The fundamental role of pipes in various industries lies in their significant contribution to the feasibility of production procedures in facilities. It is essential to protect them through control systems such as Cathodic Protection (CP).
Due to the great importance of pipes, their protection is considerable and one of the types of damage that commonly causes structural failures is galvanic corrosion, which is produced by contact between two dissimilar metals when two conditions are met: the first, that is in contact with a different type of metal (more noble ) and the second, that both metals are immersed in an electrolyte or humid medium. 1
As a consequence of this type of corrosion, pipes can have a shorter useful life and also decrease their operational efficiency. It is essential to protect it through control systems, such as Cathodic Protection, where insulating joints play a fundamental role in the process.
In Cathodic Protection, insulating joints are used to isolate different metal sections, which in contact could compromise the effectiveness of the control method. These gaskets are considerable, and must be durable, reliable and efficient to keep the system operating in optimal conditions.
What is Cathodic Protection?
Cathodic protection (CP) is a technique to control galvanic corrosion of a metal surface by turning it into the cathode of an electrochemical cell 2 . This is achieved by making the electrical potential of the metal to be protected (pipe) become more electronegative by applying a direct current or by placing a sacrificial material on it (sacrificial anode commonly made of aluminum, magnesium, among others).
Cathodic protection systems are most commonly used to protect steel, pipeline transportation and storage tanks, ships, or an oil platform, both offshore and onshore, industrial equipment, etc. It is important to constantly monitor the applied current and maximize its utility; applying external coatings and installing insulating gaskets to the pipe.
Insulating Gaskets for Cathodic Protection
Insulating gaskets are flanged components that enhance the performance of cathodic protection systems. These components are used to prevent galvanic corrosion from occurring, creating a barrier or blockage to the passage of current in the pipe and preventing them from generating a potential difference.
Its fundamental principle is insulation, with which it is possible to maintain the electric field at a level of high efficiency and reduce the costs of electricity that protects the pipe.
Figure No. 1 shows that when electrically insulating the pipe using the two insulating joints observed, the electric field would only be between the two mentioned joints, which is where the Cathodic Protection is applied to protect it from the ground.
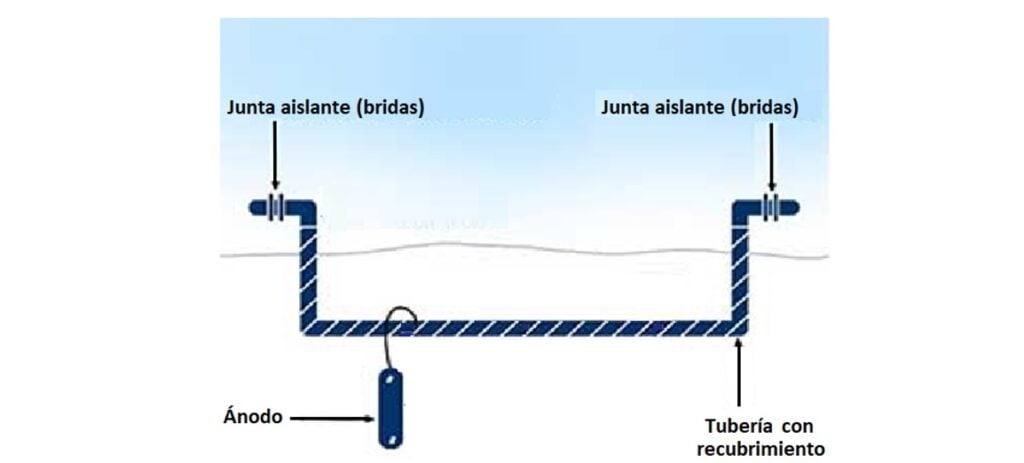
Why implement insulating joints?
Insulating joints function as the central axis of a cathodic protection system, making their implementation necessary. Using insulating joints will avoid the potential difference between different materials, reducing the probabilities of galvanic corrosion, increasing the efficiency of Cathodic Protection systems.
The protection of materials produces benefits such as: a decrease in maintenance costs, an increase in the useful life of the pipe, it further reduces the cost of electricity and maintains the electric field at an effective level.
