Table of Contents
- What is CWI certification? Importance and scope
- Essential responsibilities of a CWI in the field
- The official AWS CWI certification requirements
- Detailed process for becoming a CWI inspector
- CWI exam structure
- Metallurgy: The heat-affected zone (HAZ)
- Recommended technical preparation for passing the CWI
- Visual interpretation and dimensional measurement (VT)
- Codes and standards that a CWI must master
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques used by a CWI
- Advanced defectology for CWI
- Weldability and metallurgical fundamentals
- Document traceability: WPS, PQR, and WPQ
- CWI and operational safety
- Mechanical integrity and role of the CWI
- Total Cost of CWI Certification
- Salary of a CWI inspector in the US (CWI Salary USA)
- Job opportunities and certified schools
- CWI vs. CAWI vs. SCWI: Real Differences
- Career path to become a CWI
- The Future of CWI: Trends and Technology
- Conclusions
- References
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
CWI Certification (Certified Welding Inspector) is the most influential and globally recognized accreditation for welding inspectors. Developed by the American Welding Society (AWS), it establishes the technical standard necessary to ensure the quality, safety, and reliability of welded joints in the energy, petrochemical, oil & gas, infrastructure, and heavy manufacturing industries.
Backed by key documents such as AWS CWI requirements, AWS QC1, AWS B5.1, AWS D1.1, API 1104, and other complementary international codes, this certification ensures that an inspector masters visual, dimensional, metallurgical, and documentary criteria to evaluate and validate welds in the field and workshop. In addition, CWI certification is a fundamental requirement for audit roles focused on mechanical integrity.
What is CWI certification? Importance and scope
The Certified Welding Inspector (CWI) is the most globally recognized professional accreditation level for personnel responsible for ensuring the quality of welding operations. This certification is administered by the American Welding Society (AWS).
A CWI is accredited to supervise, inspect, and document the conformity of welds in structures, pipelines, bridges, pressure vessels, and industrial components, based on codes and technical specifications.
Key importance and benefits
The importance of having CWI personnel lies in the comprehensive management of risk and quality in critical projects:
- Risk Reduction: Minimizes the probability of catastrophic failures associated with welding defects, protecting lives, the environment, and assets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures compliance with international codes and standards (such as ASME, AWS D1.1, API, etc.), a mandatory requirement for regulators, auditors, and customers in the global industry.
- Improved Reliability: Increases service life and operational integrity in highly demanding sectors such as refineries, petrochemical plants, power generation, and transportation systems.
Professional scope
CWI certification is required by global operators, contractors, and leading organizations such as API, ASME, AMPP (formerly NACE/SSPC), and ABS as a mandatory requirement for critical work.
In addition, it serves as a solid technical foundation and initial step toward progression to higher and more specialized roles, such as:
- Welding Engineer.
- QA/QC Supervisor.
- Asset Integrity Auditor.
Essential responsibilities of a CWI in the field
The certified inspector does not just “look at welds”; they manage an entire technical process. Their main duties include:
Before welding (preparation and prevention)
- Verify base materials and consumables (WPS/PQR).
- Confirm welder qualification according to the applicable code.
- Ensure proper preparation of joints, bevels, and alignment.
- Monitor environmental conditions (humidity, temperature, cleanliness) and the application of preheating if required.
During welding (process control)
- Check parameters: voltage, amperage, feed rate.
- Ensure the use of the appropriate filler metal technique.
- Control thermal sequence and distortion.
After welding (final evaluation)
- Perform visual inspection (VT) according to AWS B1.10.
- Check for typical defects: undercutting, porosity, lack of fusion.
- Coordinate NDT tests: UT, RT, PT, MT, PAUT, TOFD.
- Prepare the final technical report in accordance with QC1.
The official AWS CWI certification requirements
The AWS CWI requirements establish rigorous criteria for CWI exam eligibility and ensure that only qualified professionals obtain the credential, ensuring that only professionals with the right combination of experience and education can obtain CWI certification.
Compliance with these requirements is the first and most critical step. The AWS requires verifiable evidence of your educational background and work experience, in accordance with AWS B5.1: Specification for the Qualification of Welding Inspectors. According to AWS QC1, the following are required:
- Academic background
- High school diploma + industrial experience (min. 5 years).
- Engineering/Advanced technical degree + less experience.
- Verifiable field experience
In inspection, welding, QA/QC, manufacturing, or NDT.
- Experience vs. Education Matrix according to AWS B5.1
The official matrix relates your level of education to the minimum amount of work experience required in the field of welding:
| Accepted Educational Level | Minimum Years of Welding Experience (Total) | Minimum Years of Leadership/Supervisory Experience |
|---|---|---|
| No high school (or equivalent) | 12 years | 8 years |
| High school diploma (or equivalent) | 8 years | 4 years |
| Two-year degree in Welding Engineering or Technology | 4 years | 2 years |
| Four-year degree in Welding Engineering or Technology | 3 years | 1 year |
Key Point: Experience must be directly related to welding fabrication, construction, repair, quality control, or inspection and must be clearly documented.
