Table of Contents
The oil and gas industry experienced some significant challenges in 2020. With the sudden reduction in fuel consumption, there was a substantial global surplus of crude oil. This situation caused storage facilities to reach maximum capacity and even tanker trucks to store unwanted products.
In this context, the abandoned storage facilities are currently undergoing restoration to put them back into service; operationally, the construction of new tanks is being considered to increase capacity to higher volumes; all of which translates into expanding the number of inspections of tanks in service to evaluate the critical components in the internal and external part of the asset.
This article will provide a comprehensive review of NDT techniques that can be applied to storage tanks put back into service.
An overview of the situation!
Content
An overview of the situation!
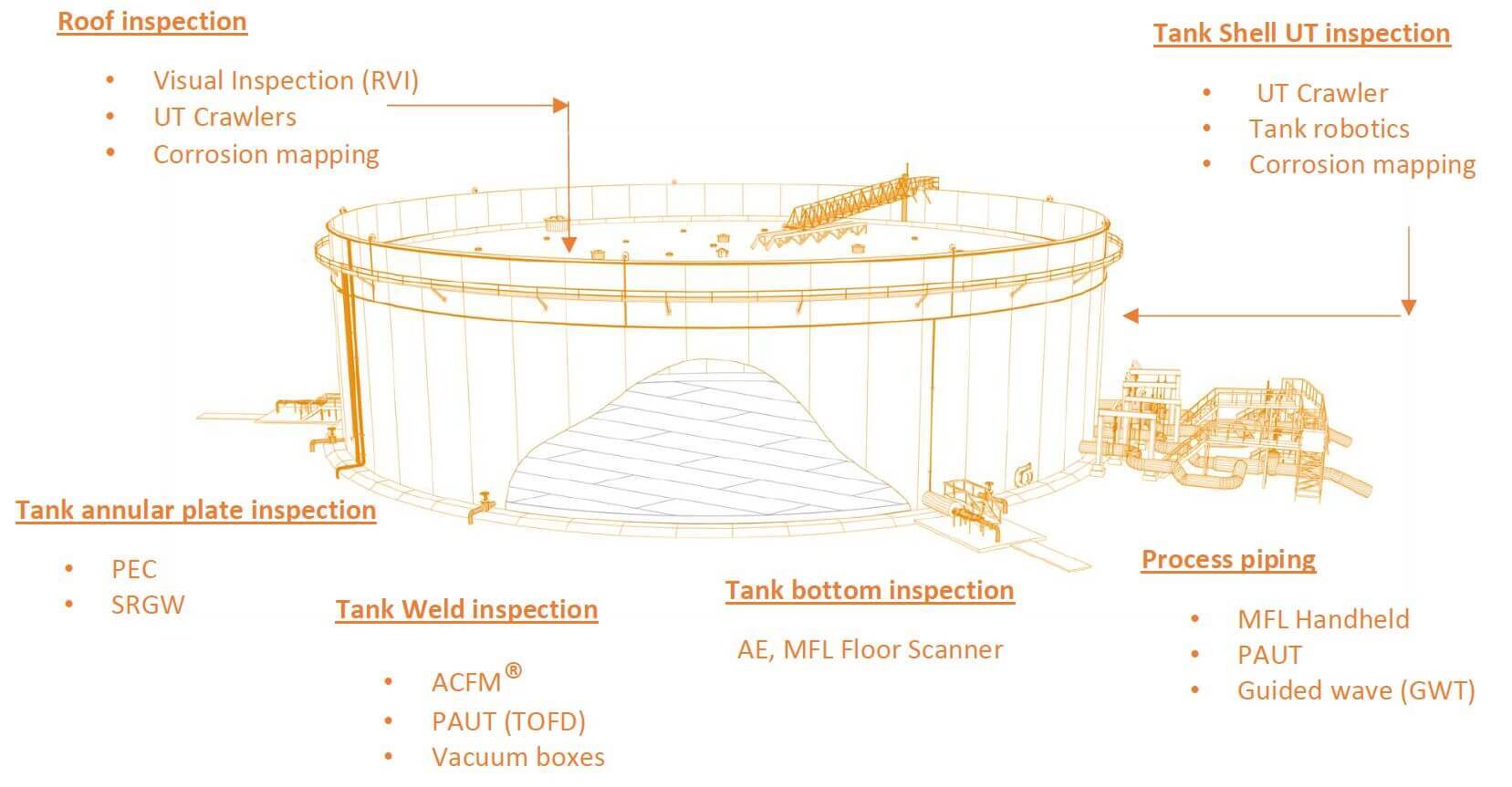
Despite its apparent simplicity, many tank components must be inspected. Tank inspection includes assessment of fixed or floating roof infrastructure including domes and seals, shell opening, settlement analysis. Both internal and external attacks typically take the form of isolated attacks governed by roof geometries, construction methods, plate flatness and sheathing conditions. Critical areas involve bottom plates, shell plates, roof plates, and all weld joints. While leakage is supposed to occur before a failure, highlighting the thin areas of a tank shell, this is not always the case; there can be a catastrophic failure without any previous leak. Monitoring the exterior of the tank for general metal loss in various areas provides a useful integrity assessment, but the extent of inspection needed depends on the product being stored, the age of the tank, and historical inspection results.