Insulation is commonly used in two ways, one with flange insulation kits, as shown in Figure 2, and another as monolithic insulation gaskets, as shown in Figure 3. Both products serve the same function, but insulation kits are predominantly found in above-ground installations, while monolithic insulation joints are commonly found underground. Insulating materials are designed according to the type of service.
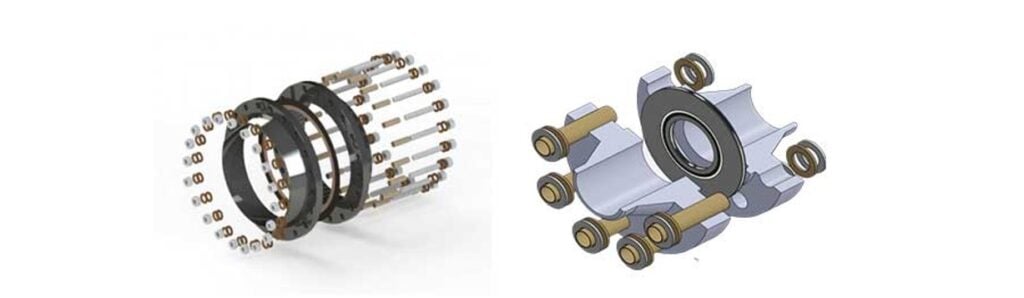

Characteristics of insulating gaskets for Cathodic Protection flanges
To further reduce the cost of electricity to protect the pipeline and maintain the electric field at an effective level, insulation is often used in the form of flange insulation kits or monolithic insulation gaskets. Both products accomplish the same task, but Flange Insulation Kits (FIK) are predominantly found in above-ground installations, while Monolithic Insulation Joints (MIJ) are commonly found underground. Insulating gaskets for Cathodic Protection flanges face technical challenges that have driven the need for innovation to develop certain characteristics such as:
- Durability: Insulating joints must resist adverse environmental conditions, such as soil moisture, temperature changes, saline atmosphere, and exposure to corrosive chemicals. Long-term durability is essential to minimize costly repairs and replacements.
- Effective insulation: For cathodic protection to control corrosion efficiently, insulating joints must guarantee total isolation between metal parts. Even a small electrical leak can compromise the effectiveness of the entire system.
- Reduced maintenance: Accessibility to insulating joints is often limited, as many are buried underground. This makes maintenance expensive and complicated, underscoring the importance of developing long-lasting, low-maintenance insulating gaskets.
- Material compatibility: Insulating gaskets must be compatible with a wide variety of materials and coatings used in the industry, hence the importance of material selection.
Technical advances in insulating gaskets for cathodic protection flanges
In response to these challenges, there have been notable advances in the design and technology of these devices. These advances are driving significant improvements in the operational efficiency of cathodic protection systems. Below are some of the most notable developments:
- Advanced materials: The introduction of high-strength polymeric materials, such as polyethylene and polypropylene, has significantly improved the durability of insulating joints. These materials are resistant to corrosion and wear, reducing the need for maintenance and long life.
- Optimized design: Advances in design have allowed better voltage distribution and greater efficiency in electrical insulation. This ensures that the joints function optimally, even in adverse conditions.
- Remote monitoring: The integration of sensors and remote monitoring technology has revolutionized the management of cathodic protection systems. It is now possible to monitor the condition of insulating joints continuously, allowing for early problem detection and predictive maintenance.
Conclusions
Insulating joints are fundamental accessories in the Cathodic Protection of pipes. Technical advances in this field are significantly improving the operational efficiency of companies by addressing the challenges of durability, effective insulation, maintenance and material compatibility.
Innovation in materials, design, monitoring and installation techniques has changed the way Cathodic Protection systems are managed. As a result, companies can operate more efficiently and safely, while complying with environmental and safety regulations.
Continued investment in research and development in the field of insulating gaskets will continue to play a very important role in optimizing operations in the cathodic protection industry.
References
- Luis Bilurbina Alter, Francisco Liesa Mestres, José Ignacio Iribarren Laco. ” Corrosion and protection.” Editions of the Polytechnic University of Catalonia , 2003. ISBN 8483017113 . Page 52.
- AW Peabody, Peabody Control of Ridge Corrosion, 2nd ed., 2001, NACE International. p.6, ISBN 1-57590-092-0