Detailed process for becoming a CWI inspector
The path to CWI certification begins with eligibility and culminates with passing the demanding three-part CWI exam:
Preparation and Eligibility
- Code Review: Determine which reference code will be your basis for the exam. The most common and recommended code is AWS D1.1 (Structural Welding Code – Steel).
- Preparation Courses: Many applicants opt for certified CWI training courses to master the material.
- Application: Submit the official application to the AWS, including verification of experience and payment of exam fees.
The CWI exam: Parts A, B, and C
The CWI exam consists of three mandatory parts, each designed to assess a different aspect of the inspector’s knowledge:
| Part | Focus | Format | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part A (Fundamental Knowledge) | Welding principles, terms, metallurgy, NDT, etc. | 150 multiple-choice questions. | 2 hours |
| Part B (Practical exam with real samples) | Ability to use tools, specimens, and visual inspection. | 46 questions using samples and visual aids. | 2 hours |
| Part C (Code Application) | Application of a specific code (e.g., AWS D1.1, API 1104, ASME B31.3). | 50 multiple-choice questions. | 2 hours |
A minimum score of 72% is required in each part to pass and obtain certification.
CWI Renewal and Recertification (CWI Renewal)
CWI certification is valid for a period of three years.
- Renewal at 3 and 6 years: Documentation demonstrating continuous performance of inspector duties and payment of the corresponding fee are required.
- Recertification at 9 years: In this cycle, the inspector must pass a shorter recertification exam or complete a number of continuing education hours (CEHs) to maintain the credential.
CWI exam structure
Part A – General knowledge
- SMAW, GTAW, GMAW, FCAW processes; basic metallurgy; common defects.
Part B – Practical test
The candidate evaluates 6–10 coupons with actual discontinuities, using:
- Welding gauges.
- Comparators.
- Magnifying glasses.
- Calibrators.
- Reinforcement gauges.
Part C – Code interpretation
The applicant selects one of these codes:
- AWS D1.1 (Steel Structures)
- API 1104 (Pipelines and Welding in Pipelines)
- ASME IX (Welder Qualification)
- AWS D1.5 (Bridges)
- AWS D17.1 (Aerospace)
Metallurgy: The heat-affected zone (HAZ)
The HAZ (Heat Affected Zone) is the region of the base material that does not melt, but whose microstructure and mechanical properties are altered due to the thermal cycle.
- Main Risk: Rapid cooling rates can result in hard and brittle microstructures (martensite), making it susceptible to cold cracking (HICC).
- CWI Control: The inspector verifies compliance with thermal control techniques in the WPS, such as Preheating (to reduce cooling rate and allow hydrogen diffusion) and PWHT (Post-Weld Heat Treatment, to relieve residual stresses and improve toughness).
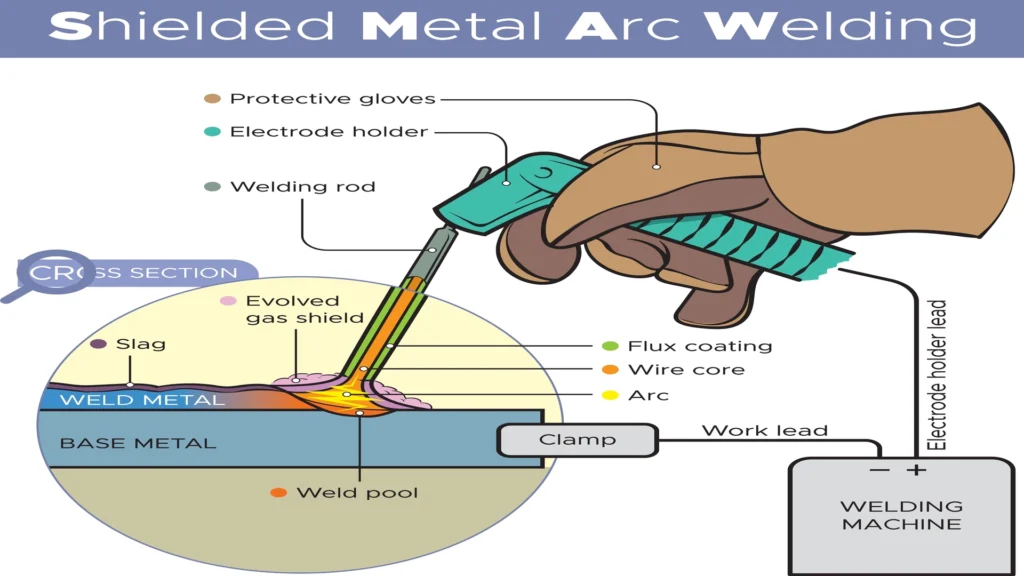
Recommended technical preparation for passing the CWI
Preparation for the CWI exam should be methodical and intensive. It includes:
- Mastery of the book Welding Inspection Technology (WIT).
