Table of Contents
- What is an elastomeric coating?
- Elastomeric waterproofing
- The process of applying elastomeric coatings
- Types of elastomeric coatings and their uses
- Physical and mechanical properties of the coating
- Advantages and disadvantages of these coatings
- Applications by industry
- Standards and regulations for elastomeric coatings
- High-performance industrial elastomers
- Conclusions
- References
- Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Are you looking for a high-performance solution to protect your assets? Elastomeric coating is an advanced polymer that has strengthened the construction industry. With its exceptional elastomeric properties, it forms a flexible, impenetrable membrane that offers superior protection against corrosion, leakage, and UV radiation.
This guide will provide you with a technical and comparative analysis of its main types, such as acrylics, silicones, and polyurethane, and how their applications extend the life of any structure.
What is an elastomeric coating?
An elastomeric coating, also known as elastomeric paint, is a thick liquid membrane that is applied to a surface to form a continuous, flexible protective film once it has cured. Unlike common paints, its elastomer-based composition gives it a unique property: the ability to stretch and contract significantly without cracking.
This flexibility is key to its performance, as it allows it to “bridge” microcracks and follow the natural movements of the substrate caused by temperature changes or structural settlement. When cured, the membrane acts as a monolithic barrier against external agents such as water, carbon dioxide (CO2), salts, and ultraviolet (UV) radiation, effectively reducing the risk of leaks, corrosion, and degradation.
Although this technology is mainly used on roofs and facades, its versatility has made it a reliable solution in a variety of environments, including the protection of industrial equipment and infrastructure exposed to harsh conditions.
Elastomeric waterproofing
This is the most widespread and strategic use of these coatings. It is a liquid membrane applied on site that, when cured, forms a monolithic and flexible film capable of sealing pores and bridging microcracks on low-slope roofs and facades. To ensure optimal performance on roofs, specialists specify a dry film thickness (DFT) that can vary.
For example, while thicknesses of 12–15 mils can be used for walls, 20–30 mils or more are recommended for roofs, depending on the technical data sheet (TDS). In addition, joints, penetrations, and critical details are reinforced with seals and reinforcements, and adequate slope is ensured for efficient drainage. It is essential to remember that silicone systems are superior at tolerating standing water, while acrylics perform better on roofs with good drainage. It is important to note that they are not suitable for continuous immersion, except for those systems that have been specifically formulated for this purpose.
