Summary
An exhibition is presented on the use of visual inspection tools in boiler pipes, external and internal, in order to identify and diagnose the integrity of the material that allows safe operation and operation. Remotely controlled visual inspection instruments are now available to determine the precise location of defects within tubes.
Introduction
We are now going to talk about the inspection of a piece of equipment that is widely used, but not so well known by the public. At least not as much as the atmospheric storage tanks that can be seen in backyards, from a highway.
This consists of one of the most widely used equipment in a variety of industries, such as chemical, textile, pharmaceutical and food, and is known by the name of boiler.
A commonly used boiler has the geometry of this figure 1.
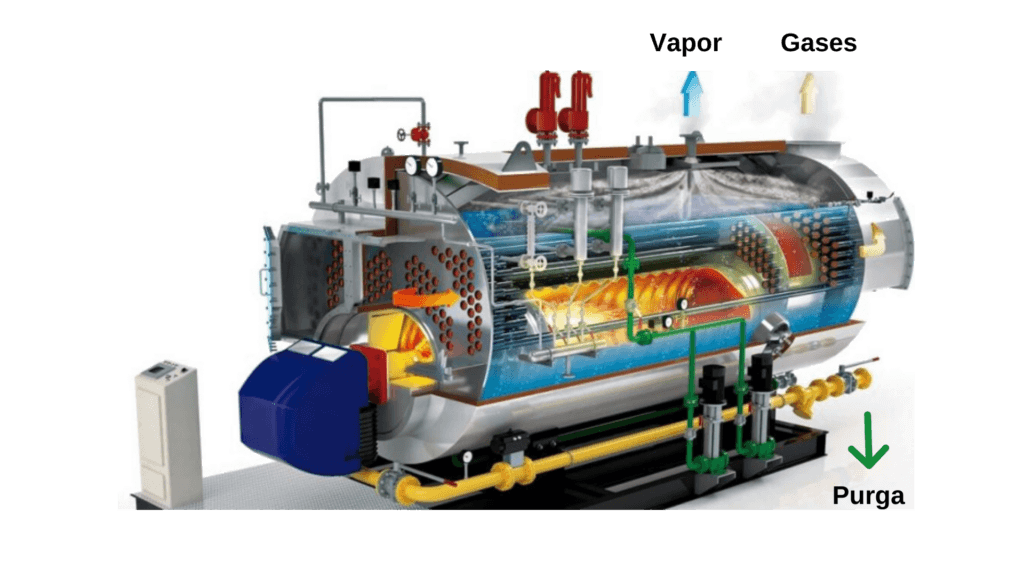
Studies have shown [1] that boiler failures are mainly the following: boiler overpressure, insufficient water level, inadequate water treatment leading to scaling, overheating and vessel failure, improper maintenance or poor maintenance methods. manufacturing, corrosion in its critical parts or lack of training of personnel in its operation.
As we can see, NDT inspectors see ourselves reflected in the mitigation of these catastrophic events. There is a huge variety of tools currently developed at our disposal and using various techniques. The advantages are considerable: ease of use and precision are constant factors that manufacturers have taken care to ensure.
And it is that one of the main applications of boilers is in the energy industry, for the generation of steam that is then fed to electric turbines. The heads and tubes of this equipment suffer high stress generated by thermomechanical loads, and are considered critical elements. Generalized corrosion, pitting, cracks, these types of defects are what you would expect to find, and in places that are quite inaccessible with common techniques: boiler headers are not very easy to inspect. Those of us who have been in front of one can attest. There are more complicated designs than others, but most are similar.
NDT instruments for boiler inspection.
Normally a visual inspection is required, although there are UT and RFET tools (special for carbon steels). To be able to inspect even 180° “U” changes of direction, tools already exist that cover 100% of the inner surface.
Virtually all visual inspection instruments are remotely controlled, regardless of technique, and include locating systems to determine the precise location of defects within tubes. Cracks can usually be detected, coating, joints, inlet and outlet pipes, etc. can be inspected.
There are devices specifically designed for the inspection of the heads; others, of smaller size, for the tubes.
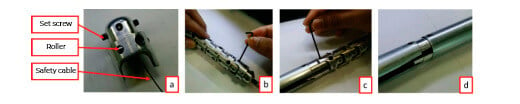
c) Modular adjustment guide d) Connection. Source [2].
There are systems called simple locomotion, although only for certain types of configurations and work environments. The figure shows a borescope, with images a and b showing the modular guides, while image d shows a slotted tube for inspection of straight tubes.
It is important to clarify that locomotion systems that integrate 2 or more types of movement mechanism improve the flexibility of the robot, although they increase the complexity of the system.
In general, there are seven types of “robots” to inspect the interior of pipes, and they are used in a variety of industries, as some authors clarify [3].
Not only visual inspection or through another technique is possible, but also the removal of small objects that have been trapped inside the tubes: there are instruments with pneumatically activated tweezers, specially designed for these rescues.
The high-resolution images available today, and extensive digital enhancement possibilities, as well as defect sizing software tools complete this set and give inspection personnel a powerful arsenal.
Robotic systems are currently available that offer location and mapping of the inspected tube; They have an encoder, a gyroscopic sensor and a camera.
The method of locomotion is not always by means of wheels; there are robots that, for example, move with a combination of sponges and traction cables, in a compressed air environment.
Due to the operating conditions of the boilers, a failure in one of these pieces of equipment has a high probability of causing severe consequences.
In subsequent articles, we will discuss the application of other techniques for boiler piping.
Stay tuned!
Bibliographic references
1. Energy Proceeds 160 (2019) 614–620 Md. Sharafat Ali and Habibullah Habibullah / Energy Procedia 00 (2018) 000–000 3.
2. Design and Development of Robotic System for Visual Inspection of Boiler Tube Inner Surface Muhammad Fairuz Abdul Jalala, Khairul Salleh Mohamed Saharia,*, Mohd Azwan Azizb, Kamal Yunosb, Adzly Anuara, Muhammad Fahmi Abdul Ghania, Dickson Neoh Tze Howa aCentre for Advanced Mechatronics and Robotics, Universiti Tenaga Nasional, Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia bMaterials Laboratory, Generation Unit, TNB Research Sdn. Bhd., Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia.
3. SG Roh and HR Choi, “Differential-drive in-pipe robot for moving inside urban gas pipelines,” in IEEE Transactions on Robotics, vol. 21(1), 2005, pp. 1-17.
About the Author

ing Jose Martinez de Munck. 15 years of experience in Equipment Inspection for the Oil and Gas Industries