- Intensive study of the selected code (min. 40 hours).
- Practice with real coupons according to AWS B5.1.
- Exam simulations with a stopwatch.
Instructor Perspective (Recommended Video): As an essential complement to your study, consult the experience and strategic advice of top AWS professionals to ensure success on the exam. Access the full video here (courtesy of AWS):

Visual interpretation and dimensional measurement (VT)
Based on AWS B1.10, the inspector shall:
- Measure reinforcement, throat, convexity.
- Identify cracks, undercutting, bites, porosity, lack of fusion.
- Evaluate distortion and alignment.
- Verify continuity between passes.
Example: On a 12″ API 5L pipe, the CWI detected partial root penetration using a mirror and flashlight before NDTs were scheduled.
Codes and standards that a CWI must master
Includes:
- AWS D1.1 – Steel structures.
- API 1104 – Welding in pipelines and hydrocarbon transportation.
- ASME IX – Qualification of welders and procedures.
- ASME B31.3 – Process.
- API 650/653 – Storage tanks.
Non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques used by a CWI
- VT – Visual
- UT – Ultrasound
- RT – Radiography
- MT – Magnetic particles
- PT – Penetrant testing
- PAUT – Phased Array
- TOFD – Time-of-Flight Diffraction
Example: In a pressure vessel, the CWI orders TOFD to measure the height of a longitudinal crack initially detected by conventional UT.
Advanced defectology for CWI
Includes study of:
- Hot/cold cracking.
- Independent and clustered porosity.
- Slag inclusions.
- Lack of lateral fusion.
- Lack of penetration.
- Severe undercutting.
- Thermal collapses in roots.
- Burn-through in pipe welding.
Weldability and metallurgical fundamentals
The CWI must include:
- HAZ (Heat Affected Zone).
- Thermal cycles and microstructure.
- Preheating and PWHT.
- Diffusible hydrogen (HICC, SOHIC).
- Ferritic and martensitic transformations.
Document traceability: WPS, PQR, and WPQ
The inspector validates:
- WPS in accordance with ASME IX or AWS D1.1.
- Mechanical testing of the PQR.
- Welder qualification (WPQ).
- Records of consumables, batches, lots, and certificates.
Example: At a petrochemical plant, the CWI rejected a batch of E7018 electrodes due to improper storage, preventing a failure due to moisture in the slag.
CWI and operational safety
Includes:
- Control of hazardous atmospheres.
- Electrical and arc risks.
- Handling of gas cylinders.
- Safe working procedures.
Mechanical integrity and role of the CWI
The CWI plays an essential role in:
- RBI (Risk-Based Inspection) according to API 580/581.
- FFS (Fitness for Service) API 579.
- Pipe inspection according to ASME B31.3/B31.1.
- Evaluation of critical structural indications.
Total Cost of CWI Certification
The cost of CWI Certification is an investment that varies annually and depends on whether the candidate is a member of the AWS. This investment is mainly divided into exam fees and preparation costs:
Official examination fees (AWS)
| Candidate | Application/Examination Fee (Approx.) | Recertification fee for 9 years (approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| AWS member | $1,050 – $1,350 USD | $900 – $1,100 USD |
| Non-Member | $1,300 – $1,600 USD | $1,150 – $1,350 USD |
Note: Costs are estimates and are subject to change by the American Welding Society.
Investment in preparation courses and materials
To ensure success, most candidates invest in:
- Preparation Courses: These can range from $1,500 to $3,500 USD.
- Materials: Code books (e.g., AWS D1.1) can cost between $300 and $700 USD.
The total investment to obtain CWI certification usually ranges from $3,000 to $6,000 USD, including the exam, courses, and materials.
Salary of a CWI inspector in the US (CWI Salary USA)
The CWI salary in the USA is one of the most competitive incomes in the sector. The salary of a certified welding inspector is substantially higher than that of an average welder or a non-certified inspector.
Average salary by experience and location
The average salary in the US is highly competitive and is influenced by experience, industry (oil and gas, aerospace, etc.), and geographic location.
| Level of Experience | Average Annual Salary (Approx.) | Maximum Salary (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Level (0-2 years) | $65,000 – $75,000 USD | $80,000 USD |
| Intermediate Level (5-10 years) | $80,000 – $100,000 USD | $115,000 USD |
| Senior/Specialized Level (+10 years) | $100,000 – $130,000 USD | $150,000+ USD |
Source: Based on recent employability data in the USA.
Semantic Entity: Inspectors who also hold advanced certifications (such as SCWI) or who work on onshore/offshore energy projects tend to report salaries significantly above average.
