Table of Contents
- What is comprehensive health and safety?
- Understanding comprehensive occupational health
- Components of a Comprehensive Workplace Health and Safety (CWHS) program
- The pillar of occupational health is the prevention of occupational risks
- Most prominent international standards and agencies governing occupational health and safety
- Current trends in occupational safety and health
- Conclusion
- References
Comprehensive occupational health has a great impact on the management of work environments, especially in high-risk sectors. This discipline transcends the prevention and control of occupational diseases and accidents, covering all factors that affect the physical, mental and social health of workers; because it not only addresses the immediate risks, but also the psychosocial and ergonomic aspects that influence the long-term well-being of workers.
Compliance with global safety regulations, such as those established by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the guidelines of the International Labor Organization (ILO), is not only a legal requirement, but also an ethical and ethical commitment. strategic of companies to safeguard the most valuable asset: their employees. The integration of occupational risk prevention practices creates a safe and productive work environment.
Implementing occupational health measures not only protects workers from work-related injuries and illnesses, but also contributes significantly to operational efficiency and business sustainability. Current trends, such as the increasing focus on mental health and the integration of sustainable practices, determine occupational health strategies. Furthermore, promoting a proactive workplace safety culture in the workplace is essential, and positively influences all levels of the organization.
What is comprehensive health and safety?
“It is the strategic and systematic integration of different health and safety programs and policies into a continuum of organizational, personal, occupational, community and environmental activities that are replicable, measurable and integrated across institutional silos, improving health and safety in general. well-being of workers and their families and prevention of work-related injuries and illnesses” 1 .
Understanding comprehensive occupational health
What exactly is comprehensive occupational health? It is an approach to occupational health that integrates activities, policy development and initiatives that improve and maintain the health and well-being of workers by providing a better quality of life in the work and personal environment; This approach adopts a broad perspective aimed not only at preventing accidents and professional injuries, but also at promoting a work environment that comprehensively supports the employee’s health. It is essentially about tailoring the job to the individual and the individual to their job.
In contrast to industrial safety, which focuses on preventing accidents and managing physical risks, comprehensive occupational health is broader; It is implemented through a Comprehensive Workplace Health and Safety (CWHS) program; where ergonomic, chemical and biological risks are evaluated and managed, as well as attention to psychological and social aspects of the work environment. This proactive and preventative approach creates work environments that are not only safe, but also conducive to individual well-being and productivity.
Health and safety integration initiatives that link in part the community, home, and workplace hold the most promise for success in addressing growing occupational health problems. The integration of these three sectors must work together and continually search for new ways to address health problems in the work environment. On a societal level, the impact of this new way of approaching health and safety in the workplace is profound.
Components of a Comprehensive Workplace Health and Safety (CWHS) program
A comprehensive health and safety program is made up of four main components, which must overlap and integrate and not be addressed separately in order to achieve the appropriate work-life balance. They are analyzed in detail below:
Health and safety at work (physical environment)
This component focuses on the promotion and maintenance of the physical, mental and social well-being of workers. It involves reducing injuries, illnesses and disabilities linked to work, facing dangers and risks in the physical work environment. By minimizing physical risks in the workplace, the stress that workers experience in the workplace is also mitigated.
Psychosocial work environment (organizational culture and work organization)
This is a fundamental aspect in health and safety programs; It is required to develop, implement and maintain over time a process that identifies real risks and dangers, both current and potential, in the psychosocial environment. In this environment, two main themes stand out:
- Organizational culture, which is characterized by the attitudes, values and beliefs that determine behaviors at work and shape the daily environment, impacting the physical and mental well-being of staff. This culture focuses on the factors that influence the interaction between the individual’s responsibilities, their work, and the organization. This aspect is the most interconnected with protection and improves mental health and general well-being.
- Correct work organization has a positive impact on the effectiveness and well-being of employees at work. Adequate health and safety management at work, with an orderly structure and planning of activities and responsibilities, successfully influences workers. The distribution of tasks also improves employee attitudes, this includes workload, quality of communication, control and freedom of decision, clarity of roles, support of necessary resources, opportunities for development and professional growth.
Promoting health and well-being at work
They are programs focused on health promotion among workers and their families through occupational risk prevention schemes and assistance in various areas; where they offer healthy living for all employees in the workplace and cover a wide range of health problems. These include environmental, cultural and policy support for: maintaining an active life, healthy eating, infectious disease care and mental health support.
Evidence shows that the most effective workplace health programs are those that incorporate the stages of change model (personal readiness to make lifestyle changes), address multiple levels of learning (awareness, knowledge development, and skills, behavior change) and make supportive environmental modifications.
Unlike traditional safety programs, employee participation in a Comprehensive health and safety program is completely voluntary. Through needs assessments, a committee or the employer determines what workers’ health needs and preferences are and then plans programs and policies in response, but it is still the worker’s decision whether to participate or not.
Organizational community participation
The commitment to corporate participation in the community is voluntary. As examples of this community commitment, an organization may choose to support local charitable causes, such as funding a group of workers to participate in a health fundraising event, facilitating the attendance of family members of employees at vaccination drives sponsored by the company, or encourage its employees to get involved as volunteers in community activities.