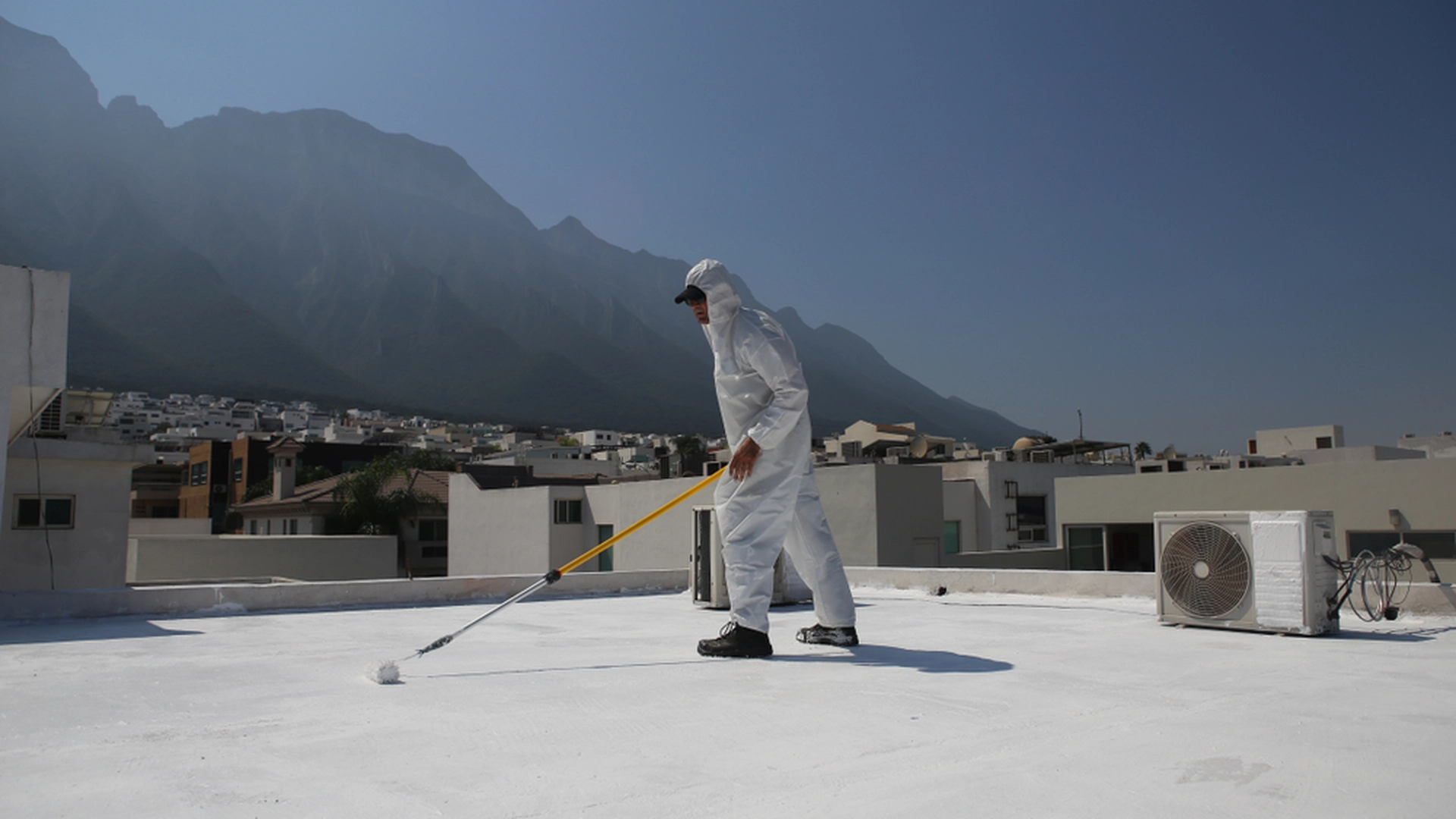

The process of applying elastomeric coatings
- Substrate preparation. Clean to remove any dirt (dust, grease, oils) that may hinder adhesion.
- Environmental conditions. Check weather conditions, avoid wind and imminent rain.
- Equipment and technique. Use a medium/thick roller or airless sprayer (nozzle according to TDS). Apply in cross coats to cover pores and avoid marks.
- Target thickness (DFT). Calculate wet film thickness (WFT) with: WFT ≈ DFT / Solids by Volume. Example: DFT 20 mils and 50% solids → WFT ≈ 40 mils.
- Number of coats. Prefer 2–3 thin coats to 1 very thick coat; observe recoat times (recoat window) indicated by the TDS.
- Curing and exposure. Protect from rain/dew until rain-safe (silicones may be faster than acrylics). Do not allow use until cured.
- Compatibility. Confirm compatibility between substrate, primer, and topcoat; on existing membranes (TPO/PVC/EPDM, mod-bit), use specific primers.
- Safety. PPE, lifelines, and VOC management according to local regulations.
Types of elastomeric coatings and their uses
The elastomeric coatings family is diverse, with different chemical compositions that adapt to the needs of each project. Choosing the right material is essential to ensure durability and performance.
Acrylics
These are the most popular and economical, making them the standard choice for a wide range of projects. Formulated from acrylate copolymers, they are easy to apply and clean, as most are water-based. They offer excellent UV protection and, in light colors, high solar reflectance, making them ideal for energy efficiency. However, their main limitation is their low tolerance to standing water, making them more suitable for use on well-drained roofs and facades.
Silicones
These coatings are derived from siloxane polymers and are the premium choice for roof waterproofing. Their greatest strength is their unmatched resistance to UV rays and standing water, forming a continuous membrane that does not degrade in extremely humid conditions. They are the best choice for flat or poorly drained roofs and in humid climates, where other coatings would fail. Despite their higher initial cost, their long service life and exceptional performance justify the investment.
Polyurethane
These coatings stand out for their superior adhesion and high mechanical and chemical resistance. Produced by the reaction between polyols and diisocyanates, they are ideal for areas with light foot traffic or where the substrate experiences constant wear. The aliphatic formulation of these coatings offers excellent UV stability, while aromatic coatings are used as base coats. There are water-based versions with low volatile organic compound (VOC) content, making them an environmentally responsible option.