Job opportunities and certified schools
Demand for CWI jobs USA remains strong in the United States, as the need for regulatory compliance and quality is constant.
- Key Industries: Oil & Gas, Construction, Aerospace, and High-Precision Manufacturing.
- AWS-accredited schools provide adequate preparation to pass the CWI exam and obtain CWI certification.
The search for CWI jobs in the USA increases every year due to technical compliance requirements in federal and private projects.
CWI vs. CAWI vs. SCWI: Real Differences
CAWI – Associate CWI
- Basic level.
- Supervised by a CWI.
- Ideal for beginners.
CWI – Certified Welding Inspector
- Standard level.
- Acceptance/rejection authority.
- Internationally recognized.
SCWI – Senior CWI
- Specialist in audits, QA/QC program design, and complex regulations.
- Requires 12+ years of experience.
Career path to become a CWI
- Technical training.
- Industrial experience.
- Preparation course (80–120 hours).
- AWS exam.
- Certification.
- Renewal every 3 years.
- Re-certification after 9 years.
The Future of CWI: Trends and Technology
The role of the Certified Welding Inspector (CWI) is undergoing a profound transformation. The industry is moving toward more automated processes, advanced materials, and digital control systems, which requires a more versatile, technologically savvy, and analysis-oriented professional profile.
Accelerated technology integration
The next generation of CWIs will work with digital tools that will increase the accuracy and speed of inspections:
- Comprehensive digitization: use of advanced software, automated reports, and real-time traceability.
- Drones and robotics: ideal for inspections at height, in confined spaces, or in hazardous areas.
- Augmented and virtual reality: defect simulation, immersive training, and remote assistance.
- Big Data applied to welding: predictive analysis to detect failure patterns and optimize quality.
Prevention, predictive maintenance, and simulation
The reactive approach is being left behind:
- Predictive performance models: enable faults to be anticipated based on discontinuity trends.
- Simulation and digital modeling: preliminary analysis of joints, welding sequences, and thermal behavior.
Globalization and standardization
Professional mobility is increasing:
- International harmonization of standards: integration between AWS, ISO, EN, and ASME.
- Mutual recognition of certifications: trend toward facilitating equivalencies between countries and organizations.
New materials and advanced processes
The industry adopts technologies that challenge traditional knowledge:
- Advanced materials: high-strength steels, special alloys, metal 3D printing, and composites.
- Innovative processes: laser welding, hybrid welding, friction stir welding, additive welding, and automated welding.
Sustainability and energy efficiency
Inspectors will also have responsibilities in:
- Sustainable welding: reduction of consumables, emissions, and waste.
- Energy optimization of processes: thermal analysis and reduction of inputs.
Key skills for the CWI of the future
To remain current, the inspector must strengthen:
- Continuous training: constant updating on standards, materials, and technologies.
- Adaptability: ability to learn new tools and change work environments.
- Critical thinking and decision-making: technical analysis based on data and evidence.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration: interaction with engineers, NDT specialists, QA/QC, and design teams.
The CWI of the future will be more digital, more analytical, and more global. Those who integrate new technologies, international standards, and advanced materials knowledge will position themselves as indispensable professionals in ensuring safe, efficient, and sustainable welding.
Conclusions
CWI certification remains the most robust credential for ensuring reliable, code-compliant welding. Those who obtain this accreditation gain access to better opportunities, higher CWI salaries in the USA, job stability, and priority in CWI jobs in the USA.
For energy and industrial companies, having a certified welding inspector means less risk, greater reliability, and full compliance with international codes. For professionals, obtaining accreditation opens doors to global positions with greater knowledge, better remuneration, and continuous growth.
It’s time to certify your experience! Ready to take the next step and get your credential? Check out the AWS-recommended CWI preparation courses now and get ready to earn the competitive CWI Salary USA.
This article is part of the editorial line of Inspenet, official media partner of global events such as: API, AMPP, SLOM, GASTECH, CINDE, NISTM, INCORRS, LATINCORR, ILTA, AEND, PAN NDT 2025.
References
- AWS QC1: Standard for AWS Certification of Welding Inspectors.
- AWS B5.1: Specification for the Qualification of Welding Inspectors.
- AWS D1.1/D1.1M Structural Welding Code–Steel.
- API 1104: Welding of Pipelines and Related Facilities.
- ASME BPVC Section IX – Welding Qualifications.
- AWS Welding Inspection Technology (WIT).
- API 579-1/ASME FFS-1 Fitness for Service.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long does it take to become a CWI?
Between 6 months and 2 years, depending on experience.
Is the English exam mandatory?
In most countries, yes.
Which code should I choose for the exam?
It depends on the sector: API 1104 (pipelines), AWS D1.1 (structures), ASME IX (processes).