The pillar of occupational health is the prevention of occupational risks
The prevention of occupational risks in the workplace is a basic aspect of occupational health and safety management. Its objective is to identify, evaluate and control the risks to which workers are exposed in their work environment to prevent accidents and occupational diseases. The main types of occupational risks include: physical, chemical, psychosocial, biological, ergonomic and environmental risks.
Most prominent international standards and agencies governing occupational health and safety
- International Labor Organization (OTI): It is a specialized agency of the United Nations dedicated to promoting social justice, labor rights and decent work opportunities for all. It is the only tripartite UN agency that brings together representatives of governments, employers and workers of its member states to set labor standards, develop policies and design programs that promote decent work. The ILO focuses on areas such as rights at work, employment, social protection and social dialogue.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): This standard promotes a safe and healthy work environment for workers by reducing and preventing occupational hazards, accidents and illnesses, and promoting safe and health practices at work. This is achieved through the implementation of regulations, workplace inspection, and occupational health and safety education and training.
- ISO 45001: Establishes the requirements for implementing occupational health and safety systems. This standard provides a solid framework to identify risks, promote safe work environments and reduce workplace accidents. It is designed to integrate with an organization’s existing occupational health and safety management processes, using the same framework/structure as other ISO management system standards, such as ISO 14001 for environmental management systems.
These standards are important because they establish an international framework for the prevention of occupational risks in the management of health and safety at work, providing guidelines and best practices to protect the health and well-being of workers through the implementation of safety programs. comprehensive health and safety in various sectors and contexts.
Current trends in occupational safety and health
Including trends in an organization provides benefits for success, since these practices improve the company’s reputation, attracting and retaining qualified talent that gives value to a work environment where the health and well-being of staff is prioritized. Here are some trends 2 :
- Technology integration: The adoption of cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, where their algorithms manage to analyze large amounts of data associated with workplace health and safety; They identify patterns used to prevent potentially dangerous occupational risks, and allow professionals to make preventive decisions.
An example is Smart Personal Protective Equipment (Smart PPE); that collect real-time data on exposure to hazardous substances, body posture and other occupational health factors. Analysis of the collected data is used to alert employees to potential dangers and take preventive measures.
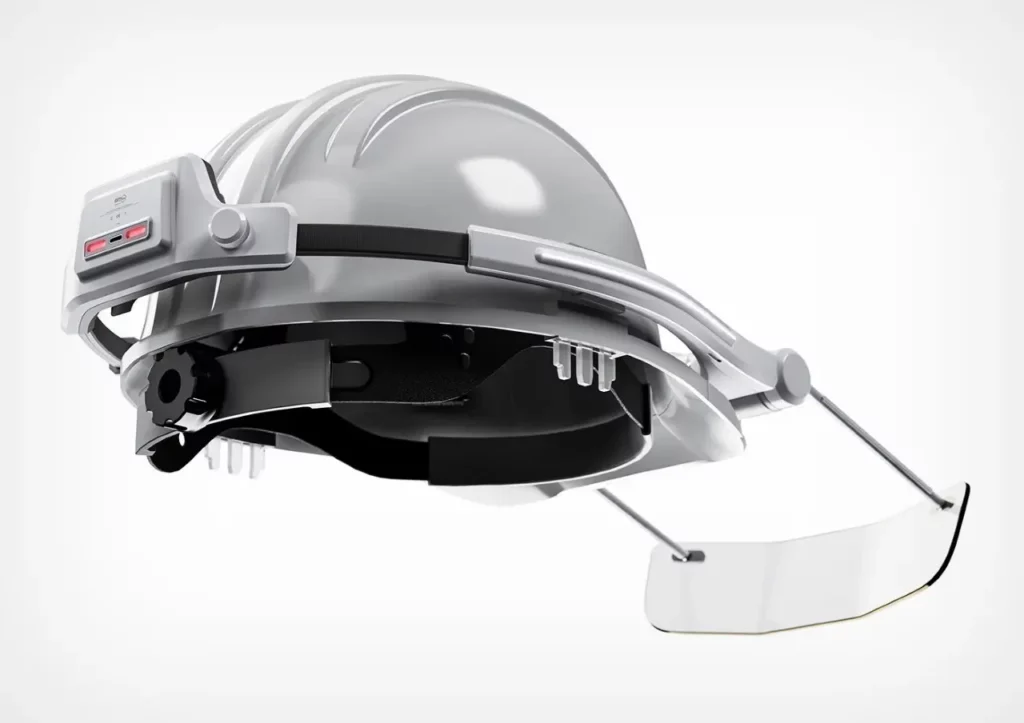

- Promote a healthy and sustainable work culture: Beyond policies and programs, creating a work culture that promotes health is necessary and must be sustained over time. This includes promoting healthy habits, detecting and valuing positive behaviors, and establishing an environment that creates a balance between the employee’s work and personal life.
- Caring for personal health: Shared responsibility is an emerging trend. Employees must take active responsibility for their well-being, taking effective measures to maintain a healthy life outside the work environment. Companies are promoting worker autonomy, providing resources and support for the self-care of their staff.