Today, any evaluation of a major asset such as a storage tank goes through a risk-based inspection (RBI) program executed by experienced professionals, which also considers: the type of product, historical conditions, construction information and years of service.
It is during this initial evaluation that knowledge of inspection technology can help make better decisions. The examination is broken down into a sequence of identified integrity risks, and each component of this inspection can be assisted with the correct technology selection.
There are continuing advances in new non-destructive testing (NDT) technologies that improve defect detection and sizing accuracy. All systems have some limitations and it is important to choose the most suitable tool or technique for each inspection. NDT methods can be complementary, and in some cases may need to be combined for best results. The actual condition of the tank being inspected will also influence the accuracy of the measurement, and this must be taken into account.
What are the most common techniques used in tank inspection?
• Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) and STARS
• Automated and manual ultrasound (UT)
• Automated and manual Phased-Array Ultrasound (PAUT)
• Alternating Current Field Measurement (ACFM®)
• Pulsed Eddy Current (PEC)
• Eddy Current Array (ECA)
• Guided Wave Ultrasound (GWUT)
Next, several cases of inspection of the sections of a storage tank by different techniques are presented.
tank floor plates
The most common technology used to inspect bottom plates for corrosion is Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) fig.1 due to its sensitivity to pitting corrosion and the ability to inspect nearly 100% of the tank bottom accurately. efficient.
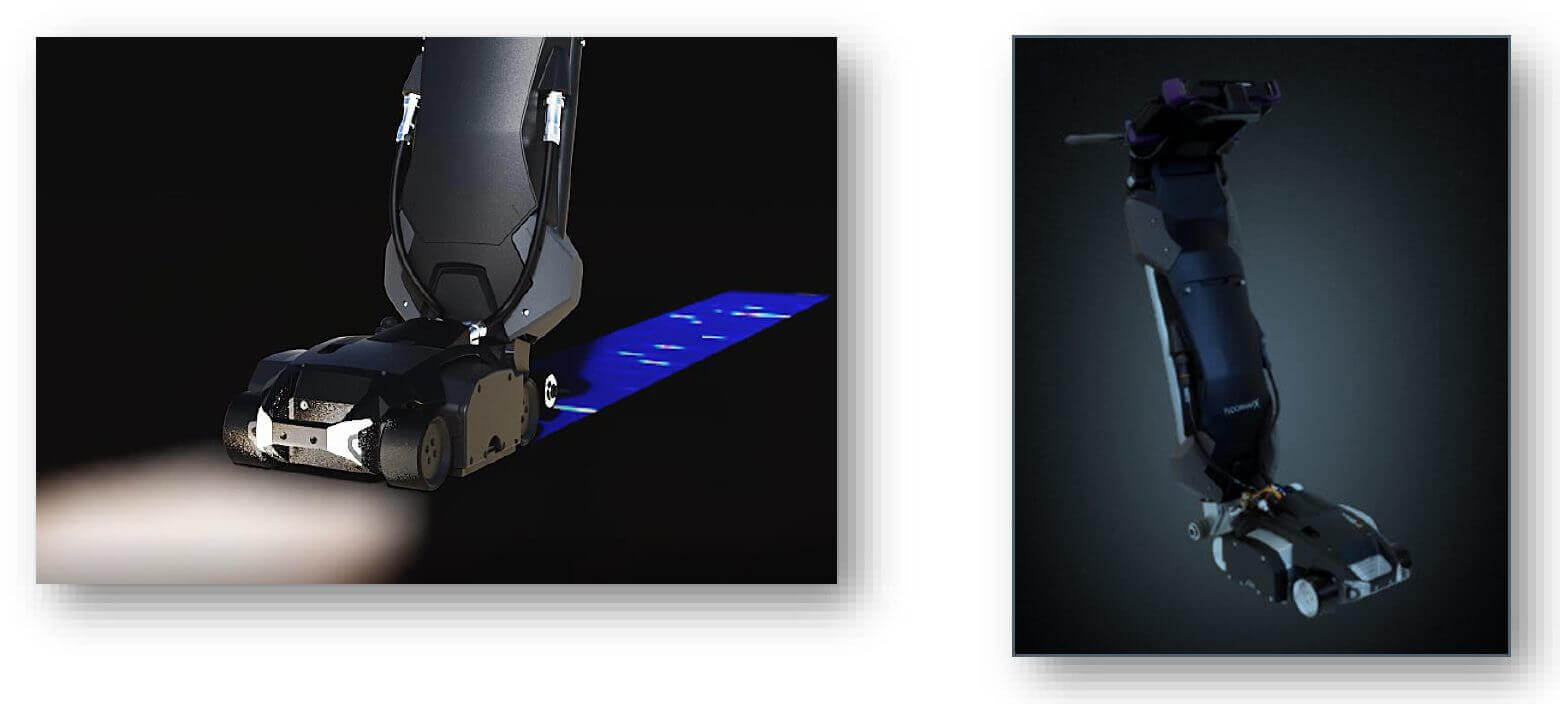

Due to the nature of MFL, it is recommended that a percentage of the detected flaws be accurately quantified by Ultrasonics (UT), typically with a UT flaw detector. With advances in technology and scanners, Phased Array Ultrasound (PAUT) fig.2 has become the technique of choice due to its superior ability to categorize and size a defect type, thus ensuring a more accurate integrity assessment.
