Table of Contents
- Introduction.
- 1 The water level .
- 2 Overheating due to the incidence of flames against the exchange surfaces.
- 5 Representativeness of the Water-Vapor Samples .
- 6 Start and Stop Procedures .
- 7 Rapid cooling or emptying procedures with the boiler still hot.
- 8 Periods of the boiler out of service without complying with a preservation procedure .
- Conclusion.
- References
Author: Lic. Carlos Lasarte – CEACA General Director , November 15, 2021.
This article aims to analyze failures in boilers by analyzing the internals of the steam generation system, auxiliary equipment, operating procedures, in order to ensure the mechanical integrity, reliability and operational safety of these equipment. They have a wide application in the oil and gas industry, as steam generators for different industrial processes.
Introduction.
The boiler is a piece of equipment used in engineering with the aim of generating superheated and saturated steam through a heat transfer process at constant pressure; They have a wide application in the heavy oil and gas industry to improve their fluidity.
Most boiler operators and authors of topics related to the functioning and operation of this equipment, consider that the first cause of damage and failures in boilers is due to the quality of the water, without analyzing that there are operational conditions that influence in these faults such as:
1 The water level .
If the water level exceeds the Normal Design Level, (Figure 1). In this case the following problems may occur:
- From the top of the level, large amounts of water and solids can be entrained. This condition will generate internal fouling of superheaters, heat exchangers and/or valve seats.
- By moving the upper part of the level away from the purge line, it will be less effective and will not be able to remove the solids that tend to go towards the supernatant and could form foams.
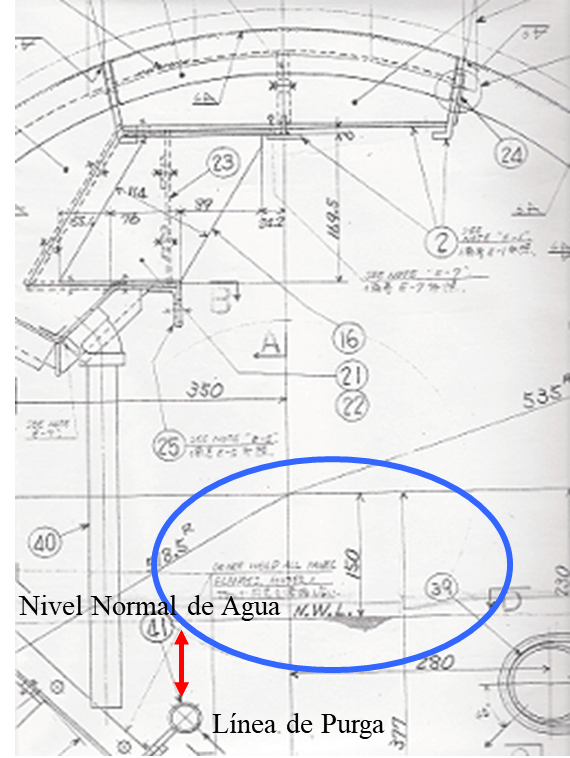
Figure 1. Boiler manufacturers define, based on design codes, what the water level should be inside the boiler. When working with a water level above the normal water level the design of the boiler is changed.
2 Overheating due to the incidence of flames against the exchange surfaces.
Under this condition, dissolved and/or suspended solids adhere to the exchange surface; therefore, overheating of the tube material will be accelerated.
3 Obstruction and plugging of gas passages.
In this case, the passage of gases can be obstructed by ashes (Figure 2), or by mechanical plugging to correct leaks in the tubes (Figure 3); therefore, the greater quantity of gases will pass through the tubes with greater freedom of passage and there will be more evaporation and encrustation, with the consequent overheating.
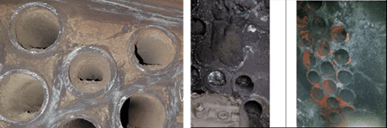
Figure 2. Pipes clogged by combustion ashes.
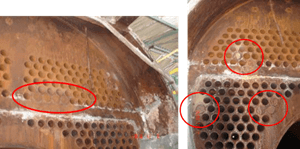
Figure 3. Plugged tubes to correct leaks.
4 A low circulation, low load operation .
When the boiler does not operate at its nominal load, normally the water circulation and water-steam mixture do not reach their circulation speed. Whereby:
- The chemicals that are dosed in the internal treatment are not homogenized and there will be different concentration conditions inside the boiler. Close to the dosing points there will be high concentrations of chemicals and low concentrations in those further away, forming a cell of differential corrosion by concentration, generating localized corrosion damage inside the boiler (Figure 4).
Chemical analyzes of the water to control its quality should be carried out a couple of times a week; which will avoid variations in concentrations, guaranteeing good operational performance.

Figure 4. Evidence of concentration of the dosed chemical and localized corrosion.
- If the load is very low, the circulation will also decrease, causing the precipitation of the suspended solids and even the separation of the water-steam / water-foam phases and exposing the heat exchange surface to overheating conditions.
