Introduction
Workplace safety is a fundamental pillar for ensuring the protection of employees and regulatory compliance. In this context, machine guards play a crucial role in mitigating occupational hazards. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established a series of strict regulations and requirements for the implementation of guards in industrial equipment to prevent workplace accidents and minimize occupational hazards1.
This technical article explores in detail what guards are, their importance, the different types recognized by OSHA, the requirements for their implementation, and best practices for their maintenance, all in the context of occupational hazards.
What are guards and why are they Important?
These are safety devices designed to protect workers from occupational hazards associated with moving parts, points of operation, and other dangerous elements of machinery. Their primary function is to prevent accidental contact with parts that could cause serious injuries, such as cuts, entanglements, impacts, or amputations, some of the industry’s most common occupational hazards. OSHA regulates the use of these guards through specific standards to mitigate these occupational hazards, requiring companies to implement adequate protective measures on all machines that pose potential risks.
Types of guards according to OSHA
OSHA recognizes and regulates several types of guards, each designed to perform specific functions in protecting workers from various occupational hazards. The main types are detailed below:
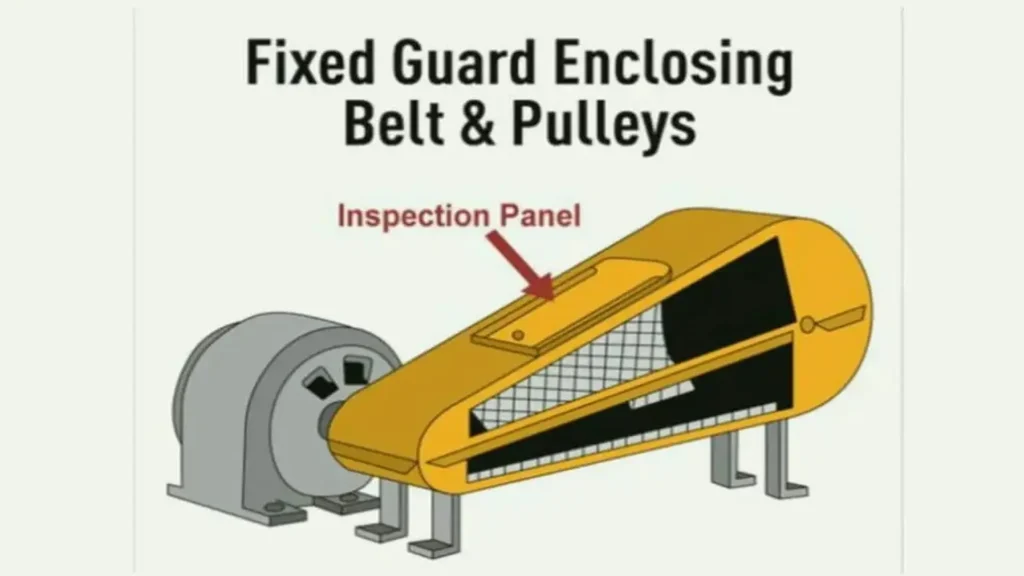
- Fixed guards: These are permanent barriers that do not move with machine operation and are designed to protect workers from dangerous parts and occupational hazards, such as belts, pulleys, gears, and chains. They are very effective because they do not require operator intervention for operation, which minimizes the possibility of human error2.
- Interlocked guards: These are connected to a system that automatically stops the machine when they are opened or removed. They are ideal for situations where access to parts of the machine is necessary for maintenance or adjustment tasks, as they ensure that the machine cannot operate unless the guard is in place.
- Adjustable guards: Can be modified to fit different tasks or material sizes. They are primarily used in machines that handle varying sizes of materials, such as presses and saws. The flexibility of these guards allows for greater versatility in their use, but careful attention is required to ensure they are always properly adjusted.
- Self-Closing Guards: These devices automatically function to protect operators when a hazardous situation is detected. For example, when a worker removes their hands from the point of operation, the guard automatically closes to prevent access. They are common in presses and other machines that present a high risk of injury at the points of operation.
Watch this video to learn more about the types of machine guards. Fuente: SawbladeUniversity

Types of machine guards.
OSHA Requirements for guard implementation
OSHA has established a series of specific regulations for the implementation of guards in machinery, aimed at reducing occupational hazards. Among the most important regulations are 1910.212 and 1910.219, which require companies to ensure that all machines that pose a risk have adequate guards to mitigate risks and that they are in good operating condition.
- Standard 1910.212: This standard sets the general requirements for the protection of dangerous parts of machines. All machine parts that may present risks must be guarded, and these guards must be robust, well-secured, and designed to prevent access to hazardous areas. The regulation also specifies that guards should not interfere with the machine’s operation or create new hazards.