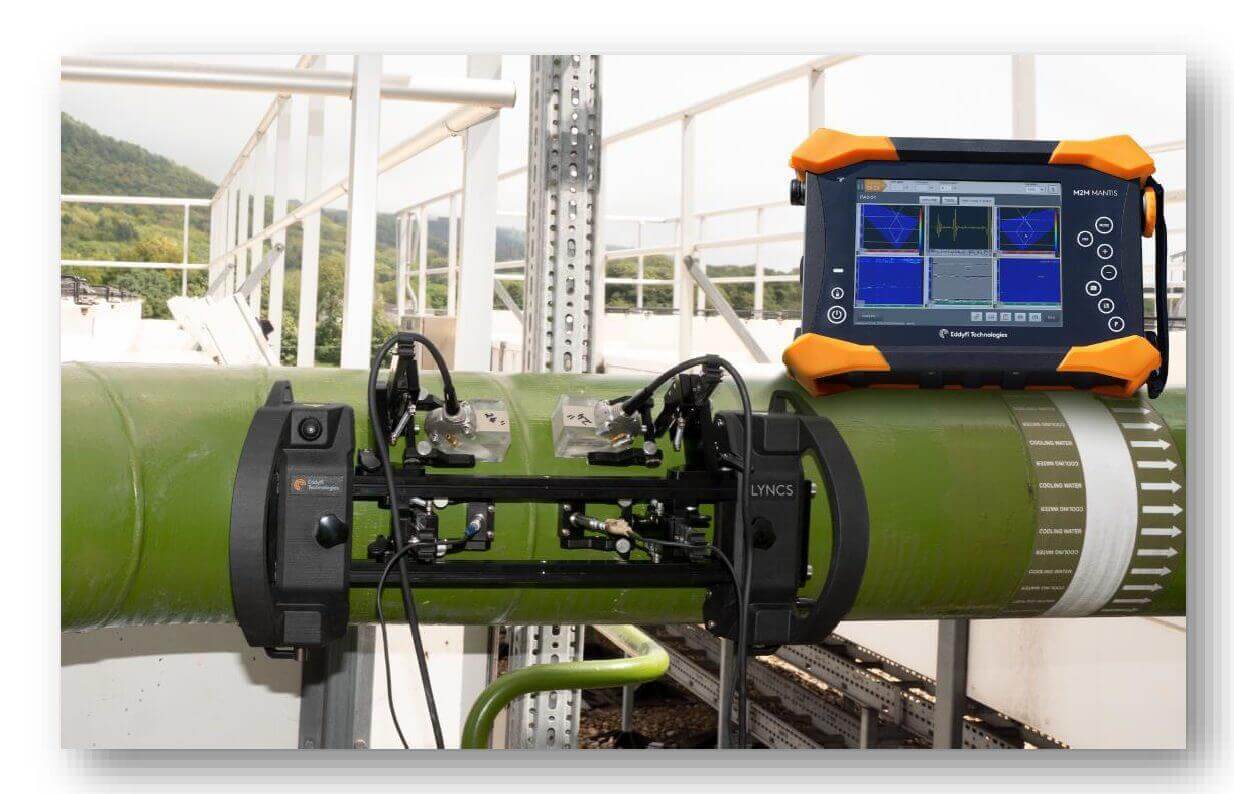

Fig.2. Mantis and LYNCS (PAUT & PA-TOFD scanner, courtesy of EddyFi), Portable Phased Array to inspect tank plate, weld pipe
Learn more about NDE for STORAGE TANK inspection here! Don’t miss part 2 of this article, we will look at another very important group of NDT techniques!
References
Own source