- In the case of fire-tube boilers, when working at low loads, in addition to low circulation, the burner will be operating at low fire, the flame will be incident on the upper part of the furnace, where there will also be a significant amount of sludge deposited, if really the quality of the water treatment is not good. Under this condition, that marked area (figure 5) will overheat and eventually fail.
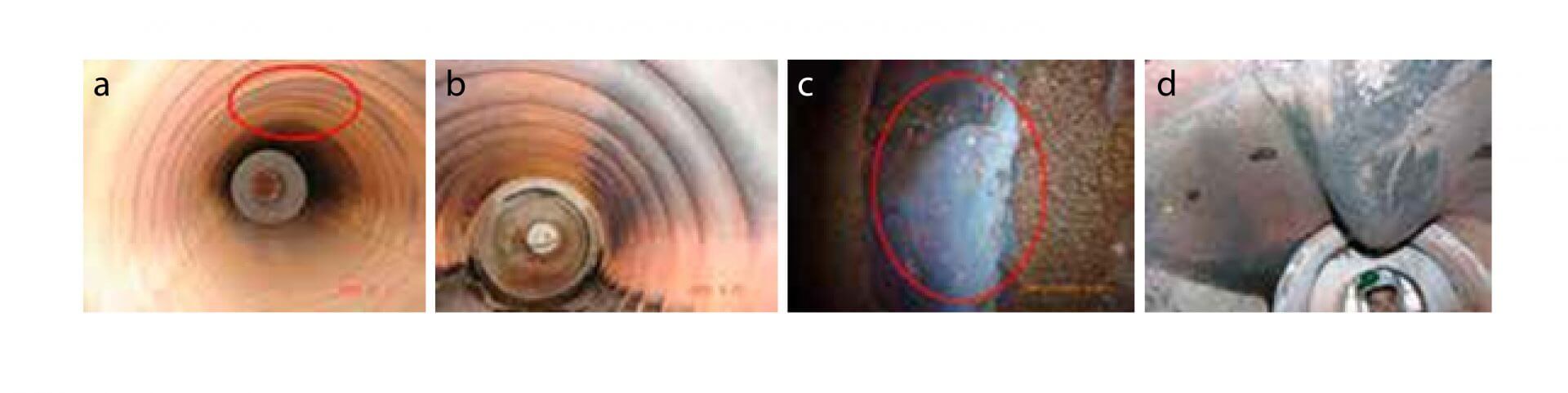
a) Area where the flame strikes, b) Flame incidence, c) Incidence of flame and excessive accumulation of sludge seen from the water side, d) When a level loss event occurs, that area where the flame strikes at low load – under fire, is sensitized or aged and deforms.
Figure 5. Problems in fire tube boilers due to low water load.
5 Representativeness of the Water-Vapor Samples .
On the other hand, are you sure that the surface blowdown or continuous blowdown of the boiler really has the capacity to capture the suspended solids? Is it a perforated pipe running through the boiler…or is it just a hole?
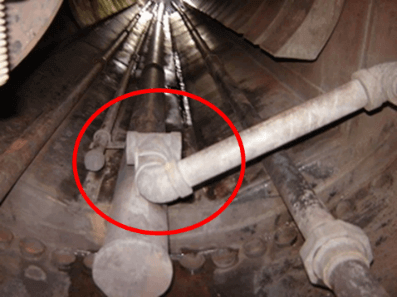
The purge intake – boiler water sample must be a perforated line that takes a sample or purges water from the entire boiler, never a hole that captures only one point of it.
6 Start and Stop Procedures .
If the boiler start-up curve or procedure is not complied with, in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions; that is, if quick starts are made, to operate the boiler as soon as possible.
- The water will not circulate at an adequate speed and will not cool the exchange surfaces,
- Vapor bubbles will be generated, which will not move and will form vapor barriers that can overheat on the surface and the maximum temperature allowed for the material of the tubes will be exceeded.
- In the case of superheaters, they will exceed the maximum temperatures allowed for the materials; therefore, the boiler will not generate the necessary steam to cool them and they could break due to rapid overheating.
7 Rapid cooling or emptying procedures with the boiler still hot.
- Following rapid cooling procedures, in addition to the damage generated on the refractory system, will also affect the joints or expansion between tubes and plates or domes, and in the short term they will cause leaks in said joints.
- If the boiler is emptied while still hot, the solids that may be in suspension will stick to the exchange surfaces, become encrusted and eventually accelerate the overheating of the tube material.
8 Periods of the boiler out of service without complying with a preservation procedure .
The boilers must be conditioned for the periods in which they are out of service, either wet or dry, in order to guarantee that corrosion processes will not occur due to the entry of air when depressurizing it.
Conclusion.
For the proper functioning of a boiler, it is important not only to consider the quality of the water for steam generation, but also all the operational conditions, exposed and analyzed in this work; which can cause damage and failure, when the appropriate operational procedures are not carried out to preserve the physical integrity and reliability of these assets.
References
Own source
Lic. Carlos Luis Lasarte V.
General Director – Consultant Combustion, Energy & Environment, SA ( carlos.lasarte@ceaca.com )