Other elastomers
In addition to the most common types, there are other types of elastomers with specific properties, such as butyls (known for their very low air and water vapor permeability, making them excellent vapor barriers) and polyureas (ultra-fast curing two-component systems that offer extreme resistance to abrasion and chemicals, ideal for heavy-duty industrial environments).
Physical and mechanical properties of the coating
The performance of elastomeric coatings is based on their advanced physical and mechanical properties, which are evaluated through laboratory testing.
- Flexibility and elongation: A quality elastomeric coating can deform without cracking. Elongation, measured as a percentage, indicates how much the film can stretch before breaking. For example, acrylics for roofs typically have an elongation greater than 100%.
- Elastic recovery: This is the material’s ability to return to its original shape after being stretched. This property ensures that the membrane maintains its continuity and ability to bridge microcracks, even after repeated cycles of expansion and contraction.
- Tear and abrasion resistance: These properties are required in light traffic applications or in areas exposed to wear. They ensure that the coating maintains its integrity against mechanical damage.
- Adhesion: The strength with which the coating adheres to the substrate is vital to prevent delamination or peeling. Proper surface preparation and the use of a primer (if necessary) are essential to ensure lasting adhesion.
- Water vapor permeability: Elastomeric coatings allow for the controlled passage of water vapor from the inside to the outside. This “breathability” prevents the accumulation of moisture trapped under the coating, which could cause blisters or failures.
Advantages and disadvantages of these coatings
While elastomeric coatings offer superior performance, both their benefits and limitations must be considered.
Main advantages
- High durability: they act as a sacrificial protective layer that absorbs damage that would otherwise affect the substrate, and they resist weathering, UV radiation, and mild chemicals, reducing the need for repairs. In addition, their flexibility allows them to withstand extreme temperature cycles (from intense heat to freezing cold) without cracking or losing integrity, extending the life of surfaces.
- Crack-bridging capacity: this is one of the most valuable properties of elastomeric coatings, as it allows them to cover cracks and prevent them from spreading. Due to its high flexibility, the material expands and contracts to accompany the natural thermal movements of the substrate. Thus, they can seal existing cracks (up to 1.5 mm wide) and prevent incipient microcracks from developing, protecting the structure from future damage, leaks, and the entry of contaminants.
- Energy efficiency and sustainability: white or light-colored coatings have a high solar reflectance index, a property that causes the surface to reflect much of the solar radiation instead of absorbing it, reducing the load on air conditioning systems, contributing to sustainability, and decreasing energy consumption.
- Continuous waterproof barrier: when applied as a liquid, it forms a continuous, monolithic membrane without joints, seams, or seams. This barrier eliminates the weak points common in other waterproofing systems (such as prefabricated membranes) and effectively limits water leakage, corrosion, and moisture damage.
Main disadvantages
- Initial cost: They have a higher initial cost compared to standard architectural paints.
- Surface preparation: They require thorough surface preparation and rigorous control of dry film thickness to ensure proper adhesion and performance.
- Service limitations: Some types, such as acrylics, do not perform well with standing water. The choice of elastomer type must be consistent with the environmental conditions.
Applications by industry
Although the construction industry is its main market, the versatility of elastomeric coatings allows them to protect assets in various sectors.
- Construction: Their most widespread use is in the elastomeric waterproofing of roofs and facades. Silicone is preferred for roofs with standing water, while acrylics are chosen for facades and roofs with good drainage due to their balance between cost and performance.
- Oil and gas: They protect steel equipment and structures from corrosion, abrasion, and chemical exposure. They are mainly applied to flanged joints, valves, pipes, and tanks to extend their service life. They are also ideal for the rehabilitation and protection of buried pipes.
- Coastal infrastructure: Silicone coatings are ideal in areas exposed to salt spray and high UV radiation. They protect decks and walkways, maintaining their integrity and water repellency.
- Automotive industry: They are used to waterproof underbodies and provide corrosion protection and soundproofing.
Elastomeric Coating vs. Acrylic Paint
| Characteristic | Elastomeric Coating | Traditional Acrylic Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Flexibility / Bridging | High; accommodates movements and seals micro-cracks. | Low; may crack with substrate movement. |
| Impermeability | Continuous and effective barrier that seals pores and micro-cracks. | Lower; may allow water ingress through the film. |
| Durability | Greater durability and color retention. | Lower durability; degrades and fades over time. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost due to advanced properties. | More economical. |
Standards and regulations for elastomeric coatings
The quality and performance of elastomeric coatings are governed by international standards that ensure their reliability. Professionals rely on these specifications to guarantee that products meet the requirements of each project.