- Standard 1910.219: This standard focuses on the protection of rotating parts, such as shafts, pulleys, and belts. It states that these components must be covered by guards that prevent accidental contact. Additionally, it specifies that guards must be easily accessible for inspection and maintenance but should not be removable without tools.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial not only to avoid penalties but also to ensure a safe working environment. Companies that do not meet these requirements risk significant fines and, more importantly, expose their employees to unnecessary risks.
Examples of guard use in industry
Tese are used across various industries, each adapting these devices to their specific needs. Here are some examples of how guards are implemented in different sectors:
- Manufacturing Industry: In manufacturing, fixed and adjustable guards are essential for protecting workers from cutting machines, presses, and material handling equipment. For example, in an auto parts factory, are used to cover the moving parts of hydraulic presses, ensuring that operators cannot access hazardous areas during operation.
- Construction: In the construction industry, interlocked types are common on heavy machinery such as excavators and cranes. These devices ensure that the machinery cannot operate unless all moving parts are properly secured, protecting workers from potential entanglements or impacts.
- Food processing: In food processing plants, self-closing guards are used to protect workers from hazards associated with automated packaging lines. These automatically close when a risk is detected, minimizing the possibility of employees coming into contact with dangerous parts.
- Oil & Gas industry: In the oil and gas sector, are crucial for protecting workers from the moving parts of drilling equipment, pumps, and compressors. For example, on a drilling platform, fixed and adjustable are employed to cover the mechanisms of the drillers, ensuring that operators cannot access moving parts while the machinery is in operation. Additionally, interlocked are used in high-pressure pumping systems to prevent the machine from operating if any part is improperly secured, thereby reducing the risk of serious accidents in an already hazardous environment.
How OSHA affects productivity: Practical examples
Compliance with OSHA regulations not only focuses on worker safety but also has a significant impact on a company’s productivity. Below are some practical examples of how OSHA can affect productivity:
- Reduction in accidents and downtime: The implementation of effective guards significantly reduces the number of workplace accidents. Fewer accidents mean less downtime for investigating incidents or repairing damaged machinery. This translates into a more continuous and efficient workflow, increasing the overall productivity of the company.
- Preventive maintenance and equipment optimization: Complying with OSHA requirements involves regular inspections and maintenance of guards and other safety equipment. This preventive maintenance not only ensures that safety devices are in good condition but also helps identify and solve mechanical problems before they become costly failures. Keeping equipment in optimal condition extends its lifespan and reduces downtime due to unplanned repairs.
- Improvement in worker morale and satisfaction: A safe work environment, where workers feel protected, contributes to higher morale and job satisfaction. Employees who know that their company takes their safety seriously tend to be more engaged and productive. Additionally, fewer accidents mean less absenteeism and lost time, which improves operational efficiency.
- Reduction in Insurance costs and legal liability: Complying with OSHA regulations can reduce costs associated with liability insurance and workers’ compensation. Fewer workplace accidents result in fewer claims, which can lead to lower insurance premiums. This frees up financial resources that can be reinvested in the company to improve productivity.
Best practices for guard maintenance
Regular maintenance of guards is essential to ensure their continued effectiveness and compliance with OSHA regulations. Here are some best practices for maintaining these devices:
- Regular Inspections: It is crucial to conduct regular inspections of guards to detect any wear, damage, or malfunction. These inspections should be carried out by trained personnel and should include a verification of the structural integrity as well as their correct adjustment and fastening. These regular inspections help identify potential problems before they become serious risks, ensuring always perform their protective function.
- Maintenance Records: Keeping detailed records of all inspections and maintenance work is a good practice that helps ensure that these are always in optimal condition. This record is not only useful for internal tracking but may also be required during OSHA audits to demonstrate continuous compliance with regulations.
- Continuous Training: Workers should receive ongoing training on the importance of guards and how to use them correctly. This training should include procedures for reporting any problems with guards and the importance of not tampering with or removing these devices without authorization. A well-trained workforce is essential to maintaining a safe and productive work environment.
- Replacement of Components: Any guard that is damaged or not functioning correctly must be repaired or replaced immediately. It is crucial that companies do not delay these repairs, as a defective guard can jeopardize worker safety and, consequently, negatively affect productivity.
Conclusions
Machine guards are a vital component of occupational safety, and their correct implementation and maintenance are essential not only for complying with OSHA regulations but also for maintaining a safe and productive work environment. The specific examples from the Oil & Gas sector highlight the importance of these devices in industries where risks are particularly high. Moreover, OSHA’s positive impact on business productivity demonstrates that safety not only protects employees but also improves operational efficiency and reduces costs.
By adopting a proactive approach to guard implementation and maintenance, companies not only avoid penalties and protect their workers but also optimize productivity and improve their competitiveness in the market. Compliance with OSHA regulations should be seen as an investment in the company’s future, ensuring that both employees and resources are protected, thus contributing to the sustained success of the organization.
References
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
- https://www.hseblog.com


