of traditional toxic inhibitors in processes involving acidic media, reducing environmental risks and improving operational safety without compromising the protection of metal equipment.
- Finally, in the energy sector, the use of green inhibitors helps extend the service life of industrial equipment, including turbines, heat exchangers, and storage systems, offering a sustainable solution to corrosion degradation under severe operating conditions.
Taken together, these applications demonstrate that ecological inhibitors not only play an efficient protective role, but also represent an environmentally responsible alternative to traditional synthetic compounds, aligning with the sustainability goals of modern industry.
Conclusions
Green organic inhibitors provide a sustainable and effective alternative to traditional chemicals, delivering Eco friendly corrosion control by forming a protective layer that blocks active corrosion sites and extends material lifespan.
Their mode of action, dependent on molecular composition and environmental conditions, shows that natural compounds are a reliable and environmentally responsible option for implementing Eco friendly corrosion control across industrial settings
References
- Al-Amiery, A., Wan Isahak, W. N. R., & Al-Azzawi, W. K. (2024). Sustainable corrosion inhibitors: A key step towards environmentally responsible corrosion control. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 15(5), Article 102672.
- Miralrio, A., & Espinoza Vázquez, A. (2020). Extractos de plantas como inhibidores de corrosión verdes para diferentes superficies metálicas y medios corrosivos: una revisión. Procesos, 8(8), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8080942
FAQs. Questions about eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors
What are eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors?
They are biodegradable compounds, usually extracted from plants, that reduce corrosion by forming a protective film without polluting the environment.
Add image
How effective are green corrosion control methods?
Depending on the concentration and medium, they can exceed 90% efficiency, similar to or higher than synthetic inhibitors
In which industries are eco-friendly inhibitors used?
They are used in sectors such as oil and gas, energy, water treatment, and the maritime industry, where they contribute to eco friendly corrosion control without compromising the integrity of the equipment.
How do organic inhibitors act on metal surfaces?
They adsorb and form a hydrophobic film that blocks active sites, reduces the transport of aggressive ions, and slows down corrosion reactions.
.