- Performance specifications: ASTM D6083 is one of the most widely applied standards for acrylic coatings used on roofs. It defines the minimum properties that a product must have to be considered high performance.
- Physical tests: Specific tests are performed to measure the most important properties of the coating, such as elongation and tensile strength (ASTM D412), which measure how much the material can stretch before breaking; and flexibility (ASTM D522), which evaluates its ability to bend without cracking.
- Optical and thermal properties: For cool roofs, standards are used to certify their energy efficiency. ASTM C1549 measures solar reflectance (how much sunlight it reflects), ASTM C1371 measures thermal emissivity (how well it radiates absorbed heat), and ASTM E1980 combines both to calculate the SRI (Solar Reflectance Index).
- Adhesion: ASTM D4541 evaluates the adhesion of the coating to the substrate. This test is essential to ensure that the membrane does not peel off over time.
High-performance industrial elastomers
Securit™2 elastomer: an advanced coating for harsh industrial environments (mining, petrochemical, maritime). It combines high flexibility and durability on steel, concrete, and non-ferrous metals. Its formulation is designed to operate in high humidity and in the presence of contaminants such as SO₂ and CO₂, creating a barrier that reduces corrosion and maintenance costs by extending the useful life of equipment and structures.
TOFF TO-6080: a 2K modified polyurea elastomeric coating, 100% solids, mixed at the point of application. It cures in seconds (touch dry ~10 s; pressure resistant ~1 min), allows for high thickness to be built up in multiple passes, and forms a continuous, adhesive, anti-corrosive membrane on concrete and metal. VOC- and CFC-free, with naturally sourced polyols, it offers high performance and rapid commissioning.

GacoFlex A48 (acrílico): lanzado en 2023 por la marca GacoTM, es un revestimiento acrílico de un solo componente y gran espesor que se puede aplicar hasta 80 milímetros húmedos en una sola pasada. Queda listo para la lluvia en aproximadamente 30 minutos y cura totalmente en unas horas. Ofrece alta reflectividad y resistencia UV, lo que resulta útil para reducir costes energéticos y simplificar la aplicación en techos que requieren renovación de superficie sin necesidad de desmontaje.
GacoFlex A48 (acrylic): Launched in 2023 by the GacoTM brand, this is a single-component, high-thickness acrylic coating that can be applied up to 80,000 wet square feet in a single pass; it is rain-ready in ≈30 minutes and fully cures in hours. It provides high reflectivity and UV resistance, useful for reducing energy costs and simplifying application on roofs that require surface renovation without dismantling.
Conclusions
With the constant improvement of its formulations and a growing demand for sustainable and durable solutions, elastomeric coating is establishing itself as a strategic ally in infrastructure protection. While the initial cost and application requirements may be higher than those of standard paint, its long-lasting resilience and ability to extend the useful life of assets to more than 10 years fully justify its adoption.
Choosing the right system—whether acrylic, silicone, polyurethane, or butyl—should be based on a careful assessment of the substrate, climate, drainage, and specific project needs. Making an informed decision ensures superior protection that extends the life of assets and delivers a return on investment.
References
- Advantages of an Elastomeric Waterproofing, conultado en https://blogs.ampp.org/protectperform/advantages-of-an-elastomeric-waterproofing-system
- BOP. Propiedades de los elastómeros y dónde utilizarlos. Consultado en https://www.bop-products.com/blog/elastomers/elastomer-properties-and-where-to-use-them/#:~:text=Other%20elastomer%20properties%20are%20hardness,permeability%2C%20and%20elongation%20at%20break
- AMERICAN WEAHERSTAN. Elastomeric Coating: The Definitive Guide. en https://www.americanweatherstar.com/elastomeric-coating-the-definitive-guide/
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Is elastomeric coating waterproof?
Yes, it is completely waterproof. Its function is to create a continuous, seamless membrane that seals pores and microcracks, preventing water infiltration. Its effectiveness depends on the thickness of the layer and correct application.
Can it be applied to concrete?
Yes, concrete is one of the most common substrates for its application. The surface must be clean, dry, and in good condition for the elastic layer to adhere firmly and provide excellent protection against moisture.
What are the best substrates for application?
It works well on a wide variety of surfaces, including concrete, metal (to prevent rust), polyurethane foam (which protects against UV rays), and old asphalt membranes to extend their useful life.