- Use of Big Data to prevent, detect and manage occupational risks: The collection and analysis of large volumes of data provides important perspectives to prevent and manage risks at work. Identifying patterns, evaluating characteristic risks and personalizing health and safety strategies are possible thanks to the intelligent application of Big Data in occupational health.
- Telemedicine and digital health: Telemedicine is improving the way healthcare is delivered. Technological advances in communication allow occupational professionals to perform remote evaluations, diagnoses and follow-ups, improving the efficiency and accessibility of care for workers. An example is the use of wearables that include sensors for constant monitoring of workers’ health, which record blood pressure, heart rate and stress.
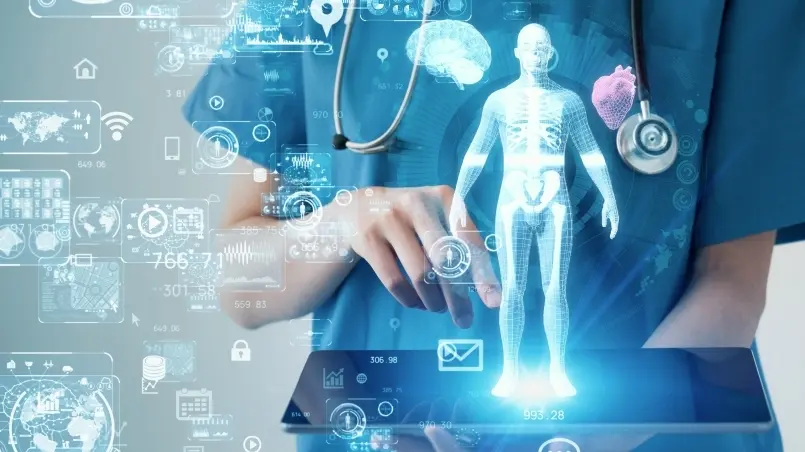

- Interest in emotional health: Recognizing the importance of mental health in the workplace, companies have developed and implemented specific strategies, programs and policies to address and safeguard the emotional well-being of employees. Strategies such as emotional support programs, work flexibility and resilience training are on the rise.
- Ergonomics and workspace design: The implementation of ergonomic modifications in the workplace is receiving greater attention for the benefit of occupational health. Optimizing work environments to promote proper posture, reduce physical load, and minimize ergonomic risk factors are critical to preventing injuries and improving worker well-being.
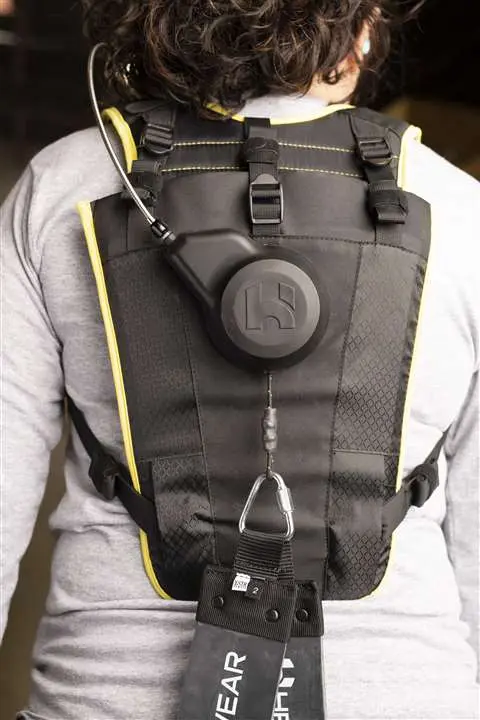

By implementing these trends, organizations not only protect the health and well-being of staff, but also ensure their own viability; Investing in occupational health is a smart business strategy that brings sustainable and sustainable benefits for both parties.
Conclusion
Comprehensive occupational health is a field specialized in creating a safe and healthy work environment, encompassing more than the prevention and control of occupational diseases and accidents, it includes physical, mental, psychosocial and ergonomic aspects that impact the long-term well-being of employees. workers and their environment. Compliance with international regulations and the integration of occupational risk prevention practices contribute significantly to business efficiency and sustainability.
Promoting a workplace safety culture that is proactive and adopting current trends, such as the focus on mental health and the use of advanced technologies, are essential to effectively address occupational health challenges in the modern work environment. .
References
- https://journals.lww.com/joem/fulltext/2015/05000/integrating_health_and_safety_in_the_workplace_.15.aspx
- https://occupationalhealth.com.mx/tendencias-de-salud-ocupacional-que-transformaran-el-2024/#:~:text=Esto%20implica%20fomentar%20h%C3%A1bitos%20saludables,trabajo%20y%20la%20vida%20personal
- https://www.ilo.org/global/topics/labour-administration-inspection/resources-library/publications/guide-for-labour-inspectors/how-can-osh-be-managed/lang–es/index.htm
- https://www.fusionoh.com/trends-in-occupational-health-for-2024/
- https://www.ccohs.ca/oshanswers/psychosocial/wh/mentalhealth_work.html
- https://www.ilo.org/safework/areasofwork/workplace-health-promotion-and-well-being/lang–es/index.htm